 |
||
|
||
| ||
BFG GeForce 8600 GTS OC2 256MB ThermoIntelligence, Chaintech GeForce 8600 GT 256MB, Chaintech GeForce 8600 GTS 256MB, ECS/Elitegroup GeForce 8500 GT 512MB, ECS/Elitegroup GeForce 8600 GT Plus Edition 256MB, Point Of View GeForce 8600 GT Ratatouille Edition 256MB |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BFG GeForce 8600 GTS OC 256MB PCI-E Chaintech GeForce 8600 GTS 256MB PCI-E |
|
|
Each graphics card has 256 MB of GDDR3 SDRAM allocated in four chips on the front side of the PCB.
Samsung memory chips (GDDR3). 1.0 ns memory access time, which corresponds to 1000 (2000) MHz. |
 |
| ECS/Elitegroup GeForce 8500 GT 512MB PCI-E | |
|
The graphics card has 512 MB of GDDR2 SDRAM memory, allocated in eight chips on the front side of the PCB.
ProMOS memory chips (GDDR2). 3.0ns memory access time, which corresponds to 333 (666) MHz. |
 |
| BFG GeForce 8600 GTS OC2 256MB PCI-E with ThermoIntelligence | |
|
The graphics card has 256 MB of GDDR3 SDRAM allocated in four chips on the front side of the PCB.
Hynix memory chips (GDDR3). 1.0 ns memory access time, which corresponds to 1000 (2000) MHz. |
 |
| ECS/Elitegroup GeForce 8600 GT Plus Edition 256MB PCI-E | |
|
The graphics card has 256 MB of GDDR3 SDRAM allocated in four chips on the front side of the PCB.
Samsung memory chips (GDDR3). 1.2ns memory access time, which corresponds to 800 (1600) MHz. |
 |
| Chaintech GeForce 8600 GT 256MB PCI-E | |
|
The graphics card has 256 MB of GDDR3 SDRAM allocated in four chips on the front side of the PCB.
Samsung memory chips (GDDR3). 1.4 ns memory access time, which corresponds to 700 (1400) MHz. |
 |
| Point Of View GeForce 8600 GT Ratatouille Edition 256MB PCI-E | |
|
The graphics card has 256 MB of GDDR3 SDRAM allocated in four chips on the front side of the PCB.
Qimonda memory chips (GDDR3). 1.4 ns memory access time, which corresponds to 700 (1400) MHz. |
 |
| Comparison with the reference design, front view | |
|
BFG GeForce 8600 GTS OC2 256MB PCI-E with
ThermoIntelligence
|
Reference card NVIDIA GeForce 8600 GTS
|
|
Chaintech GeForce 8600 GTS 256MB PCI-E
|
|
|
BFG GeForce 8600 GTS OC 256MB PCI-E
|
|
|
Chaintech GeForce 8600 GT 256MB PCI-E
|
Reference card NVIDIA GeForce 8600 GTS
|
|
ECS/Elitegroup GeForce 8600 GT Plus Edition
256MB PCI-E
|
|
|
Point Of View GeForce 8600 GT Ratatouille
Edition 256MB PCI-E
|
|
|
ECS/Elitegroup GeForce 8500 GT 512MB PCI-E
|
Reference card NVIDIA GeForce 8500 GT
|
| Comparison with the reference design, back view | |
|
BFG GeForce 8600 GTS OC2 256MB PCI-E with
ThermoIntelligence
|
Reference card NVIDIA GeForce 8600 GTS
|
|
Chaintech GeForce 8600 GTS 256MB PCI-E
|
|
|
BFG GeForce 8600 GTS OC 256MB PCI-E
|
|
|
Chaintech GeForce 8600 GT 256MB PCI-E
|
Reference card NVIDIA GeForce 8600 GTS
|
|
ECS/Elitegroup GeForce 8600 GT Plus Edition
256MB PCI-E
|
|
|
Point Of View GeForce 8600 GT Ratatouille
Edition 256MB PCI-E
|
|
|
ECS/Elitegroup GeForce 8500 GT 512MB PCI-E
|
Reference card NVIDIA GeForce 8500 GT
|
All the 8600GTS cards are based on the reference design. Even the overclocked BFG card with a blue PCB. They are based on a compact PCB, which still requires external power supply. Unlike GTS models, the 8600GT cards have a simpler power supply unit, no external power connector, and smaller PCBs.
