Architecture
Since GeForce GTX 590 is based on two GF110 GPUs, there's no sense in repeating what we already wrote in the aforementioned reviews. So we'll just give you a brief account of the key features. Creating GF110, NVIDIA focused on improving its power efficiency. The GPU was overhauled to reduce leakage currents and optimize power consumption.
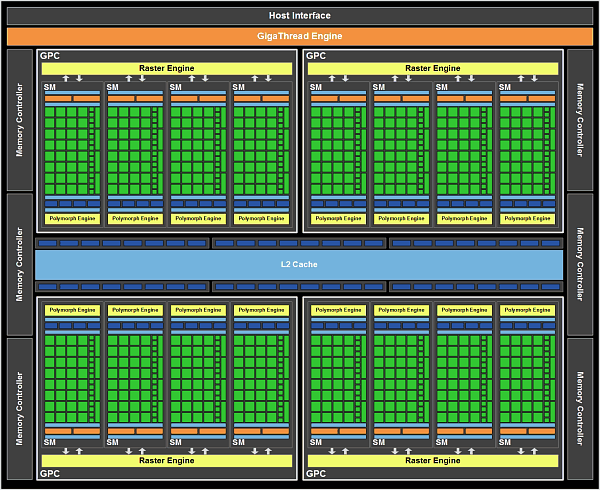
In terms of architecture, GF110 GPUs of GeForce GTX 590 do not differ much from GF100 that GeForce GTX 480 is based on. Both processors have the same multiprocessor configuration and consist of four Graphics Processing Clusters.
Each of the two GF110 processors features 4 GPC clusters, 16 Streaming Multiprocessors, 6 64-bit memory controllers connected to L2 cache and featuring 8 ROPs per each. Each GPU features 512 stream processors in total, organized as 16 SM with 32 stream processors in each. And, like we already said, all of them are enabled and working.
Each multiprocessor has 64KB of on-chip memory that can be configured as either 48KB shared memory plus 16KB L1 or, vice versa, 16KB shared memory and 48KB L1. Besides, GF110 has 768KB of unified L2 that serves all requests for loading and storing data as well as texture fetches.
It's interesting that while NVIDIA hasn't reduced the number of active stream processors, it considerably reduced GPU clock rate. And it seems that it's been done due to power consumption, even with a couple of 8-pin power connectors. Would it be better if they created a dual-GPU card based on two GF114s with fewer stream processors, but much higher clock rates?
Power design
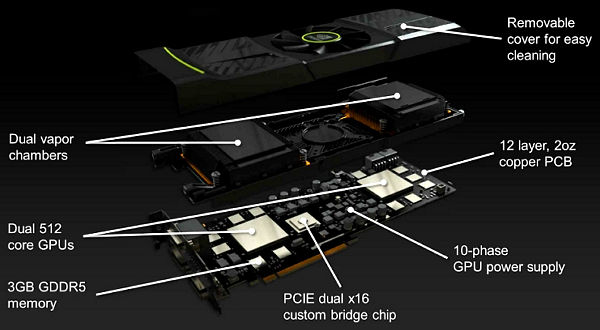
As you probably understand, creating a graphics card based on two very powerful and power-hungry GPUs is not an easy task. So, GeForce GTX 590 features a 12-layer PCB, and power layers also contain lots of copper to improve heat dissipation and increase card's life cycle. The GPUs are powered by a 10-phase system with a digital controller, and another two 2-phase controllers are used to power GDDR5 memory.
The bandwidth of one PCI-Express 2.0 x16 slot (up to 8GB/s) is shared between the GPUs by means of a special NF200 PCIe switch that's been used since GeForce GTX 295. This switch provides 16 PCIe lanes to each GPU, but at one half of the bandwidth. Unlike AMD that sticks its labels onto PLX devices, NVIDIA uses its own developments.
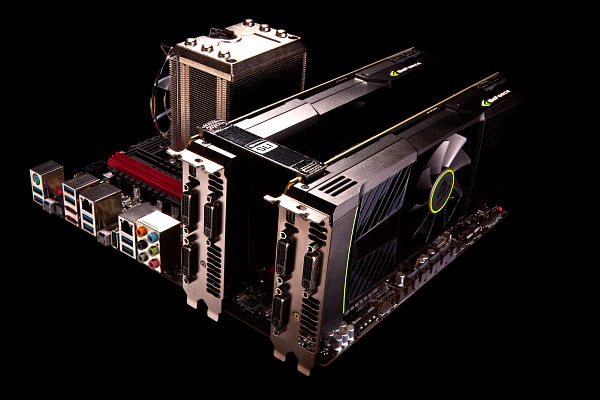
Keeping such a hot dual-GPU card cool is probably even harder than creating it, but NVIDIA has done a great job. One important advantage of GeForce GTX 590 the company underlines is the 90mm low-noise, low-speed fan.
The cooler of GeForce GTX 590 features two separate heatsinks, each with a vaporizing chamber. To further improve cooling efficiency, elements on the back of the PCB are covered with aluminium plates. Oh, and there's also a glowing GeForce logo, but it doesn't help much.
The new cooler is noticeably more efficient compared with counterparts. As a result, exactly GeForce GTX 590 is the quietest dual-GPU solution, and not just today. According to NVIDIA, the new cooler is quieter than that of GeForce GTX 295 and GeForce 9800 GX2, not to mention Radeon HD 6990 that's quite noisy under heavy workload.
The rest of GeForce GTX 590 is not much different from a couple of GeForce GTX 570 or GeForce GTX 580 working in a SLI configuration. Each GeForce GTX 590 card has three Dual-Link DVI connectors, as well as one mini DisplayPort one. With 3D Vision Surround, this lets you output stereo image to three monitors at once:
Obviously, dual and quad-GPU configurations need much power to work. PSUs providing at least 800W of power are recommended, because one graphics card alone can consume up to 365W (actually even more). And you'll also need to create proper airflow inside enclosure. Considering this, NVIDIA and partners introduced certification of machines suitable for Quad SLI configurations.
One requirement is that a motherboard must have enough space between PCIe x16 slots — two graphics card must be separated by at least one expansion slot (in case of air cooling; liquid won't require another slot). As you might have expected, the list of certified motherboards already features top-end models from all major manufacturers.
Power requirements are quite strict, too. In a Quad SLI machine, a PSU must have four 8-pin PCIe connectors, providing up to 150W to each. So far the list of certified PSUs is not long, mostly featuring 1100W~1500W models.
There are certain requirements to enclosures as well. An enclosure must provide enough cooling to system components and a stream of air aimed directly at the graphics cards.
Write a comment below. No registration needed!