 |
||
|
||
| ||
By Vladimir Romanchenko (lone@ixbt.com)

It happened so that speaking of December news, I must mention that besides the quarter-end, it's the year-end as well with all corresponding analytics. It seemed makers, our main news source, got tired after Comdex Fall 2002 and freed the "newsway" for analysts with both reports for 2002 and provisionals for the next year. Well, this might be a December tradition as well. Production, technologies, toolsThe end of the year brought us two important exhibitions for semiconductor industry: SEMICON Japan and IEDM (International Electron Devices Meeting). Analysts and market researchers started to make reports more and more often at such events. Another tradition is that every time they have to share news about bad state of semiconductor industry (though keeping future forecasts bright). SEMICON Japan brought the updated and less comforting data about the semiconductor equipment market. Basing on October and November sales analysis, Stanley Myers, CEO and president of SEMI (Semiconductor Equipment and Materials International), announced that the worldwide chip-making equipment and materials shipments will reduce by over 32% in 2002 down to $18.9 billions from $28 billions of 2001. Though SEMI believes the situation will improve within the following years due to the improvements of the industry, indicated by the increased load of facilities in 2002. According to SEMI, already next year capital construction investments will increase up to the 15% equipment market growth ($21.8 billion). In 2004 we should expect another considerable 21% growth ($26.4 billion). And only by 2005 the growth will reduce to 4% (and the market will be $27.5 billions already). iSuppli announced the Top 30 semiconductor vendor rating for 2002, enabling to have an in-depth look at the market state. 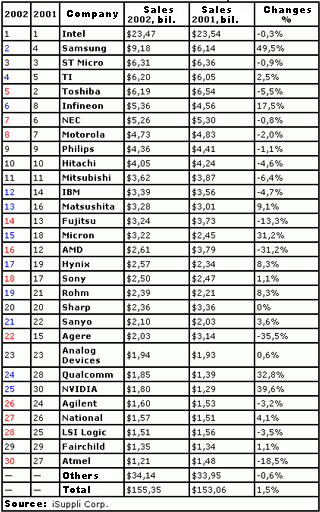 The rating contains not only the chip makers like Infineon, Micron, or Samsung, but also the suppliers, selling chips under their brands, including those without own production like NVIDIA, Qualcomm, etc. As the Q4 is not finished yet, the results are compiled, using the provisional forecasts. Well, nobody doubted that Intel was to remain on top. It's interesting that, besides staying on the first place, the company could keep the sales on the level of 2001. Samsung showed the highest sales growth rate in 2002, having occupied the second place from the former fourth. Who could believe that a company can double the sales volumes in a hard year! The third STMicroelectronics remained on the same position, and the following Texas Instruments went one place up. It's interesting that DRAM makers with all their complaints about the low market prices have significantly improved their businesses, achieving higher rating places. Micron Technology had time to increase the sales volumes by almost one third in this year. NVIDIA and Qualcomm continue to achieve high sales volumes growth rate, at that not having any own facilities. Positions of Toshiba, Agere, LSI Logic, Atmel, and Fujitsu got worse. AMD lost four places at once, its sales volumes might reduce by $1 billion or almost 1/3 this year. IDC published the information on the PC segment, specifically, in December. Though there's no final data yet, the company forecasts the total PC shipments will make 136.2 million units, that's 1.6% more than past year and 2.6% less than in 2000. In 2003 most PC market growth (provisionally, up to 8%) will be provided by consumer and enterprise shipments in USA and the governmental shipments will be reduced due to cut budgets. In 2004 IDC expects at least 11% growth, and in 2005 this process should slow down again. Despite the PC demand growth in USA, political unstability, mostly the possible war in Iraq, might deliver a strong blow to the economics. Besides, in the next off-election year, USA will considerably cut budget program expenditures (that scientists begin to feel already) and shipments to the governmental segment will be significantly reduced. In Western Europe analysts mark the exceeding of forecasted consumer and enterprise shipments, though this region suffers a slight downturn of 0.5%. Nevertheless, the next year might bring about 6% growth. The Japanese market, suffered most from the global