MSI K9NGM3 — motherboard based on NVIDIA GeForce 7050 (Socket AM2) chipset
|
HDMI port steadily advances towards becoming customary. Its appearance on AMD 690G chipset motherboards is followed by introduction of this rectangular port to GeForce 7050 chipset motherboards. Based on comparison of these chipsets we have established their equivalence "in points". The reason why board manufacturers are not responding very actively to GeForce 7050 is the delay in its release. Whereas AMD has already attracted all major manufacturers and most of small ones (including even very small ones, if one takes a look at what is being offered in the rather conservative industrial board segment).
Nevertheless, just as we have predicted NVIDIA fans and ordinary users, who have a clear idea of their requirements and who have come to prefer GeForce 7050, will find their needs satisfied. We have already examined their first possible choice — Biostar's board. Today it is MSI's turn.
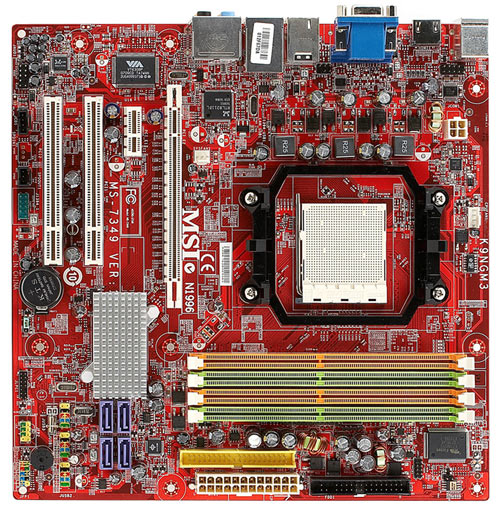
MSI developers, in contrast to their colleagues from Biostar, used the layout provided by single chip chipset not to place peripheral ports more freely, but rather to leave more room around the processor socket. On one hand it is good, because it allows to install a massive CPU cooler, on the other hand the placement of chipset in the area of expansion slots suggests using a low-profile heat sink, which, to make things worse, turns out to be in still-air zone (while large video adapter coolers can additionally block airflow to the chipset).

Then, even in the case of the previous model MSI K9NGM2 with a much more heat-emitting GeForce 6150 MSI made do with modest heat sinks. Therefore, further simplification seems logical this time, given the significantly reduced need for cooling. The board successfully passed all tests, though the chipset heat sink of course was hot in modes of maximum load on the graphics core. Significantly hot, in the opinion of some testers, who for whatever reason think that while measuring temperature "by touch" one's finger "must bear the heat", but who disregard the fact that operating temperatures of modern chips may be much higher than what the pain threshold allows. They sometimes reach over 100 degrees C, as is the case with video adapter components, and it is not a reason for concern unless glitches are detected.
The three-channel impulse voltage stabilizer uses 2 field transistors per channel (wiring layout allows 3), 5 capacitors of 1800 microfarad each and 4 of 1000 microfarad each. Capacitor manufacturer couldn't be identified. The board houses all elements provided for by design except a DVI-port. Board's form factor is microATX (245x245 mm). It is mounted to the chassis using 8 screws while the lower right corner remains unfixed.
System monitoring (Fintek F71882FG, from BIOS Setup data)
- CPU voltage, +3.3, +5, +12 V and 5 V Stand-by;
- Temperature of CPU (by built-in CPU sensor) and board (by on-board sensor);
- Rotation frequency of the two fans;
- Smart Fan — automatic rotation frequency control of CPU fan depending on CPU temperature. Adjustable temperature threshold (40—60 degrees), below which a set rotation frequency is maintained (from 0 to 87.5% of maximum, though zero doesn't correspond to stand still, but rather to rotation at minimum rate). Once threshold is exceeded rotation frequency is gradually increased to maximum. Frequency control is only supported for fans with 4-pin connectors.
Ports, connectors and sockets on board surface
- Processor socket (Socket AM2, declared support of all AMD Athlon 64/X2/FX and Sempron CPUs produced for this socket);
- 4 DDR2 SDRAM DIMM slots (up to 8 GB DDR2-400/533/667/800, dual-channel mode);
- 1 PCIEx16 video accelerator slot;
- 1 PCIEx1 slot;
- 2 PCI slots;
- Power supply connectors: standard ATX 2.2 (24 pins, can use a 20-pin connector), 4-pin ATX12V, 350 W or above PSU is recommended;
- FDD slot;
- 1 IDE (Parallel ATA) slot for 2 ATA133 devices — "chipset";
- 4 SATA-II (Serial ATA II) slots for 4 SATA300 devices — "chipset", disks can be combined into a RAID-array of level 0, 1, 0+1, 5 and JBOD;
- 3 expansion card slots for 6 additional USB ports;
- 1 expansion card slot for an additional FireWire port;
- TV-out header;
- CD/DVD-drive audio-out header;
- Block of analog audio-in/out connectors for the computer's front panel;
- 1 slot for S/PDIF-Out expansion card;
- 1 slot for COM-port expansion card;
- 1 socket for open chassis detector;
- 1 socket for TPM 1.2 module;
- 2 fan sockets, including a 4-pin CPU fan socket that supports monitoring rotation rate and intelligent rotation frequency control.
