 |
||
|
||
| ||
Spring and summer of the year 2000 were not less active for the market of 3D graphics accelerators, than in 1999. The same corporations were the leaders of the market but the two following features should be mentioned:
The strong delay of the output of production of the corporation ATI from the competitors was noticed during the last year and a half. Especially the reputation of the corporation was "beaten" by systematic delay of the output of real production to be compared with periods of announcements. Let me recollect about the chip ATI RAGE 128 PRO, the cards on the basis of which were declared in October, 1999, however it was possible to buy them only in spring of this year. This situation effected on a financial state of the company, and we together with the investors could see joyless financial reports ATI for the last quarters. As is found, the corporation does not accept its fault and considers the suppliers and manufacturers of components to blame for it. In spring of this year we became the witnesses that the corporation ATI Technologies has made the jerk forwards and announced the geometry processor of the last generation, by possibilities not yielding to novelties from NVIDIA and 3dfx. I want to mark, that for the first time it has taken place not in one half-year after an output of competing chipsets but literally after them. The informal specifications of new GPU with a code name RAGE6 and information about the card on its base in the beginning of March gave the basis to believe, that the corporation at last realized the importance of writing drivers steadily operating and permitting to the new chip to realize the potential. Already then it was possible to assume, that the productivity new GPU from ATI will be at height. Unfortunately, nevertheless delays have arisen. The new chip from ATI was announced in May but the videocards on it were represented only in the middle of July. For this time cards on base NVIDIA GeForce2 GTS already became much cheaper, therefore to novelties from ATI will be not so simply to occupy a worthy place in the market. But there is also a pleasant moment for ATI: the company 3dfx does not strongly hurry up to fill the market by the cards Voodoo5 5500, which only - only began to occur on counters, and under the super high prices. If ATI does not lose its chance it will have a good opportunity to make the way on the market and to capture a powerful part for its products of a new generation. However they are only suppositions, we shall consider realities: possibilities of the new geometry processor from ATI - RADEON GRAPHICS. In further I shall name it simply RADEON. So, we shall look at the main characteristics GPU RADEON:
3D a graphics:
Video:
Here I would like to analyze only basic characteristics and features of RADEON. As it is possible to see, the list of advantages of the new chip is extremely great and it may be able to create almost photorealistic graphics. Certainly, it is necessary to mention that for the last year the corporations - manufacturers of geometry processors approached the high quality of three-dimensional graphics permitting in real time fulfilling renderings of the most complicated objects and scenes. Unfortunately, I should remind once again, that not everything depends on desire and possibilities of the manufacturers GPU. Even if there is a superb processor with the amazing characteristics giving the speed more than 100 fps in all main resolutions and the amazing quality, there won't be more new games realizing these possibilities fully. The manufacturers of games should be more active, inventive, creative and provide a great variety of games for every taste. I shall agree, that all off-the-shelf videocards have the high prices that are not permitting them to become mass accelerators. By this the manufacturers of games permanently justify the unwillingness to spend resources and time for development of "cool" games where GeForce or RADEON are used, which may not be able to cover expenses. However I consider that this fact at all does not justify unwillingness of the manufacturers of games to make their production planned using the set of 3D-accelerators of different types and possibilities. It means that the game should be set up under a videocard, and by NVIDIA GeForce256/2 