The 8500GT cards are based on the 6600 and 7600GS designs, which use eight memory chips on the front side of the PCB.
All these cards have TV-Out with a unique jack. You will need a special bundled adapter to output video to a TV-set via S-Video or RCA. You can read about the TV-Out in more detail here.
Analog monitors with d-Sub (VGA) interface are connected with special DVI-to-d-Sub adapters. Maximum resolutions and frequencies:
What concerns MPEG2 playback features (DVD-Video), we analyzed this issue in 2002. Little has changed since that time. CPU load during video playback does not exceed 25% on all modern graphics cards. What concerns HDTV and other trendy video features, you can read the first of our reviews here.
The 8600GTS-based cards require additional power supply, so they are equipped with a black 6-pin connector at the end. The cards are bundled with a splitter to connect to any power cable with a Molex in case your PSU does not have this cable.
Now about the cooling systems. I shall not describe coolers of the reference 8600GTS cards - we have already examined them.
We monitored temperatures using RivaTuner (written by A.Nikolaychuk AKA Unwinder). We got the following results:


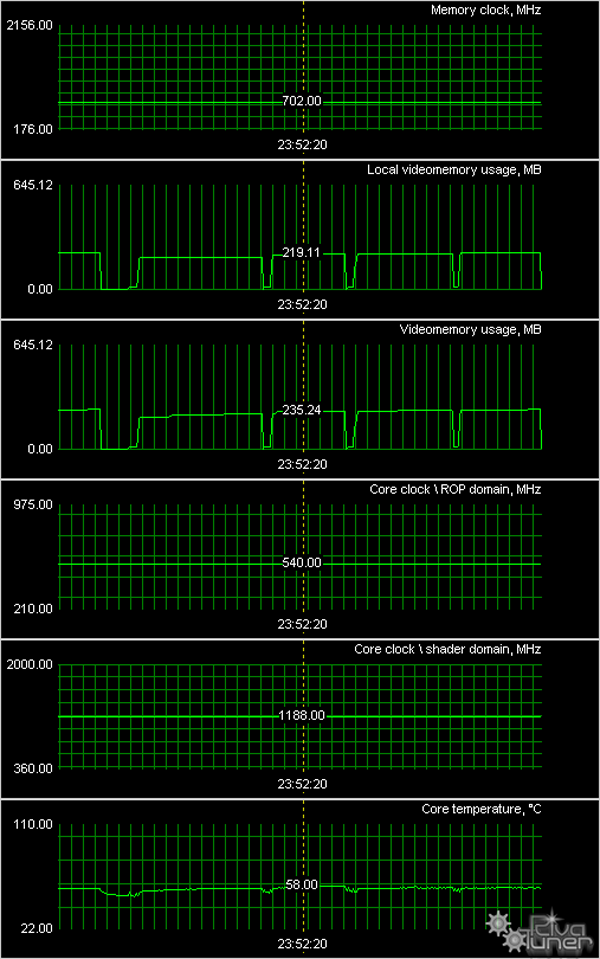
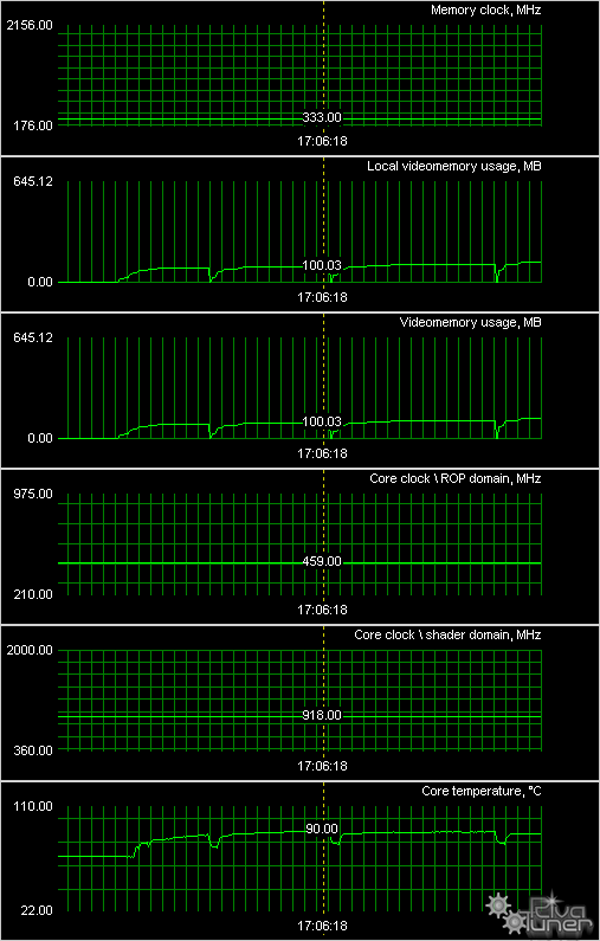
Alas, ECS cards have problems with cooling. They get very hot, especially the 8500GT. That's what a weak quiet cooler can do... The only thing we can do it to complain. Besides, a situation with the 8600GT from the same manufacturer is no better.
