 |
||
|
||
| ||
This motherboard (brief manufacturer's designation is MS-7350) is a classic example of a plain ATX product. While it doesn't have top notch "goodies" like an integrated Wi-Fi adapter, two Gigabit Ethernet ports or a bunch of SATA RAID ports, it can still serve as a good foundation for a powerful and rich computer system. Besides, an additional distinguishing feature is that the board is based on an alternative chipset (for an Intel platform anything that doesn't use Intel chipsets is traditionally considered alternative). Thus, one may say that MSI P6N SLI is a motherboard for those who on one hand can afford buying more expensive products, but on the other hand are not going to pay more for what they do not plan on using. The fate of such products on the market is often predictable: they are purchased by two kinds of "self-assembly" fans (DIY):
Let us then evaluate this product based on the two aforementioned positions. 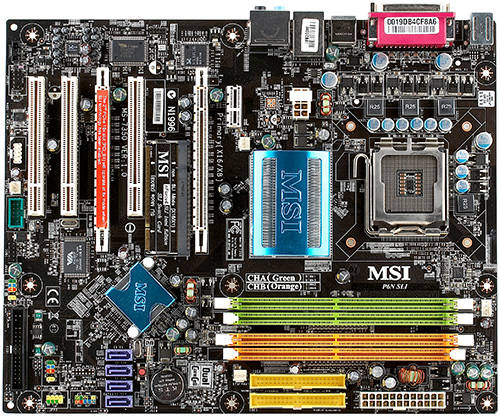 The motherboard's wiring layout is overall good. The location of the socket for connecting a floppy drive is the only possible flaw. Indeed, many other manufacturers choose the same placement, but that still doesn't make it convenient. On the other hand, if we consider this socket rudimentary (like the LPT port) then it would seem quite logical to put it as far away as possible and out of the way. :) Passive heatsinks are used for cooling chipset's northbridge and southbridge. Northbridge heatsink's design seems adequate: many slim fins should in theory provide more efficient cooling than a few thick ones that are used on standard ordinary heatsinks. Space around the CPU socket is left free to the maximum. There should be no problems with installing even very large coolers. Design of the CPU supply voltage stabilizer (4-channel impulse stabilizer with 3 field transistors per channel) is a copy of the one used in the more expensive MSI P35 Platinum. This fact is an advantage: P6N SLI has borrowed one of the more important parts from the high-end products. In general, the motherboard is indeed a plain ATX with nothing to make it stand out. Conservatives will definitely be happy to see the 3 PCI slots, the maximum possible number nowadays. System Monitoring (Fintek F71882FG, From BIOS Setup and Windows Utilities' Data)
Brand MSI Dual Core Center utility besides the aforementioned abilities allows keeping track of the memory and chipset northbridge voltages, while the universal SpeedFan utility also allows monitoring the voltage of the battery and +3.3 V Standby. Ports, Connectors and Sockets on Board's Surface
Board's Rear Panel (Left to Right, by Blocks)
Click for the 3/4 view
Package Contents
Integrated Controllers
We have evaluated quality of the integrated audio in 16-bit 44-KHz mode using RightMark Audio Analyzer 6.0 testing suite and ESI Juli@ sound card:
Overall rating: Very good - according to our test results the quality of analog audio output is on a very good level even for HDA codecs. Brand Technologies and Features
Settings
For testing we used BIOS version 2.3 dated 07/12/2007, which was the latest available at the time. The aforementioned BIOS capabilities are available in the specified version of the BIOS. Non-standard settings were not tested for operability. The motherboard supports accessing boot device selection menu by pressing F11 key during POST procedure. This conveniently allows performing a one-time boot, for example using a CD drive, without having to change corresponding settings in BIOS Setup. In addition, BIOS Setup includes the MSI D.O.T. (Dynamic Overclocking Technology) option. According to the manufacturer dynamic overclocking is initiated only when there is a real need in increased performance. The following settings are available: Disabled, Private (increasing FSB frequency by 1%), Sergeant (3%), Captain (5%), Colonel (7%), General (10%) and Commander (15%). PerformanceTestbed configuration:
We have compared P6N SLI in speed characteristics to two other motherboards based on Intel P35 chipset - fast (P35 Platinum) and not so fast (P35 Neo), as well as to the only motherboard based on equivalent chipset tested up to date - ECS NF650iSLIT-A.
As you can see the motherboard is overall not the fastest one. Despite that, in the most critical applications and modes the loss to the other boards is minimal. That is why we shall not recommend MSI P6N SLI to those, who really love speed and high fps. And to the rest we can say: performance characteristics are acceptable. Of course, the motherboard hasn't demonstrated extraordinary results, but neither have the tests uncovered anything fatal. Compatibility ProblemsUnfortunately, in the process of testing we have found an incompatibility of this board with our standard Promise SATA 300 TX2Plus PCI SATA-II controller. The motherboard failed to detect the controller itself and, naturally, the disks connected to it. In principle, there is nothing terrible about that. Every board is most likely incompatible with something. Besides, one can't call SATA 300 TX2Plus a wide-spread device. However, this is a fact that we have no right to leave undeclared. ConclusionAs we have promised our conclusions will be based on presumable demand for the products that are similar in characteristics to the one being examined. Thus, consider the first potential user category: "not so rich enthusiasts". They will get an adequate product, which implements everything that was announced. An almost perfect case: one can get a clear picture of the board's capabilities by looking at the specifications. Everything that is listed is, in fact, present. According to our tests everything works as it should. Device conforms to specifications. As to the problems with expansion cards, no one can promise universal compatibility. Moreover, users from this category usually look for a motherboard with built-in capabilities that fully satisfy their needs. That is what they will get - within the board's own limitations. The "thrifty pragmatic" users of the second category don't like to change fundamental components and use them to the last degree. They prefer to replace or add components to the computer without reassembling it completely. In contrast to the first category, the incompatibility that we have uncovered will be critical for them because of the mere fact of its existence, which may theoretically cause trouble in the future. In this case, the manufacturer has a good reason to make efforts and find the cause of this vexing glitch. Besides, it can most likely be fixed by releasing a new version of BIOS without having to redesign the board. In addition to that, one can suppose that this product can appeal to one more group of users. We shall nickname them "antiquity lovers" due to the fact that this motherboard includes three PCI slots with native support of two Parallel ATA IDE channels for four devices. A real refuge, so to speak, for the old expansion cards, hard disks and optical drives. :) This model on the manufacturer's website
The board provided for testing by the manufacturer We thank the Corsair for testbed memory modules Stanislav Garmatyuk (nawhi@ixbt.com) October 22, 2007 Write a comment below. No registration needed!
|
Platform · Video · Multimedia · Mobile · Other || About us & Privacy policy · Twitter · Facebook Copyright © Byrds Research & Publishing, Ltd., 1997–2011. All rights reserved. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||