 |
||
|
||
| ||
Chipset manufacturers, as well as CPU manufacturers, just love dividing the market into segments, which are getting narrower in time, and offering different modifications of the same product for each segment. We have an impression that a user will soon be suggested to take into account the color of his/her PC case or what browser he/she uses, "because these are very important nuances, taken into account in our products!" However, at the sight of so many chipsets, motherboard manufacturers do not think about the color of a browser. They ponder whether they will have to create individual designs for each modification. There is nothing unnatural about it for motherboards on expensive chipsets. But it's much more convenient to have a minimal number of modifications in the economic segment to be manufactured on a mass scale. On the other hand, we can understand chip makers wanting to save on inexpensive chipsets. It makes it inexpedient to produce low-end pin-compatible models with sterling chips and some functions locked on the logical level. 
But in case of GeForce 6100 + nForce 400 and GeForce 6100 + nForce 405 chipsets, NVIDIA did not niggle and used the same dies, even though the junior model supports only two PCI Express lanes, while the top model — 10 lanes. We can easily see it on the photo. They are certainly compatible in connections as well, which allowed Foxconn to use the same design for motherboards on both chipsets. Foxconn WinFast MCP61VM2MA-RS2H
Foxconn WinFast MCP61SM2MA-ERS2H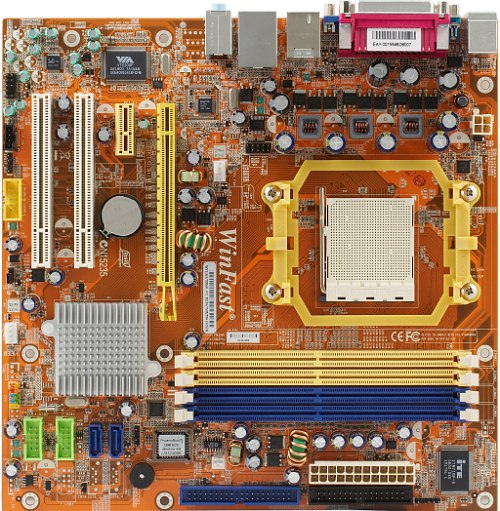
On the whole, this design is praiseworthy. The only drawback is memory slot latches blocked by a video card. As you can see on the photo, the model on GeForce 6100 + nForce 400 is equipped with a graphics port, even though the chipset officially lacks it. Foxconn engineers got the most out of the existing two PCI Express lanes, having installed two ports. One of them indeed accepts any video card, and seems to work as any sterling PCI Express x16. If you enable the corresponding BIOS option, integrated video can work together with discrete video, so we get an opportunity to connect three monitors. We are going to evaluate how "defective" this radical reduction of PCI Express lanes is from the point of view of gaming performance. What concerns heat dissipation, the cut-down nForce 6100 is up to the mark. It's definitely an absolute champion in this parameter on the market of desktop chipsets. I have an impression that motherboard manufacturers can do without heatsinks for these models. However, we'd like to see the heatsinks to be sure that such a motherboard will be stable even in a tight PC case working under load for a long time. What's really topical for top GeForce 6100 and 6150 models in nasty conditions, it won't fail due to systematic overheating. The 3-phase switching voltage regulator of the processor incorporates three field-effect transistors per channel, five 3300 uF capacitors from OST and four 1500 uF capacitors from United-Chemicon. Memory voltage regulator is reinforced with L elements. It uses OST capacitors. According to the official web site, motherboards come in two bundles. Along with our samples, there exist their full counterparts - RS2HV and ERS2HV. The letter V stands for the official certificate of compatibility with Windows Vista Premium. Nevertheless, we hasn't found out what will stop Vista from running on a computer with a motherboard without V. We successfully installed this operating system. What concerns the letter E, it stands for a FireWire controller in a Foxconn motherboard. Motherboard dimensions — 245×245 mm (microATX), nine-screw mount, all corners are firmly fixed. System monitoring (ITE IT8716F-S, according to BIOS Setup)
Onboard ports, sockets, and connectors
Back panel (left to right, blockwise)Foxconn WinFast MCP61VM2MA-RS2H
Click the image to open the rear view of this motherboard
Foxconn WinFast MCP61SM2MA-ERS2H
Click the image to open the rear view of this motherboard
Package Contents
The set of proprietary utilities includes: Tiger One for system monitoring (it alerts a user when monitored parameters go beyond the admissible limits), overclocking (similar to BIOS tools), and Fox LiveUpdate for automatic BIOS updates (it can also check for updates on the official web site). The bundle also includes Norton Internet Security 2006. Integrated Controllers
The integrated audio quality was tested in 16bit, 44 kHz using the RightMark Audio Analyzer 5.5 test application and the ESI Juli@ sound card:
General performance: Good. The inexpensive HDA codec from Realtek does not produce good impressions. According to our objective tests, it's no better than an average AC’97 codec. To all appearances, it's not installed very well, as we have already met this codec in motherboards, where it demonstrated a tad higher results. Hence the natural decision to use the 6-channel output instead of the 8-ch one. You will hardly want to build a good audio system with this integrated solution. As both motherboards demonstrated similar results with deviations within the measurement error, we publish only results of the MCP61VM2MA-RS2H. Proprietary technologies and peculiarities
Settings
We used BIOS P23 dated 29.11.06, the latest release version. The mentioned BIOS parameters are available in this version, but the viability of non-standard settings hasn't been tested. Variety of overclocking functions in BIOS seems complete. As these are almost the cheapest motherboards from Foxconn, they do not belong to the group of products for enthusiasts, we can only conjecture the reasons why engineers decided to offer so many functions. Anyway, test results are somewhat disappointing. It's evidently not enough to open these options in BIOS, which are usually locked in inexpensive motherboards. OverclockingIn order to evaluate motherboard and its BIOS, we overclock our testbed processor
to a maximum stable level. We use all features of the motherboard
in this test, including rasing CPU voltage and adjusting multipliers
and frequencies of system and peripheral buses, if necessary (but
if, for example, reducing Hyper-Transport frequency does not improve
overclocking, we leave the default multiplier). Memory is set to the
standard frequency for a given memory module (multiplier correction),
if a manufacturer does not publish any ways to improve memory overclocking.