GTS, ATI RADEON to use complex objects, realistic lighting (using possibility Hardware T&L), loading the central processing unit of the system by more exact calculation of physics, for example, movement of water (waves), heroes in games, even the expression of their faces. And with Voodoo2/3, for example, the same game can use the simplified graphics, not involving textures, reducing quantity of polygons in objects to provide a higher speed for the game. It is very difficult to make such games, however their period of life and popularity will be so great, that it can pay back all expenses. While we have to be satisfied with the announcements of cool games and demo programs, showing us possibilities the most modern GPU. And each of demo-programs shows only features connected with it GPU, sometimes demonstrating strange behaviour on other chips. Below I shall show it in practice. What new does ATI RADEON give us? First of all this is a new graphics core, which has nothing in common with the previous. The analogy arises: NVIDIA GeForce 256 and Riva TNT2. Really, the jerk is available, however it is much stronger, than it was in the autumn of 1999, when NVIDIA GeForce 256 appeared. Charisma EngineThe geometrical block Charisma Engine has the following possibilities: The hardware support of vertex lighting. It is expected, that at usage more than one light source such as Directional Lights (directed lighting, aka Infinite; in this case light source is treated as a point located on infinite distance from visible objects of the scene) falling of productivity will be less essential in comparison with GeForce256. The hardware transformation of coordinates of vertices of polygons from 3D coordinates of the simulated scene in 2D coordinate of the screen of the screen monitor in view of correction of distances, so-called operation of transformation of a perspective. At the hardware level the process of cut of polygons, invisible in the final scene, - Clipping is supported. In spite of the fact that GeForce 256 supports Clipping at the hardware level, its geometrical coprocessor is usually named as the reduced name HW T&L. Now even more often block of geometrical operations and the installation of vertex lighting is named in abbreviated form HW TCL, underlining the presence of hardware Clipping, though also old abbreviation "HW T&L" isn't worse. The declared productivity HW TCL for RADEON - about 30 mil. polygons per second. Taking into account, that for GeForce 2 GTS productivity in 25 mln. polygons per second is declared, the block of geometrical operations for RADEON potentially is the fastest in industry today. Running forward, I can tell, that it's not so. At the hardware level a number of special operations can be fulfilled, which support is realized in Charisma Engine: Vertex Skinning and Keyframe Interpolation. The hardware support Triangle Setup, i.e. process of conversion of floating coordinates of vertices of triangles to integer coordinates in the frame buffer and installation of other parameters coupled with vertices, for example of binding of textures. Vertex SkinningIt is a method of correct transformation of vertices of a geometrical grid in places of a model's bend, i.e. the operation goes only with geometry, but not textures. The textures on the correctly transformed geometry will be stretched correctly. Vertex skinning (single-skin effect) technique is applied to make the geometry transform correctly, especially on bends and concatenations (for example, all joints at simulation of a body of the man). Let's remark, that vertex skinning is a subset of a method of interpolation of vertices (vertex blending). As a matter of fact, vertex blending it as alpha blending, but for vertices, instead of pixels (V = V1*alpha + V2 * (1-alpha)). A method of vertex skinning is vertex blending for vertices processed by different matrixes (V = V1*M1*alpha + V2*M2 * (1-alpha)). Let's underline: the correctness of mapping of textures on bends is a consequence of correct layout of vertices, which is achieved with the help vertex skinning. Vertex Skinning is applied to make transitions on junctions of textures be smooth and natural, especially during movement. The interpolation of vertices is carried out with the help of matrices called Skinning Matrices.   