downturn, continues to shrink. In China things are vice versa with governmental shipments exceeding any expectations. Though China is still the only Asian-Pacific country with the stable PC market growth. Speaking of the technological events, I'll mention the 90-nm process technologies, offered by Intel and IBM at IEDM 2002. At International Electron Devices Meeting 2002 (IEDM) Intel and IBM presented their 90-nm process technologies and reported about the benefits of the proprietary logic production technologies and the excellent results. However, each company used different techniques: IBM used the partially depleted SOI and Intel - the concept of the strained silicon in its "1262 process technology". Besides, each company used its own measuring system. IBM announced that its 90-nm CMOS process enabled the maximum self-excitation, and Intel, not using the auto-oscillation generation results, offered the fastest current transfer for the 90-nm silicon. According to Intel, the strained silicon enabled to improve the results by at least 20%. Intel's new 90-nm 1262 process technology will be launched on 300-mm wafer fabs next year for making the next-generation P4s codenamed "Prescott". To create the strained lattice Intel plans to use the epitaxial germanium dopant on the upper silicon layer with the moderate 17% germanium atom concentration. According to Intel, the change in the germanium atom quantities will enable the company to easily move to the 65-nm process technology without transition to SOI. Besides, Intel will use the basis of 90-nm process technology to develop the new technology of making comm chips, combining the bipolar SiGe transistors, passive and other elements. The first chips, made using the Intel's new 90-nm SiGe process are expected in about the late 2003 - early 2004. By a twist of fate, for the last five year IBM has remained one of the most active adepts of the strained silicon, offering IEDM numerous research docs. However, it seems that Intel will launch this technology earlier than IBM and others. IBM plans to launch the strained- lattice silicon on SOI while moving to the 65-nm process technology. The presented IBM's 90-nm SOI process technology enables to speak of the auto-oscillation circuits with about 4.5-5 picoseconds latency. For several month I see rumours about nanoimprint lithography in the Web, that's claimed to be better than traditional. There were several conferences held in Europe, USA, and Japan and in December MII (Molecular Imprints Inc.), whose first customer is rumoured to be Motorola, offered the first specs. 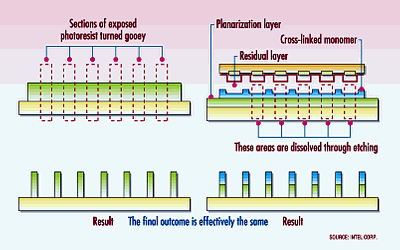 It's believed that in the future using nanoscopic polymer printing with 1:1 masks and using UV range will be more cheaper than traditional methods, involving complex and expensive optics. Currently industry uses 4:1 masks and further shrinking will require better optics as well. Sometimes, phase-shifting masks are used as an alternative, but the price problem arises here too. In nanoimprint lithography the process of mapping before etching or sputtering doesn't depend on optics quality. Similar to PCB photoresist, the monomer, coating the crystal surface, polymerizes and hardens under UV rays, but unlike photoresist, it is present in the solution and can be easily removed if needed, leaving only the desired scheme. At that it requires just a few nanoliters to form a print. By the moment nanoimprint lithography gets commercialized developers promise to raise the performance of such plants up to fantastic 2500 wafers/hour. Besides, this technology should open new horizons for molecular electronics, enabling to almost literally print circuits with precision of several monomer molecules. Another new technology was presented at IEDM by Toshiba and Sony. Together they announced the development of 65-nm chip production technology. Companies spent three years and 15 billion yens ($120 million) for the work and plan to commercialize it by March 2004. So, transistor gateways are 30-nm wide, utilizing 1-nm high nitrated dielectric with high nitrogen content. Gateway action time is 0.72 picoseconds. The companies underline that the new technology enables to create 256 Mbit DRAM and 64 Mbit SRAM chips. Toshiba and Sony's development is designed for 193-nm litho tools. 