Otherwise, we analyze their efficiency as well. In order to evaluate
stability of the overclocked system, we load Windows XP and run WinRAR
performance test for 10 minutes (Tools — Benchmark and hardware
test). As overclocking potential is an individual property of a given
motherboard sample to some degree, we don't set the task to determine
overclocking potential to within a single MHz. In practice, we are
to find out whether CPU overclocking will be limited by a motherboard
as well as to evaluate its behavior in non-standard modes, including
automatic restoration of a correct frequency after a failed overclocking
attempt, etc.
The result is not bad at all, though it does not break any records (our processor can do better with increased voltage; but in this case, the motherboard was a limiting factor, to be more exact the motherboards — they demonstrated identical results). The impression was spoilt by operating instability. Having reset parameters, we made another overclocking attempt on one of the motherboards, but we failed to achieve such high results, even though we tried to raise voltage at the chipset, HT bus, and changed other settings (nothing of the sort was done for the first successful attempt). Aware of this peculiarity, we tested the second motherboard more thoroughly and repeated overclocking three times. Two times out of three we managed to reach maximum frequency, but then the motherboard just stopped responding to the increased frequency - it restored the default frequency each time we rebooted the computer! By the way, the emergency frequency reset procedure is not ideal. Once you increase the frequency, the motherboard after emergency reset will fail to overclock until you clear CMOS with a jumper (just like we have mentioned, it just doesn't respond to setting an increased frequency). PerformanceTestbed configurations:
We decided to compare our motherboards with the ECS GeForce6100SM-M on NVIDIA GeForce 6100 + nForce 405. Its performance is on the level with motherboards on GeForce 6100 + nForce 410, including games, even though only 8 PCI Express lanes are allocated for the graphics port.
A video card with less memory indeed "helps" detect the advantage of a fast interface, especially in high resolutions. But it only concerns rather simple games from the point of view of modern GPUs. But the current tendency implies increasingly complex shader computations, which may turn even the most powerful processors (which determine the resulting fps level) into a bottleneck in high resolutions. On the contrary, video memory is getting cheaper and it's not difficult to install sufficient memory so that a GPU does not need system memory. It's all the more expedient, considering that video memory size in system requirements of games is often a determining factor. Lots of users go to shop for a video card "supporting DirectX 9.0 and equipped with 256 MB of memory". To all appearances, actuality of enlarging graphics bus throughput is not growing in time. It even goes down (at least for systems with a single video card). And from the practical (users')point of view, the probable upgrade to PCI Express 2.0 in the nearest future is no more justified than the upgrade from AGP x8 to PCI Express x16. It does not mean, of course, that assembling a gaming computer now, you should consider motherboards with a cut-down graphics bus (fortunately, the choice and prices of motherboards with sterling PCI Express x16 are more than acceptable). But if a user of this motherboard decides to buy a decent video card with a state-of-the-art GPU and sufficient memory, it will be able to play decent games. ConclusionsProceeding with our analysis of motherboards on "twice" integrated chipsets GeForce 6100 + nForce 400 and GeForce 6100 + nForce 405, we found out that despite the obvious positioning of such motherboards for the market of inexpensive office computers, they can also be used for inexpensive home PCs. Considering the high efficiency (minimal heat dissipation), such motherboards look well in compact PC cases for low-noise systems, entry-level media centers. What concerns motherboards from Foxconn, being good in design and implementation, they are still less attractive than competing products as a fault of irritating BIOS bugs. They appear only when you try to get most of your BIOS settings. Besides, BIOS updates come out on a regular basis, so at least Smart Fan will be fixed. What concerns overclocking, successful attempts are rare for motherboards of this class. It makes sense for Foxconn to grow in this direction, if the company wants to use overclocking options as a competitive advantage. Otherwise, it would be better to limit the choice of settings to fully functional ones. Foxconn WinFast MCP61VM2MA-RS2H on the manufacturer's web site Foxconn WinFast MCP61SM2MA-ERS2H on the manufacturer's web site
The motherboards are kindly provided by the manufacturer
Dmitry Laptev (lpt@ixbt.com) February 16, 2007 Write a comment below. No registration needed!
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Platform · Video · Multimedia · Mobile · Other || About us & Privacy policy · Twitter · Facebook
Copyright © Byrds Research & Publishing, Ltd., 1997–2011. All rights reserved.