 |
||
|
||
| ||
Read also: Here we are testing the controllers' characteristics and possibilities of the software to determine a failure of one of array's discs (the failure was modeled by disconnecting a power cable) and to recover a mirror when a 3-disc configuration with a spare drive is used. The discs were connected as "master" in both channels and the spare was set as "slave" in the first channel. The results will be compared with 1-disc configuration. Ziff-Davis WinBench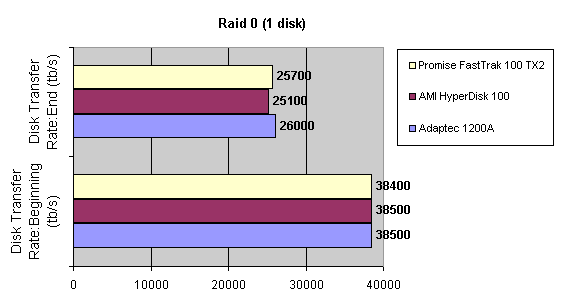 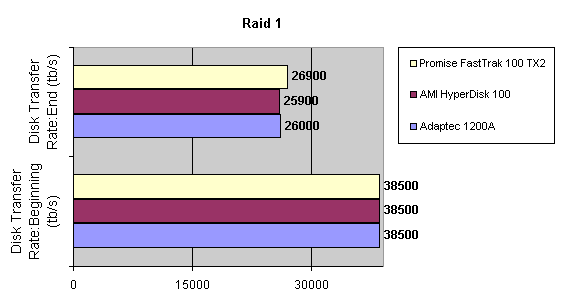 No considerable changes in the reading speed. All controllers, except the Adaptec, lifted the reading speed in the end of the disc at the expense of optimization of reading (the controller can read data by turns from two discs). The Promise shines in it. 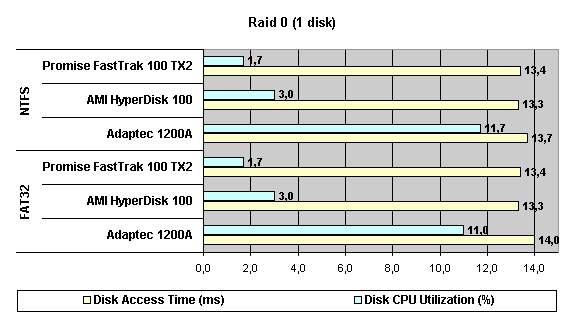  The mirror support doesn't require many extra CPU resources (a maximum of 0.7% over for the AMI). The Promise has a lower access time, the Adaptec has it the same, and the AMI has a higher access time. The FastTrak TX2 realized this mode the best way. 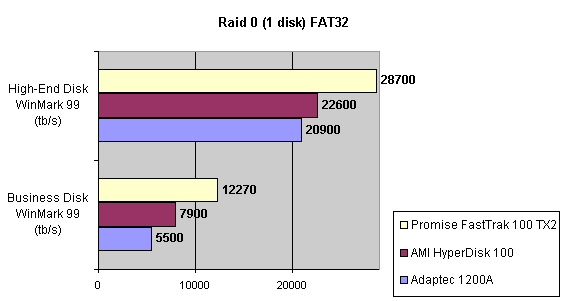 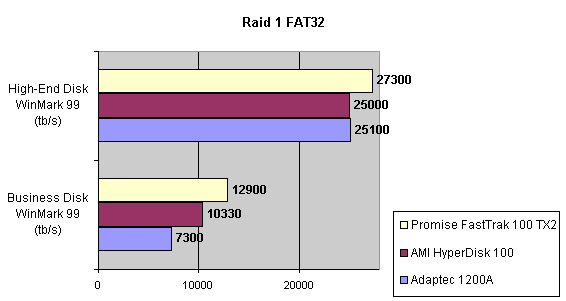 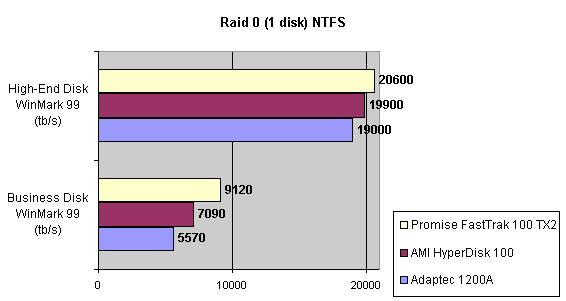 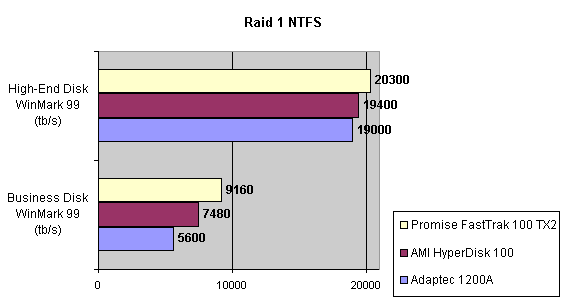 In the FAT32 the overall performance has become better, except the Promise in the High-End Disk WinMark. In the NTFS, in the High-End Disk WinMark