It is possible to see, that on the left interpolation goes according to 2 matrix scheme and on the right - on 4, that allows for this cat to remove artefacts as acute corners on bends of paws. In D3D there is a support for 2, 3 and 4 matrix interpolations of vertices. A 2 matrix interpolation in most cases is enough. However on the junction of a trunk with a neck and hands it is more preferable to use 4 matrix interpolation, and on the junction of a trunk and two legs - 3 matrix interpolation. Nevertheless, improvement from 3 and 4 matrix interpolations of vertices are visible only by long consideration of the character by a size in all screen. In GeForce256 2 matrix interpolations are supported at the hardware level only. Keyframe InterpolationThe interpolation on key frames allows to realize at the hardware level change of appearance of the displayed object by the definition only of initial frame, final frame and key intermediate frames, all other conversions are fulfilled automatically. Differently Charisma Engine inserts the necessary number of the interpolated frames between key frames and as a result, for example, it is possible rather simply to realize change of the expression on the face of the character of the game. It is clear, that execution of operations TCL, and also Vertex Skinning and Keyframe Interpolation require much CPU power. For RADEON, by everything, there are no problems with it. In result the developers of games can use the greater number of polygons at tessellation stage and apply various special effects, that will make 3D the world in the game by more real. The developers of games can use the liberated CPU time for example for calculation AI. For matching, in the games which are not oriented to usage HW TCL for calculation AI up to 5% of CPU time is usually given but in new games oriented to usage of possibilities HW TCL for calculation AI till 30-40% of CPU time will be possible given and it means, that your virtual opponents will become more treacherous and sly (at least, it is possible to hope on it). Besides the freed CPU time are possible to be used for account of physical effects of the boosted complexity, for example, with gravitation, atmospheric effects. It is necessary to note, that if the possibilities HW TCL are used in the game but the freed CPU time are not used, the user all the same will receive magnificent on quality and very fast graphics, though will not remark any other pluses. I shall repeat, that it will all become possible only in case of revising by the manufacturers of games of the ratio to writing games operating all innovations, available in last chipsets. Pixel TapestryExcept the possibility to accelerate a geometrical stage at rendering the image, RADEON, certainly, knows how to accelerate a stage of rasterization. For this purpose the architecture of pixel rendering and block with the same name - Pixel Tapestry also was created. This block of rendering is built in RADEON and was specially created for implementation of operation three texturing of blocks on each of the available rendering pipelines. In RADEON there are two pipelines of rendering, on each of them - three texturing blocks are presented. It allows:
Besides with the help of a block Pixel Tapestry the support is realized:
It is not a secret that the more textures on pixel for clock tick, the more realistic and more detailed result image lossless in common productivity turns out. The textures are applied to overlay of lighting cards, cards of shadows, simulation of reflections and mirror surfaces, relief (bump maps) etc. Especially it is necessary to mark support relief texturing (EMBM), which while is supported only by chips of a series G400 from Matrox, but is used in several tens games. The positive moment is the support RADEON of a method of cubic mapping of cards of the environment supported in D3D 7.0. In this method there is no dependence on a point of the browse, but 6 textures are used. Except for this method RADEON supports also a spherical method (1 texture, there is a dependence on a point of the browse), double parabolic method (2 textures, dependence on a point of the browse). To make the scene in the game look realistically and had depth the simulation of shadows is used. For overlay of natural shadows discarded by objects of the