Another important event of December is Microsoft's official announcement of DirectX 9.0 along with the DirectX 9.0 Software Development Kit (SDK), including the HLSL (High-Level Shader Language). I guess, there's no need to describe Microsoft DirectX 9: "a group of technologies designed to make Windows-based computers an ideal platform for running and displaying applications rich in multimedia elements such as full-color graphics, video, 3D animation, and rich audio. DirectX 9.0 includes security and performance updates, along with many new features across all technologies, which can be accessed by applications using the DirectX 9.0 APIs". In December the HDMI (High Definition Multimedia Interface) workgroup, having announced the HDMI v 0.9 in June, released the 1.0 final.  Currently the list of HDMI co-founders includes Hitachi, Matsushita Electric, Philips, Silicon Image, Sony, Thomson Multimedia, and Toshiba. As you might know, the HDMI standard combines the support of hi-res video and multichannel audio in the single digital interface with up to 5Gbps throughput. The HDMI bases on the digital DVI specifications, being backward compatible with it. The new specs define the usage of a miniature and simple connector suitable for mobile devices like digital video cameras. Basing on the CEA (EIA/CEA-861x) standards compatibility, HDMI ensures the lossless video signal transfers. Besides, HDMI supports most AV.link-compatible protocols popular in Europe. The new standard also supports the High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection (HDCP) developed by Intel and Silicon Image to protect the Digital Visual Interface (DVI). The current HDMI 1.0 specification in detail describes all capabilities HDMI provide, including the 15-mm 19-pin HDMI interface for portables. The spec contains all information necessary for the development and making of HDMI-compatible products. HDMI is already supported by such brands, as Fox and Universal, DIRECTV and EchoStar, and the number of electronics makers. ProcessorsDecember became a kind of off-season for the x86 processor market: almost everything presented at Comdex Fall 2002 is expected at January CES 2003. Nevertheless, there are some December events to mention. Intel officially informed about the termination of the latest 1.4GHz Socket 370 Celeron production. The last orders for box and OEM versions of 0.13-micron processors will be accepted up to February 7. The box shipments will continue up to July 11, 2003 ãoäa, OEM shipments - up to December 12, 2003. So, Intel has completely turned to Socket 478 desktop solutions, having actually made the Socket 370 market secondary, and freed it for VIA in a certain way. ;) AMD announced the new Athlon MP 2400+, being the logical continuation of the dual-CPU server and workstation line. The processors operate at 2.0GHz, support 266MHz FSB, and are made at the Fab30 in Dresden using 0.13-micron process technology. The wholesale price (over 1000-unit quantities) of AMD Athlon MP 2400+ is $228. Systems on the new CPUs have already been announced by 47 companies. Along with the new processor, AMD announced the price cut for the previous Athlon MP products. The wholesale price of Athlon MP 2200+ (1.80GHz) was reduced by 7% from $224 to $208, of Athlon MP 2000+ (1.67GHz) - by 14% from $178 to $153. Besides, in December AMD decided to move the low-end Athlon XP 1700+ and 1800+ to 0.13-micron Thoroughbred stepping B0 core, initially used in some higher-end CPUs. Other processor-related news were about 2003 roadmaps and bright sales forecasts for Q4 2002. Motherboards and chipsetsIt's still about a quarter until new Pentium 4 with 800MHz FSB and Hyper-Threading support appear in the marker, however, the discussion of licensing payments to Intel for the new bus is at peak. As you know, Intel itself