 |
||
|
||
| ||
ECS used the previous integrated chipset from ATI/AMD with the Radeon Xpress 1150 core to launch ECS RS485M-M - almost the cheapest cut-down solution for Socket AM2. And now the company decides to carry on the same policy for the AMD 690G chipset. It's rather strange on the face of it, because we've got cut-down 690V for this purpose. It would have been logical to use it in simple motherboards. However, VGA and DVI outputs on the rear panel that appear owing to the senior chipset are a good excuse for a virtual excess in payment caused by the price difference between the chipsets.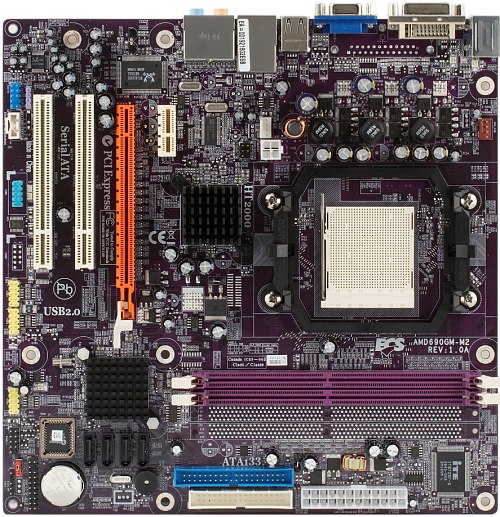  PCB layout resembles ECS RS485M-M and is just as praiseworthy - connectors and the clear CMOS jumper are arranged rationally. We can only reproach it for the layout of SATA ports - a long video card may block several ports. But it's a virtual problem. In practice, this motherboard will hardly be used with a maximum number of hard drives and an expensive video card. 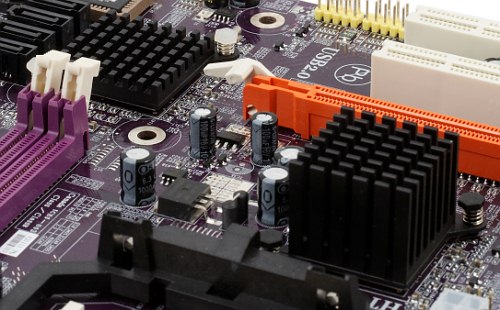 This chipset is said to demonstrate praiseworthy heat release. Its heatsinks remain just warm to the touch even under long-term maximum load. This chipset probably outscores the previous leaders in economical operation from the single-chip GeForce 6100 + nForce 400/405 family. Thus, its heatsinks should suffice, even if the motherboard is installed in a compact PC case with awkward ventilation. You shouldn't worry about additional chipset cooling when you choose a CPU cooler (you can see on the photo that fins of the heatsink go parallel to the processor socket, so it's not designed to be cooled by a CPU fan). There is only one nuance to be taken into account for any motherboard with passive chipset cooling, especially when the chip is close to a processor socket. If you deliberately limit rotational speed of a CPU cooler without a safety margin as far as thermal capacity is concerned (for example, you use a boxed cooler and set the target temperature of Smart Fan to 50° and higher), the elements around a processor will get much hotter. As chipset elements channel just as much heat away through the PCB as they do through the heatsink, chipset temperature may grow significantly. A conclusion is evident. When you experiment with CPU cooling, pay attention to surrounding elements. The motherboard has empty seats for two memory slots, LPT port, and a connector for the second COM port. The other functional (from users' point of view) components are installed. The 3-phase switching voltage regulator of the processor incorporates three field-effect transistors per channel (this PCB layout can accommodate four), six 1800 uF capacitors from an unidentified manufacturer, and three 1500 uF ones from OST. Motherboard dimensions — 245×245 mm (standard microATX), 8-screw mount, bottom edges are not secured, but it has no effect on contact reliability between the motherboard and connected components. System monitoring (ITE IT8726F-S, according to BIOS Setup):
Onboard ports, sockets, and connectors
Back panel (left to right, blockwise) Click the image to open the rear view of this motherboard
Package Contents

Integrated Controllers
The integrated audio quality was tested in 16bit, 44 kHz using the RightMark Audio Analyzer 5.5 test application and the ESI Juli@ sound card:
General performance: Very good (details). Integrated audio support is praiseworthy. Settings
We used BIOS dated 13.01.2007, the latest release version. The mentioned BIOS parameters are available in this version, but the viability of non-standard settings hasn't been tested. The choice of overclocking options is very good for an entry-level model. But GPU frequency controls turned out to be inactive - the motherboard just ignored their changes (performance would not change). A GPU can be overclocked only synchronously to a CPU by increasing FSB clock and setting the GPU clock frequency synchronous to the system frequency. The integrated core endured 232 MHz FSB (maximum overclocking) during our tests. Its temperature did not grow much in the process. In return, performance gain in games reached 10—15%. Overclocking
In order to evaluate the motherboard and its BIOS, we overclock our
testbed processor to a maximum stable level. We use all features of
the motherboard in this test, including raising CPU voltage and adjusting
multipliers and frequencies of system and peripheral buses, if necessary
(but if, for example, reducing Hyper-Transport frequency does not
improve overclocking, we leave the default multiplier). Memory is
set to the standard frequency for a given memory module (multiplier
correction), if a manufacturer does not publish any ways to improve
memory overclocking. Otherwise, we analyze their efficiency as well.
In order to evaluate stability of the overclocked system, we load
Windows XP and run WinRAR performance test for 10 minutes (Tools —
Benchmark and hardware test). As overclocking potential is an individual
property of a given motherboard sample to some degree, we don't set
the task to determine overclocking potential to within a single MHz.
In practice, we are to find out whether CPU overclocking will be limited
by a motherboard as well as to evaluate its behavior in non-standard
modes, including automatic restoration of a correct frequency after
a failed overclocking attempt, etc.
The result was predictable. Overclocking is limited by BIOS capacity to increase FSB clock. But unlike most inexpensive motherboards, we didn't have to adjust HT bus multiplier. PerformanceTestbed configuration:
We decided to compare the motherboard under review with ECS RS485M-M on ATI Radeon Xpress 1150 - an immediate ideological predecessor in this ECS line.
Despite the lack of manual memory timings control, ECS AMD690GM-M2 works with memory more efficiently than its predecessor. ConclusionsEntry-level models with two video outs and modern peripheral functionality can be only welcome. ECS AMD690GM-M2 can be used to build a production office PC. And considering minimal heat release of the chipset, it can also be used for an inexpensive media center. Besides, it will also do for a home computer intended for a multi-monitor setup. The motherboard is kindly provided by the manufacturer
Write a comment below. No registration needed!
|
Platform · Video · Multimedia · Mobile · Other || About us & Privacy policy · Twitter · Facebook Copyright © Byrds Research & Publishing, Ltd., 1997–2011. All rights reserved. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||