 |
||
|
||
| ||
The true is learnt in comparison. It is possible now to test 3 cameras together: Toshiba, Sony and Casio and the results of the tests will be ignited. The camera Casio QV-3000 was already tested by me. There is a brief introduction here and then in detail about cameras Toshiba and Sony.  They are 3-megapixel cameras with identical as it seems to me lenses. They say Toshiba's lens is from Canon and Sony's one is from Carl Zeiss. It seems to me that for digital cameras the standard lens was formed. As a lot of film cameras were completed by lenses such as Tessar-Industar so for digital cameras the certain standard was formed: a focal length of 7-21 mm, 8 elements in 7 groups and all details of a lens and a lock visible from a surface seem to be absolutely identical. Cameras Casio, Epson, Toshiba and Sony are completed with such lenses nowadays. Certainly the lenses besides evident and easily measured characteristics have some more peculiarities which can be described only at a level of sensations.  From tested cameras only Casio has the possibility of data transmission through the serial port, the cameras Sony and Toshiba have nothing in common with the past and use USB. It is natural that Sony uses Memory Stick for record and Toshiba - its own map SmartMedia. But as against Memory Stick, the map SmartMedia is used not only in cameras Toshiba but also in Olympus and AGFA. Casio is not going to make a new standard and as well as others uses CompactFlash. Despite of the difference in mediums each of cameras can be used as the universal device for reading maps. At connection of camera through USB port to the computer you have exchange disk store where you can store photos or textual documents in the folder "my computer". Taking into account the spread of USB it is a quite good way of data transfer from one computer to another.  The same situation is and with accumulator. Casio uses 4 standard elements of supply of size AA, it can be both Ni-Cd and Ni-MH accumulators or simple batteries of this size. Sony and Toshiba use accumulators of their own construction and if the ion accumulators NP-FM50 of capacity 1180 ìA*h are accessible enough as they are used by videocameras Sony, the accumulators from Toshiba are not only the smallest and so with the least capacity but they are also rather exotic in the north of Eurasia. Both cameras Toshiba and Sony are a charger for accumulators themselves as they are connected to alternating-current electrical system through a power supply unit. It provides both charging of accumulators and power supply. The important property of tha camera Sony is the indication of the remained charge in minutes. In my opinion the quality of image got by all three cameras is very good. And though at tests it is possible to find nuances distinguishing images got by these cameras, however the main argument at choice is functional capabilities. Tastes differ and probably each of cameras will find its supporters. So we shall speak about cameras in detail. Toshiba PDR-M70 If you have a short look at this camera, you can't notice something differs it from others. Only dictophone mode differs this camera from its digital colleagues. Thus with this camera you can get photos by the size 2048 õ 1536, videorolls 320õ240 pixel with frequency 15 frames per second and also the mode which allows to record on one frame 36 images with an interval 0,07 second and the camera is capable to play this frame as a videoroll. Besides it can provide some hours of record in Dictaphone mode. Though the camera has no completely manual control but its possibilities in control of automatics cover all sides of its activity and are probably the richest I have ever met.  Automode menu. The marks on the left allow to select one of 6
filming programs:
 Sort of screen in videofilming mode
 Priority of diaphragm mode menu. The marks on the left allow to
select:
 Tunings in filming mode menu
 Sort of screen in priority of exposure mode The framework marks
a position of an area of sampling
 Screen luminance control menu
So you can evaluate the correctness of exposure and diaphragm choice using the diagram of brightness allocation which is displayed on the screen. You can select one of 5 points where to do auto focusing and sampling of an exposition. The possibilities of manual settings are a little bit poorer than for the competitors. But they are not small too. You can film with the priority of exposure and diaphragm, to do expocorrection and it is enough to select any pair of exposure and diaphragm. But as against cameras with manual setting you should set priority of exposure or diaphragm mode and then with the help of expocorrection to achieve desirable for you second parameter. I.e. in priority of a diaphragm - exposure mode but not in priority of exposure - diaphragm mode. The possibilities of manual setting on definition are absolutely poor, it is possible to set manually only one value - infinity.    Review and set-up mode menu are not less rich:
 Filmed frame parameters review
 Brightness allocation histogram
 Frame fragment review
 Playback mode menu
 Copying between SM maps menu
 Setting menu
The camera is equipped with the standard contact for connection of external flash. There is a speaker for listening but it is also possible to connect earphones. USB and Video cables use one connector. Lithium accumulator of own construction is used for supply. It is a good accumulator but the purchase of the second one can become a problem. The camera has possibility to use optical headers but with the help of a rather exotic (the thread on the camera is 45 mm) the transition ring so that if you do not have a lathe at home, you should pay $20-30 to the corporation Toshiba.  In my opinion it is not the optimal camera for those who are professionally engaged in photofilming but it is just an ideal for reporters: it does not attract attention and has indefinitely large digital Dictaphone. And if it is necessary, it is possible to have magnificent photos and even videorolls. And there is much more place on a memory map than on a diskette that is very useful to transfer articles to the editors.   Now a few words about details. The upper LCD with illumination is a very original detail but the cover of the lens which is not connected to the camera at the open lens is easy to be lost. As against Olympus 2000 the motor of the lens can't remove it and so you don't drop it accidentally having switched on the camera. However you risk to break the mechanism of the lens if you often switch on the camera without removing the cover. SONY DSC-S70 It has almost completely steel body and it is the only camera in this review with a metal hole to connect it with a support.  