will release the Springdale chipset for the mainstream market. As the new 800MHz FSB standard will require the additional license payings to Intel from Taiwanese makers, analysts forecast the Intel's chipset market share to possibly grow the next year. As it has turned out, no Taiwanese makers have obtained Intel's license for 800MHz bus. If, for example, VIA hasn't strived for this anyway, SiS and Ali might suffer from the additional license expenses. As you know, the market share of Intel P4 chipsets grew to 60-70% in 2002. The share of SiS grew up to 20%. VIA Technologies, that hasn't obtained the license for Pentium 4 from Intel, and Ali, which hasn't shown the particular interest to this market, shared the remaining 10%. So, it seems that SiS will have to pay most to keep its market part. Ali will suffer as well, having recently announced the resumption of interest to the desktop chipset market. No one announced new chipsets in December, so most news relates to various announcements of solutions on previously presented logic. Intel announced 10 new server components, including 5 motherboards, 2 server cases, and 3 RAID controllers, designed for OEM makers and server builders that assemble systems on recently announced Intel Xeon with 533MHz FSB and Intel E7501/E7505 chipsets. The dual-CPU motherboards for Intel Xeon with 533MHz FSB - SE7501WV2, SE7501HG2, SE7501BR2, SE7501CW2 - represent the complete gamma of Intel E7501-based products; Intel SE7505VB2 bases on Intel E7505 and can be also used in workstations. SE7501WV2 is designed for Intel SR1300 1U case or Intel SR2300 2U case. It's optimized for high-density appliances like computing or multimedia streaming systems. SE7501HG2, combined with Intel SC5200 case, makes the server platform for DBMS infrastructure or department-scale apps. It can be used in a standalone or rackmount (5U) case. SE7501BR2 is also designed for the Intel SC5200 case or for the new Intel SC5250-E solution and represents the mainstream server platform for e-business and workgroups. All new platforms feature the Ultra320 SCSI interface, support RAID 0/1, Intel Server Management 5.5 software and Intel PRO/1000 Gigabit network solutions. Intel SE7505VB2, also designed for Intel SC5250-E case, is the universal server and workstation dual-processor platform with built-in Serial ATA and AGP 8X. Finally, SE7501CW2 is aimed at the inexpensive servers segment. The new Intel SC5250-E case is an inexpensive tower for small business servers and workstations. Besides, Intel released three new RAID controllers for data storage systems: Intel SRCU42L, Intel SRCS14L and Intel SRCZCR. Supporting Ultra320 SCSI and Serial ATA, they are based on Intel 80303 I/O processor. Intel has also reported about the modernization of SRSH4 and SPSH4 server platforms to support up to 2GHz Intel Xeon MP with 2Mb cache. You can read more about specifications of Intel E7205 (Granite Bay) from our review Dual-Channel Intel E7205 Chipset for Workstations. Gigabyte announced GA-8PE667 Ultra 2 motherboard on I845. It features Gigabit Ethernet (Intel 82540EM), Serial ATA Silicon Image Sil3112AT144, Ultra ATA 133, RAID 20276, two DDR DIMM sockets, 6 PCI slots, AGP 8x slot and the built-in AC97 codec. In December AOpen announced the new AX4B-533 Tube motherboard.  The board bases on 845GE chipset, supports Serial ATA (via built-in PromisePDC20375), features 4x AGP slot, 3 PCI slots, Ethernet 10/100Mbps, 3 DIMM sockets, 6 USB 2.0 ports. Audio codec: Realtek AC97, Sovtek6922 vacuum lamp. Chaintech announced Socket 478 9EJS1 (Zenith series). It bases on i845PE + ICH4 chipset bundle, supports Hyper Threading, has AGP 4x slot, 6 PCI slots, CNR slot, 6-ch. audio CMedia 8738), 6 USB 2.0 ports (2 - on the external 3.5" C-Box along with a Firewire 1394 port), LAN connectivity, and is bundled with all Zenith series accessories.  