NVIDIA GeForce GTX 480 Graphics Card
|
Card design
| NVIDIA GeForce GTX 480 1536MB |
- GPU: GeForce GTX 480 (GF100)
- Interface: PCI-Express x16
- GPU frequencies (ROPs/shaders): 700/1400 MHz (standard)
- Memory frequencies (physical (effective)): 925 (3700) MHz (standard)
- Memory bus: 384-bit
- Vertex processors: -
- Pixel processors: -
- Unified processors: 480
- TMUs: 60 (BLF/TLF/ANIS)
- ROPs: 48
- Dimensions: 270x100x33mm
- PCB color: black
- RAMDACs/TDMS: integrated into GPU
- Outputs: 2 x DVI (Dual-Link/HDMI), mini-HDMI
- VIVO: -
- TV-out: -
- Multi-GPU operation: Hardware SLI
|
 |
| NVIDIA GeForce GTX 480 1536MB |
1536MB GDDR5 SDRAM in 12 Hynix on the front side of the PCB. Peak clock rate 1000 (4000) MHz. |
 |
| Comparison with the reference design, front view |
| NVIDIA GeForce GTX 480 1536MB |
Reference card NVIDIA GeForce GTX 285 |
 |
 |
 |
| Comparison with the reference design, rear view |
| NVIDIA GeForce GTX 480 1536MB |
Reference card NVIDIA GeForce GTX 285 |
 |
 |
We compared the novelty with the preceding GeForce GTX 285 that has 512-bit memory bus. Obviously, since GeForce GTX 480 only has a 384-bit bus, and also because it lacks a dedicated NVIO unit, its PCB has become simpler and cheaper. On the other hand, the novelty has a more powerful power supply, because it consumes as much as 300W -- this is comparable to the power consumption of GeForce GTX 295.
GeForce GTX 480 doesn't have a TV-Out. This interface becomes obsolete, because HDMI is expected to replace old analog connectors.
This graphics card has its own audio codec and can transmit both video and audio via HDMI.
Note that GeForce GTX 480 has two connectors for external power supply: one 8-pin and one 6-pin. The latter are quite popular, but the former may require an adapter.
Also note that, working in SLI, this graphics card can output video signal to three monitors simultaneously.
Maximum resolutions and frequencies:
- 240 Hz maximum refresh rate
- 2048 x 1536 x 32bit @ 85Hz Max -- analog interface
- 2560 x 1600 @ 60Hz Max -- digital interface (Dual-Link DVI/HDMI)
As for the HDTV support, a review is available here.
On a side note, the markings on the GPU indicate the 4th week of 2010, e.g. the end of January.
| NVIDIA GeForce GTX 480 1536MB |
The cooler isn't fundamentally different from those used with the previous GTX solutions. A turbine drives air through a heatsink and ejects it out of enclosure. However, due to the extreme power consumption of GeForce GTX 480, the cooling system has been improved in the heatsink department. As you can see, the heatpipes only cool the core, while memory chips are taken care of by a plate under the cover.
They have probably run out of ideas on how to make a silent cooler powerful enough to deal with such a hot core. So have in mind that the cooler is very noisy. Even in the 2D mode, it works at 44%. Compare this to the 20-25% of the previous graphics cards. The noise, however, starts after 50%. So the idle mode feels like you're about to hear the noise. And you do -- in the 3D mode, when the cooler speeds up to 70-80% on average. |
 |
 |
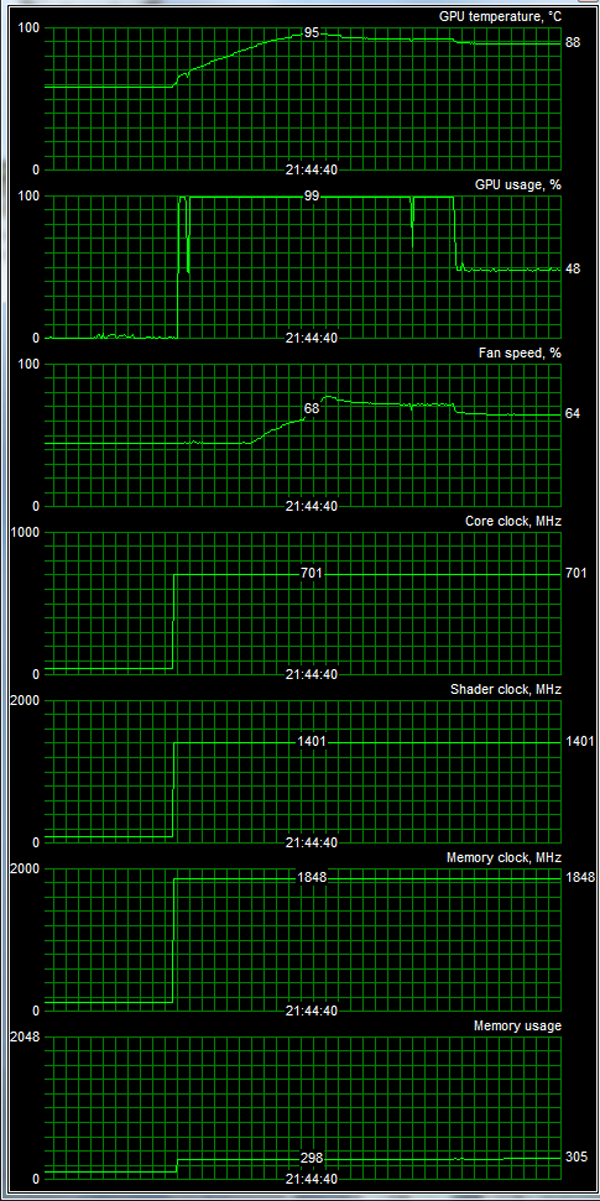
Traditionally, we monitored temperatures using RivaTuner.
NVIDIA GeForce GTX 480 1536MB
The core heats up to 95°C, so you might as well forget about quiet, even if you only want to watch a movie or something.
Write a comment below. No registration needed!
|
|
 |
Article navigation:
Page 1: Introduction, specs, key features
Page 2: GPC, SM, Scheduler, TMUs
Page 3: PolyMorph and Raster Engines, memory, ROPs
Page 4: General-purpose computing, ray tracing, etc.
Page 5: Design, cooling
Page 6: DX9 synthetic tests
Page 7: DX10 synthetic tests
Page 8: More DX10 synthetic tests
Page 9: 3DMark Vantage Feature Tests
Page 10: DX11 synthetic tests
Page 11: More DX11 synthetic tests
Page 12: Performance in games, conclusions
|
|
|