Variolens Carl Zeiss Vario-Sonnar, maximum size of a frame as well as for the rest is 2048 õ 1536, the possibility to record frames both compressed in the format JPEG and not compressed in the format TIFF. However the camera is completed with 8-mb memory map Memory Stick and the size of one not compressed file with the image in the format TIFF is more than 9 Mb therefore this format was not used. The camera is supplied by the optical viewfinder with dioptric correction that is already usual for cameras of this class and also accordingly 2-inch LIQUID CRYSTAL screen with 123000 pixel.  Unfortunately the screen here is usual - with back illumination. Sony in this camera has refused usage of the hybrid display. Though luminance of the camera is regulated but on the bright sun it helps weakly. The camera except automode has priority of endurance mode and priority of diaphragm mode. It is possible to install the distance of filming 0,5 m, 1 m, 3 m, 7 m and infinity. There is a possibility to use optical headers again having paid the corporation Sony for a transition ring. And it is possible to use as standard focal headers which I wrote in the article about and specially fitted for this cameras head lens such as wide-angle MHG07 which usage for obtaining a sharp picture should be necessarily marked in the menu of the camera.  Sort of screen in priority of diaphragm mode
 Choice of balance white menu
 Sort of screen in playback mode
 Setting menu:
It is possible to use and external flash but not with the standard synchrocontact therefore probably only Sony HVL-F1000. They say that in the USA it costs $ 120. One of the features which select this camera is format of the frame 3:2 that allows to go exactly at printing a standard card. But in black-and-white mode the camera records snapshots in format GIF. The camera has the possibility to record videorolls with sound in MPEG format. So that it is a quite perfect MPEG camera and besides the set contains the program for editing videorolls in this format. It is the second camera with the capability of recording a videoroll in MPEG format in my review. First of them - Hitachi MP-EG1A used the winchester disk 260 MB with the form factor PCMCIA type III to record a videofilm. Sony promises to install the same capability in the memory map Memory Stick soon. Results of TestsThe cameras have shown very close results both by resolution and the spectral characteristics. However it is possible to mark that the image got by the camera Casio is a little bit softer than for the rest and for the camera Sony at maximum resolutions the limiting occurs not because the luminance of light and dark bars becomes identical but because of brightly expressed tabby. 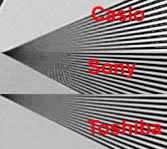 Toshiba PDR-M70
 Sony DSC-S70
 Casio QV-3000
 In a photo of the spectrum from the diffraction grating the white vertical lines mark the area visible by my eye. The filming was effected at close values of endurance diaphragm for all three ñameras. Taking into account that the sensitivity of matrix for the camera Sony is more and the spectral scope is also more.  The matching matrixes sensitivity of cameras with an intensitometer of the camera Canon EOS 50 has given the following results:
Thus the matrix sensivity approximately accord to the sensitivity of a film:
From all these cameras only Casio can communicate with the computer through the serial port. As it was already said all three cameras can be used as the device for readout of appropriate memory maps. At connection of the camera through USB bus to the computer memory maps become accessible as the removable disk in a folder " my computer ". The testing was conducted with the help of the program WinBench 99:
I want to mark that Toshiba has demonstrated for maps of its own development much more high speed than for other corporations using maps SmartMedia. The ConclusionThree cameras with approximately identical possibilities of resolution and matrix sensitivity. Their design is similar and close to traditional film cameras. The fundamental difference is in used memory maps and accumulators. The most convenient power supplies are probably the accumulators of the corporation Sony. The chambers are intended for usage in automode, priority of exposure and priority of diaphragm modes. However the camera Casio has the possibility permitting to use it and in completely manual mode. Focusing mode. The only camera permitting to conduct focusing manually on LIQUID CRYSTAL screen is the camera Casio. Thus the camera Casio does not show the distance up to the object and does not allow you to use a reel for the setting on sharpness. The camera Sony allows you to install one of 5 values a distance up to the object and to achieve exact focusing coming nearer or moving away from it. Only camera Casio has the special mode for filming a panorama however it does not prevent you from arranging a panorama from separate frames filmed by cameras Sony and Toshiba. The ñameras Sony and Toshiba allow to record videorolls with sound. Toshiba also allows to record sound separately in Dictaphone mode. The cameras Sony and Toshiba assume usage of optical headers for magnifying of the camera possibilities. The camera Casio does not assume it but it does not prevent you from deciding this task independently. The cameras Sony and Toshiba allow to regulate luminance LIQUID CRYSTAL of the screen, but the camera Casio doesn't have such possibility. These cameras have neither full remote control, nor filming control mode by from the computer as against the camera EPSON PHOTO PC 3000Z (handle from the computer) or Olympus (IR full remote control). The camera Toshiba has the standard synchrocontact for connection of external flash. The camera Sony allows to connect to it the external splash of the corporation Sony. The camera Casio allows to synchronise with external splash only after a light pulse of own splash. The cameras Sony and Toshiba communicate with the computer only through USB bus. The camera Casio allows to communicate with the computer through the serial port and USB bus and also with other cameras through a IR port by the protocol Ir Tran-P. For all memory maps there are separate readout units which you can use. The camera Toshiba has the most factual screen menu. And the camera Casio makes an index in the format html on the memory map. It is very difficult to choose the unique leader among these cameras. Probably your choice can be effected by your attitude to various types of memory maps and also by the price of these cameras. The cheapest one is still Casio, however its complete set is the poorest. Characteristics
Not documentary possibilities are marked
by red colour
PhotoFragmentsToshiba PDR-M70
198Kb
Sony DSC-S70
245Kb
Casio QV-3000
223Kb
Initial framesToshiba PDR-M70
1141Kb
Sony DSC-S70
1372Kb
Casio QV-3000
1364Kb
Write a comment below. No registration needed!
|
Platform · Video · Multimedia · Mobile · Other || About us & Privacy policy · Twitter · Facebook Copyright © Byrds Research & Publishing, Ltd., 1997–2011. All rights reserved. |