December brought numerous reports about new NVIDIA nForce2 motherboards, based on the discrete nForce2 SPP. Having announced the M7NCD, Biostar Microtech joined the companies, making boards on NVIDIA nForce2.  The novelty has the µATX form-factor and bases on NVIDIA nForce2 SPP + MCP2-T, supporting AMD Athlon XP / Athlon / Duron with FSB 200/266/333 MHz. M7NCD has three 184-pin DDR SDRAM DIMM, supports dual-channel DDR 200/266/333/400, has 3 PCI slots, AGP 4x/8x slot, CNR slot, USB 2.0, IEEE 1394a ports, integrated 6-ch. Audio (Realtek ALC650), LAN (MCP). Soltek also prepared a consignment of nForce2-based Golden Flame Socket A SL-75FRN and SL-75FRN-R.  Both boards are based on the nForce2 SPP + MCP bundle, feature AGP 8x slots, 5 PCI slots, 3 sockets DIMM (Dual DDR SDRAM 400/333/266MHz), 10/100 Ethernet LAN, USB2.0/1.1, 6-ch. audio. 75FRN-R also has Serial ATA RAID. In other words, the "all-gilded" versions are identical to SL-75FRN-R/SL-75FRN, based on violet PCB. As you remember, at the joint presentation Chaintech, NVIDIA and AMD announced the top-end Zenith motherboard on NVIDIA nForce2 - Chaintech 7NJS. The board features nForce2-ST Northbridge. 7NJL1 has AGP 8x slot, 6 PCI slots, 3 DIMM sockets, integrated 6-ch. audio, etc. Comparing to 7NJS, this board lacks only Serial ATA and ATA RAID. Naturally, the bundle includes all Apogee accessories: gilded connectors and proprietary cooler, Body Theater headphones, CBOX bay, round cables, etc.  You can read more about the performance of NVIDIA nForce2 systems from our review NVIDIA nForce2 Based Mainboards Roundup. Despite SiS and Intel continue to negotiate about the licensing of 800MHz FSB, the former has already informed about the licensing of Intel Hyper-Threading technology and announced its support in 5 current chipsets by posting some info on the website, not dissipating on any press releases. 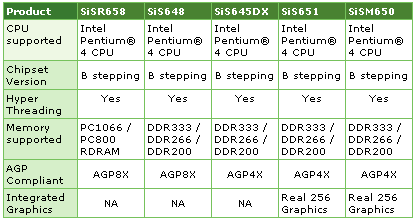 As you can see, the HT-enabled list includes SiSR658 RDRAM, mobile SiSM650 along with desktop SiS648, SiS645DX and SiS651. According to the table, Hyper-Threading is featured in new stepping B solutions. The company informed that the new chipset production will be launched in December, and in the nearest future we should also see the Hyper-Threading-enabled SiS655. AOpen AX45-4D Max announced late in December on SiS655 + SiS963 doesn't yet provide Hyper-Threading support. But along with SiS655 a version of AX45-4D Max should be soon released on the new-stepping chipset.  AOpen AX45-4D Max bases on SiS655 + SiS963 chipset bundle, supporting 128-bit DDR. The motherboard operates with Socket 478 Intel Pentium 4 with FSB 400/533MHz, has 4 DIMM sockets (up to 4Gb of dual-channel 2x64 DDR333/266). The board meets ATX standard, and also features 5 PCI slots, CNR slot, AGP 8x slot, USB2.0, IEEE1394 ports, integrated 6-ch. audio (RealTek ALC650), S/PDIF, LAN (Realtek 8100BL). Sapphire announced A4-A985 Socket 478, based on the ATI A4 (Radeon IGP 340, integrated ATI Radeon 7000 graphics) + VT686B bundle.  A4-A985 features A4 form-factor, supports Pentium 4 with 400/533MHz FSB, has 2 DIMM sockets (up to 1Gb DDR200/266 SDRAM), 5 PCI slots, AGP slot, 4 USB ports, AC97 audio codec, TV-out (PAL/NTSC), etc. MemoryFrom the bery beginning of the month there were messages from memory destributors about possible DDR contract price reduction. Despite the X-mas sales season, they were forced to do this after the launch of numerous 12" silicon wafer fabs. Samsung Electronics and Nanya Technology were the first to announce the price cut. Hynix Semiconductor followed them with its credit liability. Infineon Technologies remained the only company keeping retail prices high. By the end of the month, according to DRAM eXchange, DDR prices reduced to minimum for the last two months. Analysts