The overclocked card from BFG with a unique cooler is up to the mark. It's noiseless, and its temperature does not rise above 75°, while the noisy reference cooler allows the core to get hotter by 10°.
The cooling system from PoV is highly efficient, as we have expected, operating temperatures did not rise above 60°.
Testbed configuration:
VSync is disabled.
We used the following test applications:
If you have a decent understanding of 3D graphics, you may draw your own conclusions for the diagrams below. However, if you are interested in our comments on test results, you may read them after each test. Anything that is important to beginners and those who are new to the world of video cards will be explained in detail in the comments.
First of all, you should look through our reference materials on modern graphics cards and their GPUs. Be sure to note the operating frequencies, support for modern technologies (shaders), as well as the pipeline architecture.
If you have just begun realizing how large the selection to choose a video card is, don't worry, our 3D Graphics section offers articles about 3D basics (you will still have to understand them - when you run a game and open its options, you'll see such notions as textures, lighting, etc) as well as reviews of new products. There are just two companies that manufacture graphics processors: ATI (the graphics department of AMD) and NVIDIA. So most of the information is divided into these two sections. We also publish monthly 3Digests that sum up all comparisons of graphics cards for various price segments.
Thirdly, analyze test results of the video cards under review. We'll not analyze each test, we'll just draw a bottom line after all tests.
So, what can we say about the GeForce 8500 GT? - It's a very weak card, if it's not overclocked. Too many features have been cut down. It cannot compete with similar cards from AMD, even though they don't support DX10. However, the HD 2600 family compete well with these cards. Do these cards really need to support DX10 at all? Will DX10 games run fast enough on such a card? - It's a rhetorical question. They certainly will, if you disable maximum quality. It's a "double-edged" situation: if manufacturers don't launch Low-End cards supporting the new functions, game publishers will not introduce all these new functions into their games, motivating the decision by the lack of proper hardware on the market. On the other hand, everybody understands that such a card as 8500GT will not cope with any DX10 game even in 1024x768 with high quality settings. Thirdly: should you really buy Low-End cards with DX10 support now? - There will be no pure-DX10 games in the nearest future. There will appear some DX9-to-DX10 ports, combined titles (DX9 and DX10). But native DX10 games (that use only this technology!) may appear only the next year. And by that time there may be launched a new DX10 family of more powerful Low-End cards.
So we can say only one thing: existing games run well on the RADEON X1650, as prices for this card dropped significantly. Besides, the 7600GT/GS cards are not as expensive as they used to be. There is no need in the DX10 series. The 8600GTS card will cope with the load of future games in high quality modes, but it's quite expensive so far. The 8600GT is an intermediate solution, it's up to you to decide. You should consider frequencies and prices.
Besides... AMD has already launched a new family of DX10 cards, which compete well with their counterparts from NVIDIA. So in our opinion, your choice is a matter of your personal taste. Yep, these solutions are cut down much. But it must be admitted that the 8600 family holds some advantage over the 7600 series. However, I have already mentioned the price drop for the X1650 family. So the latter will be more interesting, if we don't take DX10 into account. It all depends on what you actually want. If you want a graphics card for old games that you play from time to time, there is no need to buy a graphics card from the new family. If you want a graphics card for future DX10 games, you should buy a 8800 card :-)
And the last point in general conclusions: a new HDTV video engine (HD video) in all 8500-8600-based cards - it's very useful in this segment, where users pay less attention to 3D than in the Hi-End segment. Read the details here .