all have worse results except the AdAptec, and in the Business Disk WinMark we can see again an overall growth. Intel IOMeterThe upper graph stands for 1-disc configuration, the lower one - for RAID1. Server Pattern 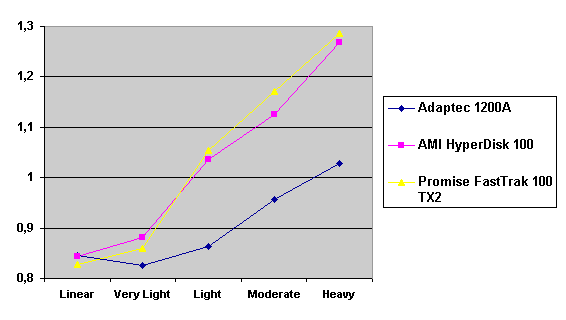 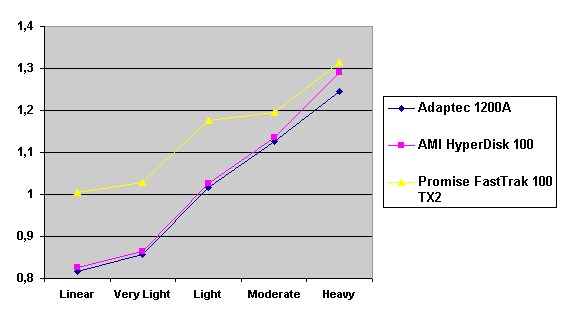 Workstation Pattern 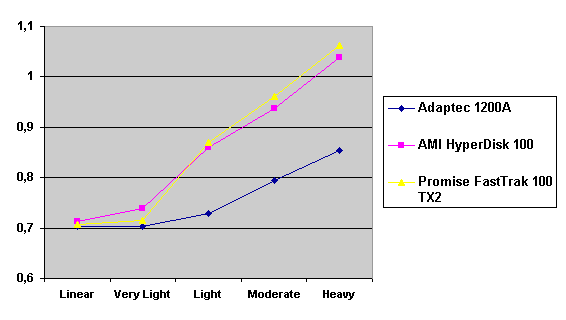 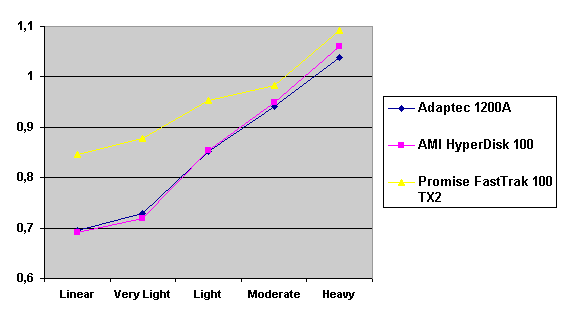 Database Pattern 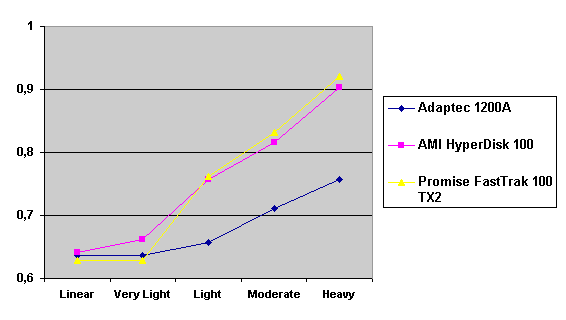 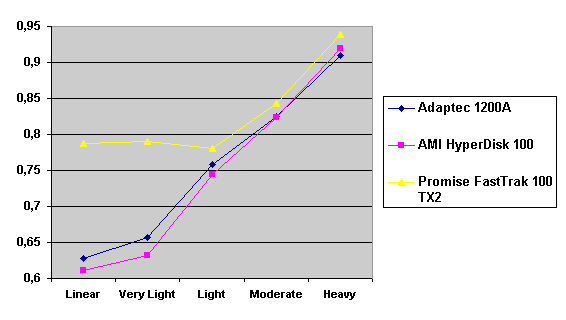 On the whole, the Promise has better scores at low loads, the Adaptec at high ones. The AMI controller doesn't "notice" a mirror. Streaming Read 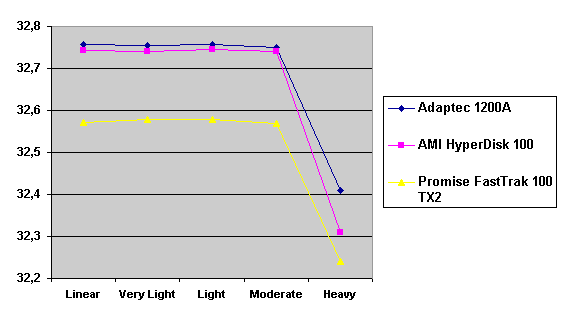 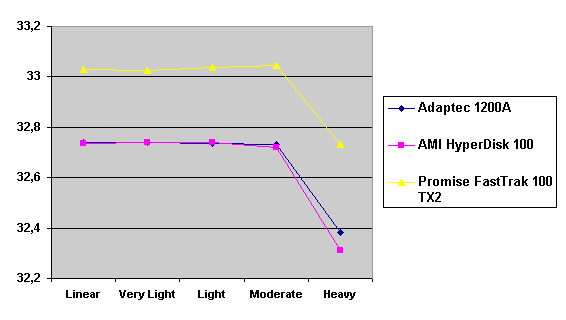 Streaming Write 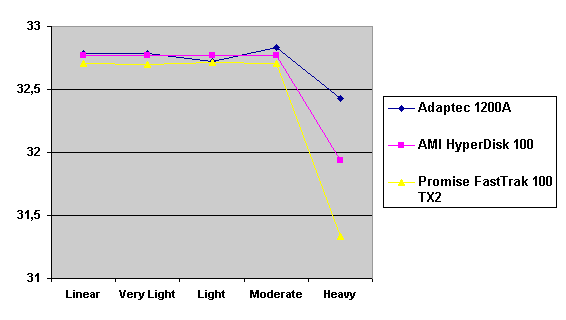 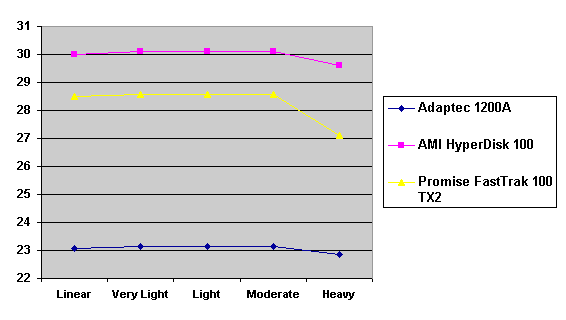 The Promise leads in reading, while the AMI is superb in writing. The Adaptec failed in this test. Random Read 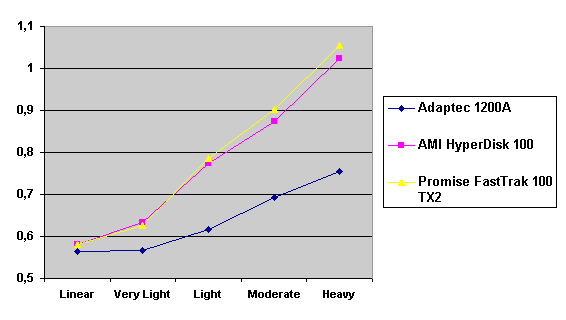 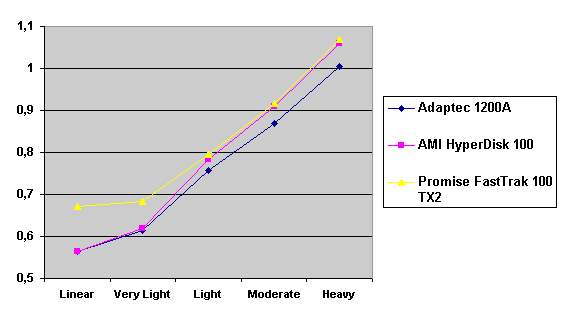 Random Write 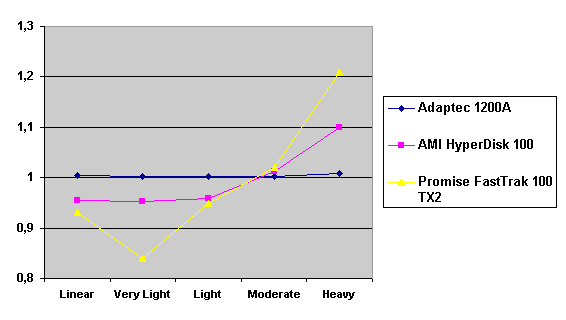 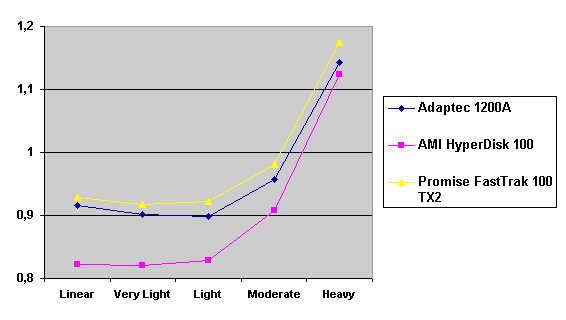 The situation is the same for Server-Database-Workstation patterns. On the whole, the Promise beats the others while the Adaptec 1200A comes the last. Now let's see how the controllers handle failures in an array. Adaptec 1200AWe created a Mirror array, started the Adaptec ATA Management Software utility, stopped