believe the main reason for this is overstocking caused by considerable increase of shipments from Micron and Hynix. Interesting that DDR333 prices started to grow. DRAMeXchange analysts reported that DDR333 price growth was related to the slow market stocking. Several DRAM makers at once finished the chip verification with OEM PC builders, so the DDR333 mainstream was directed to OEM channels bypassing the spot market. According to provisional forecasts, the growth might have continued to the end of December. It seems to be the latest DRAM forecast of this year: DRAM eXchange analysts believe the DDR spot prices will reduce slightly, as the demand will remain high enough before the Chinese New Year. At the same time SDRAM spot prices will continue to increase. Anyway, European and North American companies will keep the demand high for some time after the Christmas. Another dynamic trend of this market segment is the provisional January NOR memory price growth. Intel was the first to announce 20-40% price increase for its products. Sharp and Fujitsu followed it with similar 30-40% announcement. Without a doubt, AMD will also try to increase sales. The company has already confirmed such negotiations are in progress. As resellers have been buying lots of NOR flash from distributors for the entire December, it resulted in demand exceeding offer by 30%. Analysts forecast 84% NOR flash sales growth next year, up to $11.9 billion fiscal volume. The situation with NAND is just opposite to NOR. Prices for NAND flash have been decreasing throughout H2 2002 and seem to continue decreasing further along with the opposition of Samsung Electronics vs. Toshiba & SanDisk. Analysts believe NAND prices to at least remain the same early in 2003, but most likely, they'll continue to reduce. According to Semico, NAND sales will grow by 60% in 2003. In the second half of December Infineon Technologies and Kingston Technology signed the long-term strategic partnership and the memorandum of understanding, stating that shipments from Infineon to Kingston will make $2.5 billion within 5 years. This mainly touches the Infineon's DRAM products. Now something about actual novelties. In December NEC Electronics announced shipments of new CB-130 DRAM for embedded appliances, made using 0.13-micron NEC UX5D process technology (copper, low-k dielectrics, L-OxTM). New chips featured 8Mbit and 9Mbit capacities, up to 314MHz clock at 1.2V voltage and are designed for single system-on-chip (SoC) solutions: 10- and 40 Gbit routers, NAS, cache memory and high-end graphics. Sample shipments of 8 Mbit (64K x byte x 128 bits) and 9 Mbit (64K x byte x 144 bits) NEC Embedded DRAM had already begun. Volume production is expected in Q3 2003. On the threshold of X-mas Micron showed the first 0.11-micron 1Gbit DDR SDRAM chips, packaged in to TSOP-400 casing and designed for 2.5V voltage. New chips can be used in 4Gb Registered memory modules for high-performance servers. In December Hynix announced new 128Mbit DDR-I SDRAM chips operating at 500MHz and organized as 4Mx32 - HY5DU283222, intended mainly for graphics cards and network appliances.  The new chips feature 144-pin FBGA, have 32-bit interface and provide up to 1Gbps throughput. The samples of 500MHz-128Mb (4Mx32) DDR-I SDRAM chips have already been shipped to Hynix partners. The release of DDR-II chips is expected in Q1 2003, then we should see the new 500 MHz 4Mx32 DDR-II SDRAM. As far back as in summer Infineon announced 512Mbit samples for building 2Gb PC2100 DDR SDRAM, and early in December they reached the retail (currently Japanese). Modules are based on Infineon HYB2525D512400AT-7 chips (512Mb, 128Mx4, DDR266A, 2-3-3), which production was launched in Q3, according to the official information, and feature CL=2.    