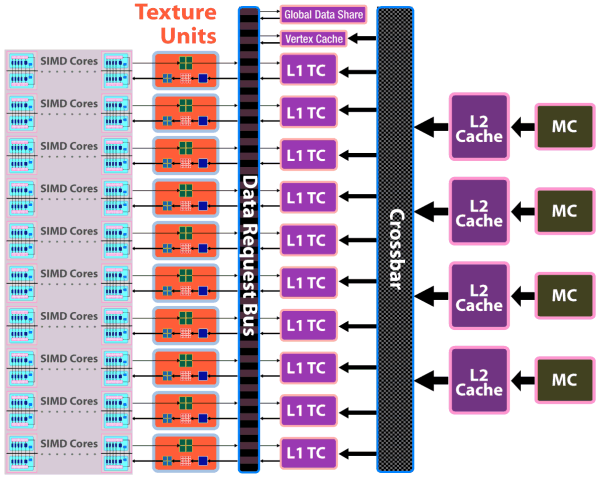
On the whole, one can expect up to 2.5-fold performance gains for bilinear filtering of 32-bit textures, and 1.25-fold gains for 64-bit textures. Other peculiarities - doubled T-Cache bandwidth versus RV670, and fetching up to 160 texture samples (Fetch4/Gather4) per cycle, which must also raise performance.
The chip uses a new design of caching units: separate vertex cache, L2 cache is tied to four 64-bit memory channels, L1 caches store unique data for each SIMD to raise caching efficiency. Bandwidth has grown as well: up to 480 GB/sec for L1 T-Cache, up to 384 GB/sec between L1 and L2 Caches.
Judging by the feature test from 3DMark Vantage, the above mentioned changes in texture units and caches make texturing performance of the RV770 twice as effective as in competing GPUs from NVIDIA (both G92 and GT200). Let's examine the ROP chart:
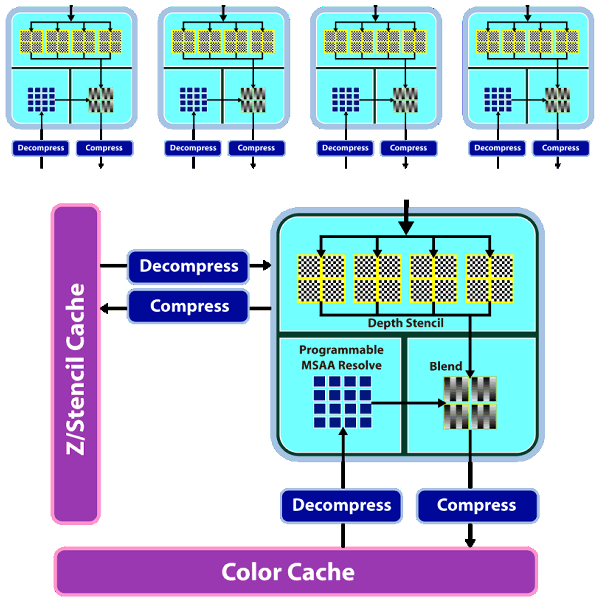
As we can see, there are not many qualitative changes in ROPs. Even though the number of ROPs hasn't changed since RV670, they can now process twice as many pixels per cycle in most cases, which is especially important for MSAA. Now algorithms of MSAA 2x and 4x come almost for "free", at least from the point of view of ROP operation. Here is a comparative table of the speed at which pixels are written into a frame buffer in various modes:
ROPs are twice as efficient almost in all modes, except for the simplest one - 32-bit color without MSAA. We should also note Custom Filter Anti-Aliasing (CFAA). The previous generation of AMD GPUs offered special antialiasing filters called Custom Filter Anti-Aliasing. We analyzed this method in previous articles. The most interesting antialiasing feature in AMD chips is edge detect used in CFAA 12x and 24x.
This method offers the highest quality. It uses the shader power of RV670 and RV770 to process images, which already went through MSAA. The method consists in detecting polygon edges (special filter) and applying additional filtering to these image areas. It does not require additional video memory as in case of MSAA 4x and 8x, and it works together with adaptive antialiasing. RV770 features minor improvements to accelerate all methods. One of them is a special fast link between ROP and shader processors.
We have information that RV770 does not use shader processors for MSAA, unlike R6xx and RV670. Standard MSAA algorithms use ROPs, only programmable CFAA uses shader resources.
Write a comment below. No registration needed!
|
|
 |
|
|
|