the power supply for one of the discs and... nothing happened. In order to discover failures in an array it is necessary to go to Configuration > Monitor > Rescan. You will see the following message: 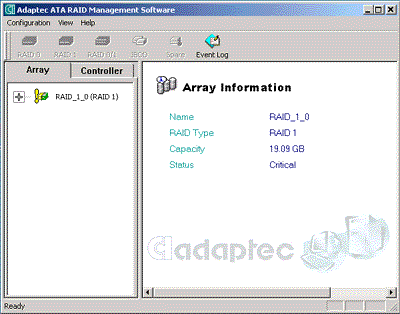 After rebooting we will be taken to the Array Configuration Utility BIOS where you will be offered either to switch off a computer and to connect a serviceable disc or to delete the array. If the Spare drive is connected the situation doesn't change except that after Rescan information will be copied to the spare drive. 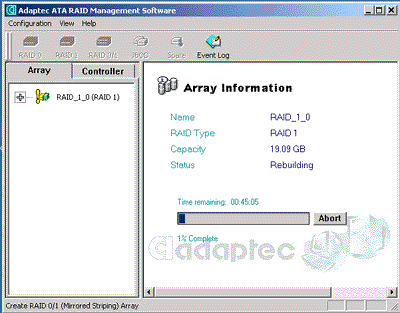 It is interesting that the program informs about creation of a RAID 0/1 (Mirrored Striping) array in the status-line! After rebooting, if the array recovery wasn't completed, the BIOS does nothing, and only the utility offers to restore the array. 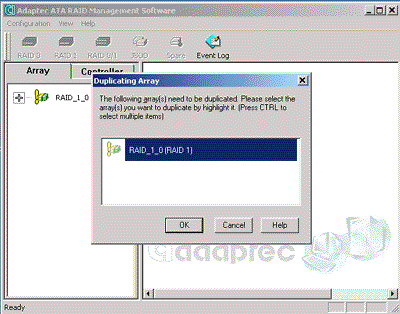 I think it is an optimal reaction to a disc failure. The disadvantage is only that a regular operator interference is required. AMI HyperDisk100When the power is off the icon in the System Tray becomes red, and you will see the following message on the screen 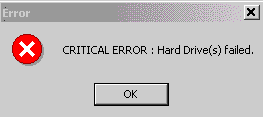 The computer starts squeaking until you click the button. After rebooting the BIOS also informs about a critical status of the array. With a spare drive provided and with the "Start Automatic Rebuilding If Error Threshold Reached" option enabled the information should start being copying onto the spare drive. But it becomes possible only after rebooting. 