BFG GeForce 8600 GTS OC 256MB PCI-E is a reference card with increased frequencies (in fact, almost all cards are overclocked now). There is nothing special. The cooler is noisy. However, this card enjoys a 5-year warranty.
BFG GeForce 8600 GTS OC2 256MB PCI-E with ThermoIntelligence is a better modification of the previous card, both in frequencies and noise. That's the best model among all 8600GTS cards, if you have nothing against BFG with their constant chapping and changing of packages and designs. Don't forget about the 5-year warranty for these cards.
ECS/Elitegroup GeForce 8600 GT Plus Edition 256MB PCI-E stands in between the 8600GT and the 8600GTS in performance. But its cooling system is far from perfect, and the card gets very hot. However, it's not critical. What's more important, it's not noisy.
Chaintech GeForce 8600 GT 256MB PCI-E is the standard 8600GT card. There is nothing to add. The cooler is quiet, operating temperatures are normal.
Point Of View GeForce 8600 GT Ratatouille Edition 256MB PCI-E is actually a usual 8600GT card. It just comes with a game based on a popular cartoon. But it's equipped with a very efficient cooler, so you should pay closer attention to this product, if you want a 8600GT card.
Chaintech GeForce 8600 GTS 256MB PCI-E is a reference card. The company brought nothing new to this product. The cooler is noisy.
I remind you that the above mentioned graphics cards are equipped with GPUs that have an updated video decoding engine. Our author, Alexei Berillo, has already published an article about it.
As always, the final choice is up to the reader. We can only inform you about products and their performance, but can't make a buying decision.
And here is one more thing, we'll repeat it in each review. Having decided to choose a graphics card on your own, you should be aware that you change one of the key components of your system unit, which may require additional configuration for better performance or you may have to enable some functions to achieve higher quality. This is not an end product, it's just a component. So you should understand that you'll have to learn 3D graphics basics in order to get maximum performance from a new graphics card. And some graphics in general. If you don't want to deal with it, you shouldn't upgrade your computer on your own: you'd better buy ready PCs with preconfigured software and technical support from your system integrator, or game boxes, where no configuration is required, everything necessary is already configured in a game.
You can find more detailed comparisons of various graphics cards in our 3Digest.
The following card get the Original Design award (August):

Our Excellent Package award for August goes to the following card:

PSU for the testbed was kindly provided by TAGAN |
The Dell 3007WFP monitor for the testbeds was kindly provided by NVIDIA |
Write a comment below. No registration needed!
|
Article navigation: |
| blog comments powered by Disqus |
| Most Popular Reviews | More RSS |
 |
Comparing old, cheap solutions from AMD with new, budget offerings from Intel.
February 1, 2013 · Processor Roundups |
 |
Inno3D GeForce GTX 670 iChill, Inno3D GeForce GTX 660 Ti Graphics Cards A couple of mid-range adapters with original cooling systems.
January 30, 2013 · Video cards: NVIDIA GPUs |
 |
Creative Sound Blaster X-Fi Surround 5.1 An external X-Fi solution in tests.
September 9, 2008 · Sound Cards |
 |
The first worthwhile Piledriver CPU.
September 11, 2012 · Processors: AMD |
 |
Consumed Power, Energy Consumption: Ivy Bridge vs. Sandy Bridge Trying out the new method.
September 18, 2012 · Processors: Intel |
| Latest Reviews | More RSS |
 |
Retested all graphics cards with the new drivers.
Oct 18, 2013 · 3Digests
|
 |
Added new benchmarks: BioShock Infinite and Metro: Last Light.
Sep 06, 2013 · 3Digests
|
 |
Added the test results of NVIDIA GeForce GTX 760 and AMD Radeon HD 7730.
Aug 05, 2013 · 3Digests
|
 |
Gainward GeForce GTX 650 Ti BOOST 2GB Golden Sample Graphics Card An excellent hybrid of GeForce GTX 650 Ti and GeForce GTX 660.
Jun 24, 2013 · Video cards: NVIDIA GPUs
|
 |
Added the test results of NVIDIA GeForce GTX 770/780.
Jun 03, 2013 · 3Digests
|
| Latest News | More RSS |
Platform · Video · Multimedia · Mobile · Other || About us & Privacy policy · Twitter · Facebook
Copyright © Byrds Research & Publishing, Ltd., 1997–2011. All rights reserved.