Board's rear panel (left to right, by blocks)

click to view the board in 3/4 perspective from the rear panel side
- PS/2 mouse and keyboard ports;
- HDMI;
- VGA;
- 2 USB and 1 FireWire 400 (6-pin) ports;
- 2 USB and 1 RJ-45 (Gigabit Ethernet) ports;
- 6 analog audio sockets (Line-In, Front-Out, Mic-In, Center/Sub, Rear-Out, Side-Out).
Clearly, rear panel space wasn't used in quite the optimal way. COM and LPT ports are not in high demand nowadays, but TV-out and S/PDIF sockets, which are compact "by nature", could have easily been included.
Package contents
- Packing: small box of a design common to inexpensive MSI boards based on integrated chipsets (our unit came as OEM-version);
- Documentation: user's guide;
- 1 Serial ATA cable;
- SATA power adapter for 1 device;
- 1 ATA66 loop;
- Rear panel plug for corresponding connectors;
- Compact-disk with drivers and brand MSI utilities including:
- MSI PC Alert 4 — utility for monitoring Windows system parameters that are available in the corresponding part of BIOS;
- MSI Live Update 3 — BIOS rewrite available from Windows including ability to search and download the latest version from the manufacturer's web-site (at the same time, rewrite from local drive is not supported and it is recommended to use standard WinFlash utility bundled with BIOS versions downloaded from the web-site);
- MSI Dual Core Center — utility for monitoring system parameters;
- MSI GoodMem — utility for RAM load optimization;
- MSI i-Speeder — utility for network traffic indication and TCP/IP-stack setup for faster Internet access;
- MSI Security — set of utilities for convenient password storage, user profile management and hard drive data encryption. Supplemented by Norton Internet Security 2005 antivirus suite and firewall.
HDMI-DVI-adapter would have been a very useful addition to the standard package, considering the lack of a corresponding port.
Integrated controllers
- Audio controller based on "chipset" High Definition Audio support and Realtek ALC888 codec provides ability to connect 7.1 audio systems via front audio-in/out connectors (including two independent channels for a separate stereo stream playback), CD-In and S/PDIF-Out;
- Gigabit Ethernet network controller based on "chipset" support and Realtek RTL8211BL PHY-controller with 10/100/1000 Mbit/s support;
- FireWire controller based on VIA VT6308P supporting two FireWire 400 (IEEE1394a) ports.
We have evaluated quality of the integrated audio in 16-bit 44-KHz mode using RightMark Audio Analyzer 5.5 testing suite and ESI Juli@ sound card:
| Frequency response (40 Hz to 15 kHz), dB: |
+0.02, -0.05 | Excellent |
| Noise level, dB (A): |
-91.8 | Very good |
| Dynamic range, dB (A): |
91.9 | Very good |
| THD, %: |
0.0022 | Excellent |
| IMD + N, %: |
0.0084 | Very good |
| Channel crosstalk, dB: |
-91.2 | Excellent |
| IMD at 10 KHz, %: |
0.0088 | Very good |
Overall rating: Very good. Results are close to upper limit for the codec being used.
Settings
| Based on jumpers and switches | CMOS reset jumper | |
| Through BIOS based on AMI BIOS v2.61 |
Ability to turn special CPU functions off |
+ |
K8 Cool-n-Quiet |
| Setting memory timings |
+ |
1T/2T Memory Timing, CAS Latency, Min RAS Active Time, RAS to CAS Delay, Row Precharge Time, Row to Row Delay, Row Cycle Time |
| Memory clock rate selection |
+ |
Auto, 400, 533, 667, 800 MHz (actually sets multiplier relative to HTT frequency) |
| HT bus operational settings |
- |
|
| Setting frequency of peripheral buses |
+ |
PCIE=100—150 MHz |
| Manual distribution of interrupts by slots |
+ |
|
| Adjusting FSB frequency |
+ |
200—300 MHz in 1 MHz increments |
| Adjusting CPU multiplier |
+ |
from x5 in integer increments |
| Adjusting CPU core voltage |
+ |
1.200—1.400 V in 0.025 V increments |
| Adjusting memory voltage |
+ |
1.80—2.20 V in 0.05 V increments |
| Adjusting chipset voltage |
+ |
1.20—1.50 V in 0.05 V increments |
We used BIOS 2.0 06/21/07 version, the only one released at that time. MSI engineers have finally added overclocking functionality to BIOS for their microATX boards based on integrated chipsets. We have only two complaints related to settings — insufficient range of CPU core voltage control (although, it is excused by the board's category) and lack of HT-bus multiplier selection (which isn't difficult to add in any case).