scene depending on remoteness from each light source, in RADEON the support special Priority Buffer (priority buffer) is realized. This buffer is formed at the expense of CPU time of a local video memory and allows to store of the information on objects discarding shadows. With the help Priority Buffer the order of usage of the data is determined and as a result a shadow from the object most approximate to the spectators starts to be formed. The mapping of shadows is carried out at the expense of transformation of textures. This method is easier and more effectively, than usage of the traditional buffer of templates. RADEON has support Range-Based Fog, i.e. mapping of a fog, which density depends on remoteness of objects from the player. One of new functional features RADEON is support 3D textures (three-dimensional textures). 3D Texture is a texture representing 3D array of pixels, instead of 2D as usually. This innovation in OpenGL1.2. Until recently support of three-dimensional textures was available only in Permedia3 from 3Dlabs. This type of textures can be used for operation with voxels (volumetric pixels), mapping of spherical textures for simulation of volumetric light sources. The three-dimensional textures simplify usage of deformable geometry; for example, it is possible to cut off a part of the object without necessity of upgrade of texture. In RADEON the support of a number of innovations is already incorporated which will be realized in future D3D8 from structure DirectX 8.0. Among these innovations it is necessary to mark support of effects Motion Blur and Depth of Field, and also Full-scene Anti-aliasing. In API D3D 8.0 the support of effects T-Buffer from 3dfx will be entered. In general, about FSAA in the press release RADEON the following is spoken: " Comprehensive support for full scene, order-independent anti-aliasing". It is quite logical to expect essential falling of productivity (up to 2 times) at application FSAA. To apply or to not apply FSAA is the problem of a user. Below I shall show, what FSAA can give on a videocard, based on ATI RADEON. The situation with support Pixel Shaders is not clear yet. Pixel Shaders is such a method of creation multitexturing effects "manually", which support will be in DirectX 8.0. The essence is that earlier it was possible to mix textures only according to several beforehand given formulas (as a rule consisted of 1-2 operations), but now Pixel Shader is a "program" of blending of textures preset manually (operations +, -, / , * and some more exotic ones which can be combined in any quantity). Pixel Shaders means operation at a pixel level, instead of at a level of vertices of polygons. No special block for application programmed and beforehand preset multitexturing effects at a pixel level in RADEON is not present, but there is a possibility to control the process of results blending of texturing blocks. It is quite enough for the application in the press release the following: "First with advanced DX8 pixel shader effects". Not long ago there was a demo program NVidia Chapel, demonstrating these methods (screenshots are removed at the placed videocard on NVIDIA GeForce2 GTS): The same program on ATI RADEON is launched only in the window mode part of units and it rather strongly brakes. A part of elements do not appear at all, dampness of driver effects implementation of a part of functions, in particular shadowing on the pixel level. Hyper ZGenerally ATI carefully hides what this technology is. From authoritative western sources it is possible to receive some items of information about HyperZ, though anybody from them has not proved yet, that they are right. So, HyperZ works on tile basis, i.e. on the basis of splitting the screen into square fragments. RADEON draws polygon first in a usual way, then in tile and if tile completely closes by itself polygon, it is discarded and eliminated from further processing. It is a simple but very effective trick, as the plot of the majority of three-dimensional games is played in the scenes containing walls, ceilings etc. ATI informs, that such approach spares up to 20 % of rendering time. What does it mean? It means most likely that the algorithm saves value only of most "remote" value Z from all tile (for example - 8õ8 pixels, which size uses ATI, I