 |
||
|
||
| ||
EPoX hasn't presented new products for Intel for a long time: in fact, the manufacturer made a pause after i945-based models. Indeed, these models provided support for dual-core Pentium D processors. And hard-driving enthusiasts (the traditional target audience of motherboards from this company) were much more interested in AMD solutions, so EPoX launched all new models for this platform. The situation has changed drastically with the release of Core 2. Now this segment of the market is of most interest. The announcement of several i965-based motherboards looks only natural. In future we can expect the chipset base to expand — in particular, to use cheap products from the NVIDIA nForce 600i series.
Our today's motherboard belongs to Middle-End and possesses usual (even limited) functionality in terms of additional controllers, which is compensated by several proprietary technologies from EPoX. At the same time, EPoX 5P965+ GLI has one unique feature. Intel removed support for IDE devices on the chipset level (since i965), but motherboard manufacturers keep it this or that way. In this case they use an unusual solution, which we'll describe in detail.
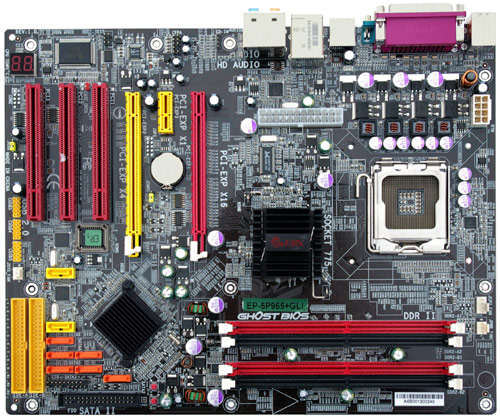 In general, this PCB layout is rather convenient, but the main power connector, traditionally placed by EPoX in the center of the board, can hamper manual installation and deinstallation of a CPU cooler with the standard ("boxed") retention module. In return, we always have access to memory slots - probably the most often upgraded elements. 5P965+ GLI has three PCI slots (quite a lot for these days). Access to them may be blocked only by a large video card installed into the second PCIEx16 slot. As this motherboard does not officially support SLI, all the three PCI slots will be accessible in most cases. There is one more hardly probable problem: as SATA and IDE slots (as well as FDD) are grouped in a corner, very long expansion cards in PCI slots may block them. There is only one absolute drawback of the PCB layout - the Clear CMOS jumper is very close to the second graphics slot: it's difficult to use the jumper even when you hold the motherboard in your hands; it becomes almost impossible when assembled with a large video card. Northbridge and Southbridge are equipped with passive cooling. We registered no failures in the standard mode. But we cannot speak of any safety margin in this case — the heatsinks are too small. However, according to readings of the external thermal sensor, temperature of the Northbridge heatsink does not rise above 60°C in the hottest spot. The 4-phase switching voltage regulator of the processor incorporates low-profile polymer capacitors (9 × 560 uF, 3 × 330 uF (16 V)). It uses two field-effect transistors per phase (they do not get very hot). Besides, EPoX traditionally pays attention to the memory voltage regulator. It uses high-quality capacitors and is reinforced with L elements. Motherboard dimensions — 305×245 mm (full-sized ATX), it's mounted with nine standard screws + another optional one, all corners are firmly fixed. The family of EPoX motherboards on Intel 965 is not numerous so far (its first representatives were announced by New Year's Eve): along with this model, there is also its cheaper modification 5P965-J (based on the same PCB), which lacks some brand features (power/reset buttons, thermal sensor), it uses ICH8 Southbridge and just one IDE bridge (for a single device). System monitoring (EPoX EP1308 (aka Fintek F71882FG), according to BIOS Setup)
Voltage, temperature, and rotational speed readings are shown when you turn a computer on, but not long enough to see forthcoming problems. Automatic fan speed adjustment is available only for the CPU cooler. Three modes are supported: Full Speed — uncontrolled mode; Duty Cycle — fan speed depends on CPU load; By Temperature — the most convenient mode, when you can specify three temperature thresholds with rotational speeds. 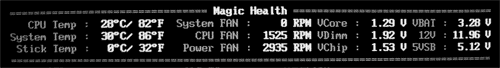 Onboard ports, sockets, and connectors
Back panel (left to right, blockwise) Click the image to open the rear view of this motherboard
Package Contents
The set of proprietary utilities includes:
Integrated Controllers
The integrated audio quality was tested in 16 bit, 44 kHz using the RightMark Audio Analyzer 5.5 test application and the Terratec DMX 6fire sound card:
General performance: Very good (details).