Overclocking
In order to evaluate the overclocking capabilities of the board and its BIOS, we overclock our testbed CPU to the highest frequency possible that also allows for stable operation. Applying this test procedure, we are able to effectively use all of the test board's supported abilities, including increasing processor core voltage, and if necessary, correcting multipliers and adjusting system and peripheral bus frequencies. However, if lowering Hyper-Transport frequency, for example, doesn't improve overclocking performance, the default multiplier is used instead. RAM is set (by using multiplier correction) to the standard frequency for the modules being used, unless the manufacturer specifies methods for improving memory overclocking, in which case their effectiveness is also explored. In order to evaluate the overclocked system's stability, we load Windows XP and run performance tests built into WinRAR (Tools menu - Benchmark and hardware test) for 10 minutes. It is important to realize that overclocking performance varies by motherboard and is, to some extent, an individual characteristic of each specific unit. For this reason, it is impossible for us, and any other review, to determine the overclocking potential of any board with megahertz precision. The practical goal of our test is to find out if the CPU's high overclocking potential is hindered by the board and to evaluate the board's behavior in non-standard BIOS modes. This test also assesses the board's ability to automatically revert to correct frequencies in the case of system hang-ups, excessive overclocking, etc.
| |
Clock rate, MHz |
FSB frequency, MHz |
Core voltage (according to BIOS system monitoring), V |
HT bus frequency (multiplier), MHz |
| Athlon 64 X2 4000+ (Windsor, 2.0 GHz) |
2600 |
260 |
1.40 |
1300 (x5) |
Taking into account the two limitations (due to the BIOS version being used) mentioned above, the result is more than decent. A rare board of this category can operate at such high HT frequency without having to raise chipset voltage. CPU overclocking capabilities at standard core voltage turned out to be the acceleration bottleneck.
Performance
Testbed configuration:
- Processor: AMD Athlon 64 X2 4000+
- RAM: 2 Kingston KHX7200D2K2/1G (DDR2-800, 5-5-5-15-2T) modules
- Outboard video adapter: ATI Radeon X1900 XTX, 512 MB GDDR3
- Hard drive: Seagate Barracuda 7200.10 (SATA-II, 7200 rpm)
- PSU: Chieftec CFT-560-A12C
- OS: Windows XP SP2
For comparison in this test we have used a Biostar TF7050-M2 motherboard, which is based on the same chipset and was previously tested in our lab.
| Test |
Integrated graphics |
Outboard graphics |
| Biostar TF7050-M2 |
MSI K9NGM3 |
Biostar TF7050-M2 |
MSI K9NGM3 |
| Data compression using 7-Zip, min:sec |
6:43 |
6:44 |
6:38 |
6:39 |
| MPEG4 (XviD) encoding, min:sec |
6:11 |
6:09 |
6:07 |
6:07 |
| Unreal Tournament 2004 (Low@640x480), fps |
48.7 |
46.4 |
60.8 |
59.2 |
| Unreal Tournament 2004 (High@1024x768), fps |
28.1 |
23.7 |
57.7 |
56.2 |
| FarCry (Medium@800x600), fps |
33.9 |
32.5 |
123.7 |
118.4 |
| DOOM III (Medium@800x600), fps |
19.1 |
18.9 |
134.1 |
128.1 |
MSI board both with integrated and with outboard video adapter is slightly behind in game tests.
Conclusions
The MSI motherboard being tested will hardly have any trouble with sales. One reason is that only two manufacturers at present provide GeForce 7050 chipset on their boards. This board has good overclocking capabilities and excellent functionality. The only disappointment is the lack of DVI-out or a corresponding adapter in the package. Well, this model wasn't intended to draw attention of those, who are interested in a simple VGA-DVI link for a multi-display configuration without any "multimedia" add-ons. Like Biostar, MSI plans to sell motherboards based on NVIDIA GeForce 7050 chipset at a higher price than the ones based on AMD 690G (with an equivalent video-out port set). Consequently, among all models based on NVIDIA chipsets only GeForce 6100-based motherboards can compete with such models as ECS AMD690GM-M2.
This model on manufacturer's web-site
Board was kindly provided for testing by the manufacturer
Dmitriy Laptev (lpt@ixbt.com)
August 24, 2007
Write a comment below. No registration needed!
|
|
 |
|
|
|