do not know), and at rendering of polygon, its nearest value for every tile which it overlaps is calculated . And if it is clarified that this nearest value is further then the most remote for tile, we at once throw out this polygon. We do not need it any more because we simply do not see it. The site of a wall covers a part of the screen with a size 8õ8, then all that is behind this site will be cut out by only one operation of matching, instead of traditional research all 64 pixels one behind another. HyperZ is individual incarnation of the technology of the hierarchical Z-buffer, about which it is possible to read "in deep" on this site. That is, as a matter of fact, HyperZ saves capacity of memory, reducing the stream of information, passing through it. All of us know how important it is for example for NVIDIA GeForce256 SDR or GeForce2 GTS, when the low frequencies of a video memory (concerning power of chipset) do not give it to realize the potential first of all in 32-bit color. For ATI RADEON the memory works on higher frequency 183 (366) MHz against 166 (333) MHz for GeForce2 GTS), and the chip on the speed of filling the scene (fillrate) is less powerful than GeForce2 GTS, therefore balance for RADEON is much higher, than for chipset from NVIDIA. Nevertheless, it is curious to find out in what resolution RADEON faces the problem of shortage capacity video memory, and where HyperZ can help very much. Ending to examine HyperZ, I want to mark, that in spite of the fact that some authoritative western observers in the Internet have declared that HyperZ is included in drivers, nobody has proved it. Represented on the site SharkyExtreme "keys" for depositing in the register on handle HyperZ simply do not work. Therefore I do not know whether HyperZ was included in testing or not. Thus, we have examined the main features of the new chipset ATI RADEON, giving to the users new possibilities in a 3D-graphics improving quality of the three-dimensional scenes and large potential on productivity. To my mind a user already is tired to read periodically flaring too optimistic articles created in marketing departments of this or that corporation devoted to the new chip. If we listen to all these slogans and shouts of delights, we can imagine that we have already had photorealistic graphics with tremendous speed. However, we are permanently deceived by offering the really powerful chip having fantastic possibilities but very expensive (and it is clear that no corporation releasing the games begins to make products for it), or by producing chip with faked characteristics first of all because of wrong drivers. Let's take two examples:
First two were released for chips NVIDIA GeForce 256 and GeForce2 GTS and support possibilities of these chips in a part of usage of the large textures, relief texturing etc. Two screenshots from Isle of Morg obtained on NVIDIA GeForce2 GTS are represented on the left and obtained on ATI RADEON - on the right. In this demo the change of day and night goes in real time (and it is possible to speed up this process through the key F7) therefore we see how the same scene in different time of day in this game looks: Day:
Night:
As we see GeForce2 GTS is all right. The sky changes its color according to general shadowing at night but for RADEON it remains of the same color as in daytime that was surprising. However not all is so bad. The chips have also common features, for example, implementation relief texturing according to the method Dot Product:  GeForce2 GTS ATI RADEON
We can see, that in both cases the implementation of this effect is carried out excellently. But in Dagoth Moor Zoological Gardens the picture differs in graphics greatly. Two screenshots obtained onNVIDIA GeForce2 GTS will be represented on the left and obtained on ATI RADEON-on the right GeForce2 GTS ATI RADEON
As it is possible to guess in RADEON's ARK all occurs just how it isn't needed, when NVIDIA GeForce2 GTS makes mistakes in implementation of this or that effect: GeForce2 GTS ATI RADEON