IDE support is based on two SATA-PATA bridges. On the whole, there would have been nothing strange in this solution (manufacturers would use IDE-SATA bridges to support the first Serial ATA hard drives). But the EPoX 5P965+ GLI solution is notable for its scalability: instead of just removing two (chipset-based) SATA ports and installing IDE, engineers use the following solution. PATA devices are connected with a standard cable to standard connectors (there are two of them on the motherboard, but each of them supports only a single device). Then corresponding special SATA connectors must be connected (with a usual or bundled short cable) to any usual SATA ports as shown in the picture.
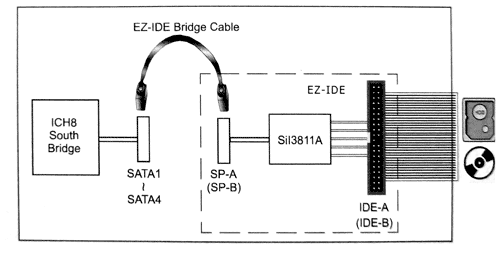 The approach itself is certainly interesting and rather convenient, but its implementation… Firstly, extra SATA connectors and connecting them with a cable look like meccano (or a funny computer game) — why not switch between the modes with a jumper or in BIOS Setup? As for now, the motherboard is a local chaos of cables. Secondly, a potential advantage of the lack of additional controllers (Silicon Image bridges are "transparent") is that no drivers are required — according to some forum posts, it solves the problems with ATAPI devices and RAID modes of the ATA controller in the chipset. It's hard to say why our sample refused to boot up from a drive connected to the PCI controller. But it may be a system error that has to do with peculiarities of the disk system in this motherboard. As a result, we have an unusual and, unfortunately, problem solution. Proprietary technologies and peculiarities
Settings
We used BIOS dated 20.12.06, the latest available BIOS version at the time of our tests. The mentioned BIOS parameters are available in this version, but the viability of non-standard settings hasn't been tested. The motherboard allows to call up a menu to select a boot device during the POST procedure, a convenient way for a once-only boot-up, for example from a CD drive, without making changes in BIOS Setup. According to the manufacturer, BIOS versions released after this article have fixed the problems with manual configuration of memory timings and installing OS on a chipset RAID. A number of users' complaints must decrease after they flash the new BIOS versions. PerformanceTestbed configurations:
The motherboard was very stable in the standard operating mode, not a single failure, freeze, or reboot were registered. As we used memory modules operating in DDR2-800 with timings 5-5-5 and higher, let's compare our results with those demonstrated in similar conditions by other motherboards based on Intel 965 chipsets.
We should mention that EPoX 5P965+ GLI with one of the old BIOS versions demonstrated slightly higher performance. But even in case of the latest BIOS, the difference between the contenders is insignificant and cannot be the reason to choose this or that model. Bottom lineWhat concerns advantages, EPoX 5P965+ GLI features support for all modern processors for Socket 775, a good bundle, and a number of proprietary functions to make your experience with this motherboard even more pleasant. However, functionality of this motherboard is rather limited for Middle-End, where this model belonged at the time this article was written: no FireWire or additional RAID controllers, just four SATA ports if you use IDE connectors, and no eSATA. Thus a user should make a choice between more interfaces or such EPoX features as POST port and an external sensor - not as a free addition to a cheap model. We should also mention passive cooling for Northbridge - it's a small heatsink, which makes us consider additional cooling, especially during overclocking experiments and when the motherboard is installed into a small PC case. While this comment is debatable, problems with IDE cannot be ignored. Thus, we call it another questionable solution (these things abound in modern products on Intel 965), but not a triumph of engineering minds. Summing it all up, this motherboard is an interesting, but not problem-free, Middle-End solution. It offers an alternative for manufacturers to attracting users with integrated peripheral controllers.
This model on the manufacturer's web site
Write a comment below. No registration needed!
|
Platform · Video · Multimedia · Mobile · Other || About us & Privacy policy · Twitter · Facebook Copyright © Byrds Research & Publishing, Ltd., 1997–2011. All rights reserved. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||