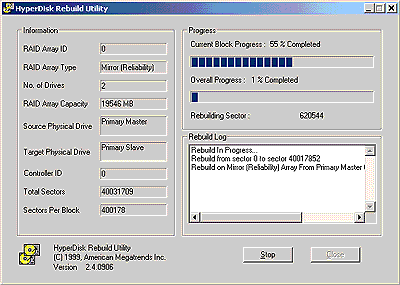 The icon, at that, becomes yellow. Promise FastTrak100 TX2This controller has a standard reaction for Promise Technology. When power gets off, the Fastcheck Monitoring Utility changes its icon and displays the following message 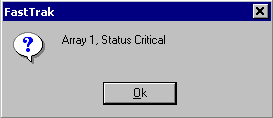 After rebooting you will be notified that the array is not serviceable. If the system has a Spare Drive, the message of the array failure is followed by copying of information on this drive. 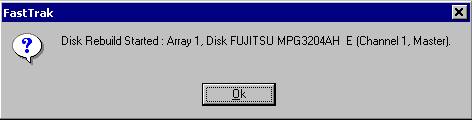 The FastBuild BIOS utility can also help you recover an array with a spare drive. It is a well thought-out algorithm. ConclusionThe Promise FastTrak100 TX2 is again ahead. It is followed by the AMI HyperDisk100, and the Adaptec 1200A is the last. The Promise and AMI controllers are equal in convenience of operation and in algorithms of array recovery. The Adaptec has one disadvantage - manual initiation of array scanning. The complete results can be found in the tables.Ziff-Davis
WinBench 99
Read also:Introduction
and summary
Write a comment below. No registration needed!
|
Platform · Video · Multimedia · Mobile · Other || About us & Privacy policy · Twitter · Facebook Copyright © Byrds Research & Publishing, Ltd., 1997–2011. All rights reserved. |