Pricing will vary with the height: 1.2" modules will cost about $2560, 1.7" modules - about $2480. OCZ Technology, known by its overclocker products, made a double announcement in December. First, it announced new 256Mb and 512Mb OCZ EL DDR PC-3700 lower-latency memory modules.  New OCZ EL DDR PC-3700 include the best-selected chips as usual and feature the ULN Technology (Ultra Low Noise) technology for lower noise pickup. New 184-pin Unbuffered 256Mb and 512Mb OCZ EL DDR PC-3700 feature CL=2.5, operate at 2.7V and 233 (466) MHz, and are bundled with copper heat-sinks in retail. Later OCZ Technology posted the specs of its 256Mb and 512Mb OCZ EL DDR PC-3500 Dual Channel memory modules of the OCZ Enhanced Latency Series.  To achieve the high memory clock, except for the testing and selection of the best 4.5ns chips, the company used the ULN Technology (Ultra Low Noise shielded PCB). 184-pin Unbuffered OCZ EL DDR PC-3500 Dual Channel modules are optionally supplied with copper heat-sinks and operate at 217MHz (434MHz DDR). They feature CL=2 and require 2.5V. The company claims the modules are capable of operating at 2.8V (with heat-sink). Transcend Information announced shipments of 1Gb CompactFlash cards, having added to the line of 16Mb, 32Mb, 64Mb, 128Mb, 256Mb, and 512Mb products.  The new 1Gb Transcend CompactFlash Type I (TS1GFLASHCP) fully meet the standard specifications, support 5V or 3.3V voltage, operate in 0°C to 70°C temperature range, and are covered by 5-year warranty. December brought some news about new standard announced by Fujifilm and Olympus - XD-Picture Card. As you know, companies announced it late in July and the first 16Mb, 32Mb, 64Mb and 128Mb XD-Picture cards appeared in the market in the fall. In December we should have seen 256Mb products with 512Mb ones to appear early in 2003, and 1 to 8 Gb versions - in H1 2003.  For some reasons Fujifilm moved shipments of 256Mb cards to the late January 2003. Olympus made the same a bit later. Hard disks and controllersDecember began with the message that USA Trade Commission approved plans of Hitachi and IBM to merge their hard disk businesses into new Hitachi Global Storage Technologies. Previously the decision of Hitachi and IBM was approved by other antimonopoly committees: Economic Commission for Europe, Japanese Fair Trade Commission, Brazilian Conselho Administrativo de Defesa Economica and Taiwanese Fair Trade Commission. Initially Hitachi gets 70% of joint-venture assets and then gets all the company within 3 years. Actually IBM sells is hard disk business with a 3-year postponement. This is a part of IBM's large-scale restructuring program. The company is to focus on microelectronics and service providing. According to Hitachi, the company plans to fully reorganize hard disk business and make it profitable by April 2003. In January at CES 2003 we should see the first iVDR (Information Versatile Disk for Removable usage) hard drives for multimedia appliances. In March 2002 eight Japanese companies, including Sanyo Electric, Canon, Fujitsu, Hitachi Manufacturing, Phoenix Technologies, Pioneer, Sharp and Victor Company of Japan (along with FCI and Mitsumi as the "associate members") announced iVDR (Information Versatile Disk for Removable usage) format. Currently the consortium includes 28 companies, including Maxtor and Seagate). iVDR standard designed for 2.5" HDDs can be used with PCs and other electronic devices. Specifications define the connector, unified interface, file system, etc. According to provisional data, the capacity of iVDR drives will initially make at least 40Gb to be increased to 200-400Gb within 2-3 years (the document even defines terabyte capacities). The dimensions of iVDR drives are 130x80x12.7 mm. According to the specification, iVDR disks will feature 5-pin connectors with at least 10,000 connect/disconnect cycles. Electrical specifications, instruction sets, etc. meet the ATA standard (ATA Standard + AV Expansion + Secure Expansion), nominal shock resistance is 900G. iVDR drives will feature their own File system for iVDR. The next stage of development was the transition to 1.8" drives.  So, after keeping silence for 10 months iVDR standard is expected to remind of itself at CES 2003, to take place on January 9-12 in Las Vegas. We should see two 2.5" and one 1.8" iVDR drives. According to the consortium representatives, 1.8" devices using up to 80-mm discs, are designed as an exchangeable storage for audio players and navigation systems. 2.5" drives using up to 130-mm discs are meant for consumer electronics and PC storage. By the way, there will be 1.8" => 2.5" form-factor adapter released as well. More numbers: 2.5" iVDR discs, to be shown at CES, feature capacities up to 80Gb (to be doubled in 2003). The retail price of the first iVDR-enabled devices will range from $166 to $249, discs themselves will cost <$90. The only problem the consortium hasn't solved yet is the content security. Supposedly, the final specification will be adopted by March 2003. Seagate announced new hard disks in the popular Barracuda line. But has changed the usual markings, replacing Barracuda ATA V with novelties like Barracuda 7200.7 and Barracuda 7200.7 Plus. It seems the new markings are more suitable for demonstrating features. New Barracuda 7200.7 and Barracuda 7200.7 Plus feature up to 80Gb per slice data density and will be produced in up to 160Gb models, both with Serial ATA, and Parallel ATA. Barracuda 7200.7 Plus has 8Mb cache and 160Gb, 120Gb capacities. Barracuda 7200.7 has 2Mb cache and 160Gb, 120Gb, 80Gb, and 40Gb capacities.
New drives utilize ultra-quiet Seagate SoftSonic chassis with Fluid Dynamic Bearing (FDB), traditional Seagate 3D Defense System - Drive Defense, Data Defense, and Diagnostic Defense. Max. non-operating shock of Barracuda 7200.7 is up to 350G. Let's hope more details are to follow. Besides, Seagate also announced budget Barracuda 5400.1, combining many features of Barracuda and U series. They feature up to 40Gb/slice density and 5400RPM. Their main improvements include 25% thinner design comparing to usual models, SoftSonic fluid bearing, suitable price. Drives feature Ultra ATA/100 interface and 12.5 ms data access time. Another record from the portable storage field: LaCie announced the family of portable plug & play Big Disk FireWire drives 500Gb and 400Gb in capacity sized as a usual 5.25" device. In case you need several LaCie Big Disk there's an option to use a special 19" LaCie Desk Rack.  Like their D2 predecessors both drives feature the stylish aluminum bodies and are supplied with the vertical mount support. For energy saving purposes LaCie Big Disk devices turn off simultaneously with PCs. Being joined, Big Disks are easily configured as RAID1 or RAID0. 500Gb model is the most interesting, featuring 8Mb-cache 7200RPM storages. The 400Gb model bases on 2Mb-cache and 5400RPM components. Both drives can use the IEEE1394 (FireWire/iLink) interface under Mac OS 8.6 / 9.x / OS 10.x / Mac OS X Jaguar or Windows 98SE/2000/Me/XP. In December Tekram presented new DC-390U4W Ultra320 (Ultra4) SCSI controller, based on LSI Logic 53C1030 chip.  It supports 64-bit/133MHz PCI-X. LSI's chip, featuring ARM architecture, supports two Ultra320 channels with up to 640Mb/s maximum throughput. Tekram DC-390U4W is backward compatible with Ultra160, Ultra2 LVD, Ultra Wide and Ultra SCSI solutions, features two internal 68-pin LVD sockets and one external 50-pin Ultra SCSI connector. Write a comment below. No registration needed!
|
Platform · Video · Multimedia · Mobile · Other || About us & Privacy policy · Twitter · Facebook Copyright © Byrds Research & Publishing, Ltd., 1997–2011. All rights reserved. |