GeForce2 GTS ATI RADEON It seems to me that 3D-textures that are unknown to GeForce2 take part in creation of clothes and face for this girl. I can be asked what I want. These are demo that aim is to show features of this or that chip and they at all are not obliged to take into account possibilities of the competitors. I want to show once again: there are new chips having different possibilities, which sometimes are unique technologies inherent only in them. A lot of new technologies have already been standardized through Microsoft DirectX, however a lot of them are outside of this toolkit permitting to the developer to be sure, that usage in the game of this or that effect through Direct3D will be realized by overwhelming majority of accelerators. It is bad that the manufacturers of chips very slowly license the operating time in DirectX or it does not occur at all. And then it is possible safely to bury these operating time and technologies. An example: S3TC was unnecessary and almost forgotten when at last S3 has found time to license the technology in Direct3D and to receive DXTC, and also to sell the license to contestant firms: ATI, NVIDIA, 3dfx. And we can see, that nowadays S3TC begins to find a market. Being reset to the object of our today's testing, we shall examine directly videocard on base ATI RADEON. CardThe corporation ATI announced at once some videocards on the basis of the new chip:
As we see complexity of cards decreases from above downwards, as however, and price for these cards. The first card is intended for the requiring players - "professionals" and also people wishing to extract from card a maximum of possibilities and comfort. The second card - for common players, represents the compromise between the price and possibilities. The third card is for cheap systems. We have a videocard of the most powerful level: RADEON 64MB DDR VIVO: The card has the interface AGP 2x/4x, 64 megabytes DDR SDRAM of memory placed in 8-ìand 64-ìåãàáandòíûõ units (on 4 on each sides PCB).  The chip-partner RAGE THEATRE which is responsible for VIVO (Video In, Video Out) is placed on PCB.  The chip works on frequency 183 MHz, active cooler is pasted on it. It seems to me that the corporation ATI develops this form of the fan because we can't meet such coolers on any videocards. The memory works on frequency 183 MHz or with resulting frequency 366 MHz, in further we shall use resulting values of frequencies of DDR-memory. PCB has traditional for ATI green color and the units responsible for regulation of power supply are also placed on card. OverclockingUnfortunately for the power users, the company ATI does not give any possibilities to increase frequencies of operation chipset and memory. The traditional utility PowerStrip in the last version 2.70.05 already has support of ATI RADEON, however it is possible to change only frequency of operation memory. Overclocked up to 410 MHz the videocard works steadily. Certainly, as well as at any overclocking, it is impossible to be without additional cooling as the fan blowing on a card. Installation and driversNow we shall pass to a practical part of our review. For the beginning I shall present the configuration of test desks: 1. Desk on base Pentium III:
2. Desk on base Athlon:
The screen monitors ViewSonic P810 (21") and NOKIA 447Xav (17") were used on both desks. All main trials and researches were carried out on the first desk and the second desk was used for demonstrating faultless operation of a videocard on the platform Athlon. We did not pursue the purpose to compare platforms. The installation of driver's occured in a traditional way from ATI - through setup. There were no problems with installation; in result we have received access to the following customizations: Direct3D:
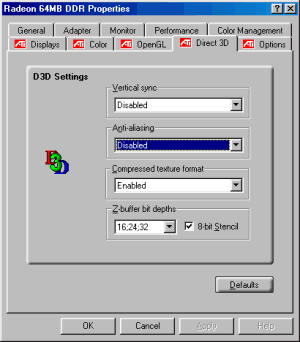 OpenGL:
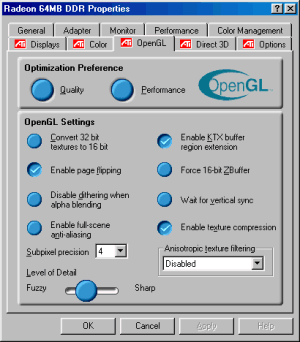 TV-out:
 As it is possible to see, the contents of customizations has not strongly changed in comparison with ATI RAGE FURY Results of the testsLet's begin from 2D-graphics. First of all I want to mark traditional for ATI quality of the image and clearness of a picture even in resolution 1600õ1200. The speed was metered with the help WinBench ' 99 (Graphics WinMark) and represented in the table below:
As we see, by speed ATI RADEON lags behind the contenders, however all the same level of acceleration two-dimensional graphics is so high, that it is enough for the majority of the users. I want to mark excellent quality of the picture even on high-resolutions (up to 1600õ1200 inclusively). For obtaining results of testing in 3D the following tools were used:
For realization comparative analysis the data on videocards NVIDIA GeForce2 GTS and 3dfx Voodoo5 5500 were used. Quake3In this test besides traditional removals of the data on productivity at standard modes, I have tested RADEON in the anti-aliasing mode, at switched on support S3TC (including at levels S3TC from S3/Diamond Multimedia - demo annihilator), and at maximum installations at a level Q3DM9 (demo quaver). The data obtained by operation RADEON on dispersed frequencies are also resulted. And the frequency of operation memory for NVIDIA GeForce2 GTS is rather easily dispersed up to 366 MHz that is before values of frequencies of memory for RADEON, therefore I bring also these results, to compare at the defined error chipsets GeForce2 GTS and RADEON. 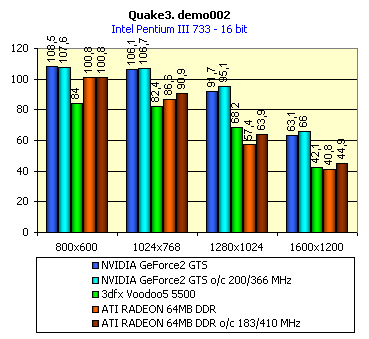 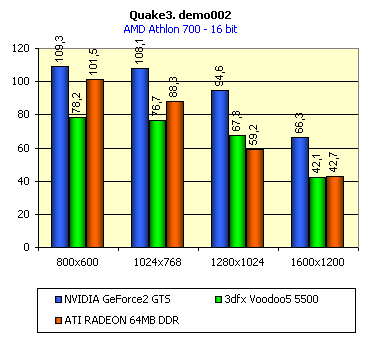 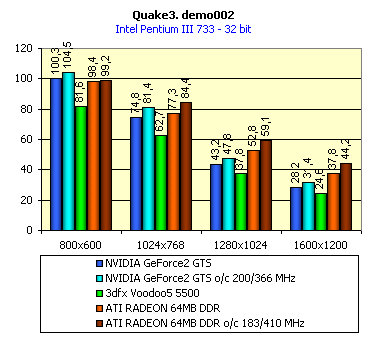 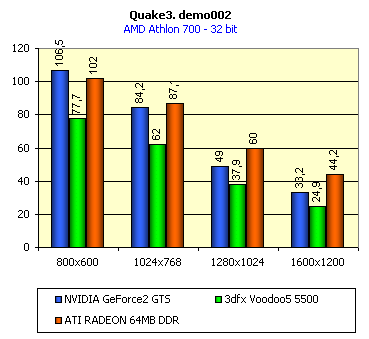 As it is possible to see, in 16-bit color RADEON strongly lags behind from GeForce2 GTS, anticipating only Voodoo5 5500, but in 32-bit color is the unconditional leader! The dispersal RADEON gives some effect, but not so strong (the dispersal only on memory effects). For an assessment work of RADEON in heavy conditions demo Quaver was used and all maximum installations of a level of detailing of textures and geometry (first-rate quality) were used there: 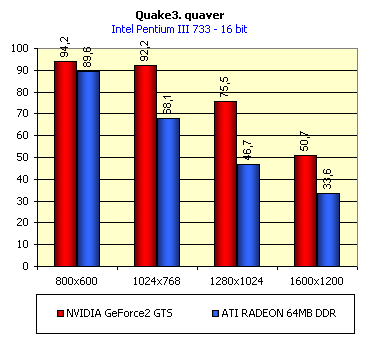 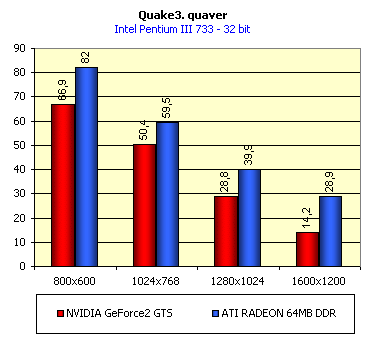 Here the picture repeats: backlog in 16-bit and advancing in 32-bit color. As is known, at inclusion S3TC through a videocard the smaller information content is sent at the expense of compression of textures that results in some growth of speed at the expense of small deterioration of quality. 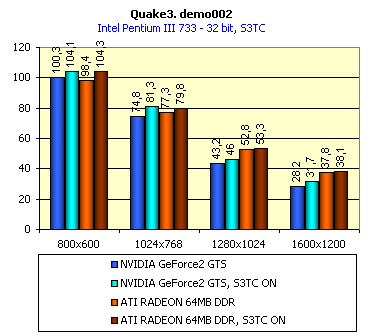 These results have confirmed it once again. Not long ago corporation S3/Diamond Multimedia has released some special levels for Quake3, operating the technology S3TC. Demo benchmark Annihilator.dm3 is based on a level dmmq3dm5.pk3: 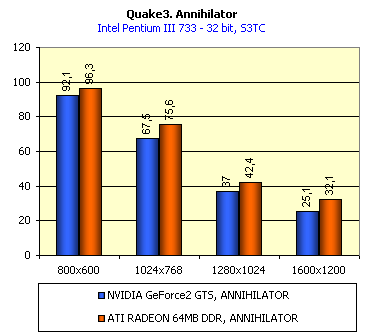 And even here RADEON has confirmed leadership in 32-bit color. Though I should mark, that artifacts with unclear drawing of some animated textures and also objects mirroring light took place. It was curious to observe falling in productivity at inclusion of trilinear and anisotropic filtering. As is known, both chips (GeForce2 GTS and RADEON) support anisotropic filtering. In drivers from ATI a maximum quality on this filtering was included. 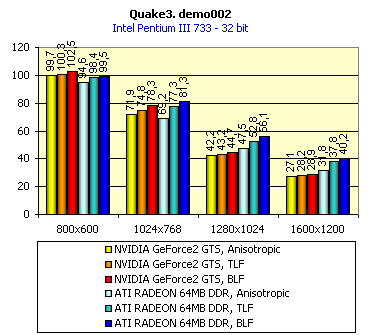 It is possible to note, that at inclusion of anisotropic filtering the falling in speed for RADEON is a little bit more appreciable than for GeForce2 GTS. However, implementation of anisotropic filtering for RADEON is rather strange. Below by examining quality in 3D-graphics I shall show it. At inclusion of the anti-aliasing mode (it is made under the scheme OGSS super-sampling so as NVIDIA makes it) we receive the following: 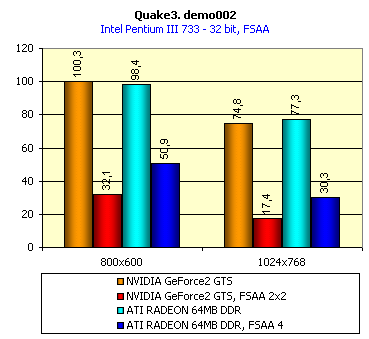 ATI names the anti-aliasing mode with coefficient super-sampling 2õ2 - FSAA4. As a matter of fact this is the same as FSAA 2x2 for NVIDIA. As it was expected RADEON kept its leadership here again. I want to mark, that with anti-aliasing the requirements to capacity of memory are increasing and so such results are not surprising. On the example Quake3 I have carried out research influence of frequency the processor for productivity RADEON (scalability): 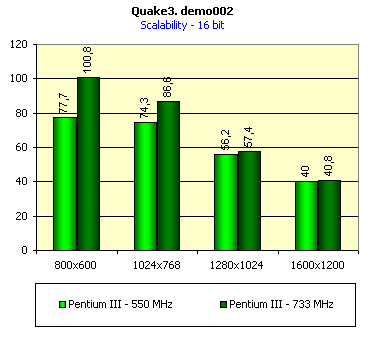 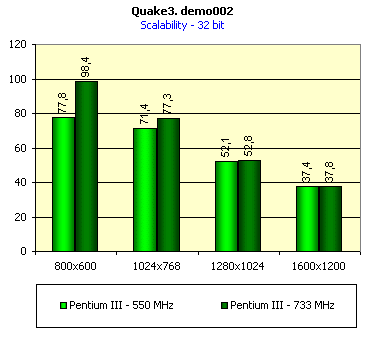 It is possible to see, that in resolutions from 1024õ768 and higher the frequency of the processor does not influence speed of a card. Certainly, this data cannot be generalized on more low frequencies of the processor, however the owners of processors with frequencies lower than 500-550 MHz just will not buy such expensive videocard. I have already mentioned that there is no sense to spend money on "cool" accelerator, having the low-power processor. ExpendableThis game by results of testing can produce not only average value FPS, but also minimum, that is rather important moment. You see playability in this or that resolution just determines minimum FPS. 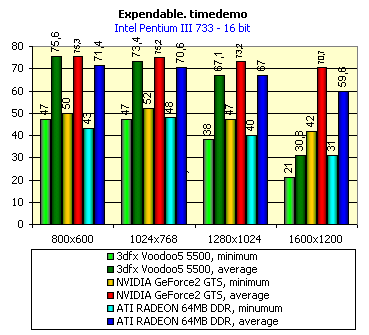 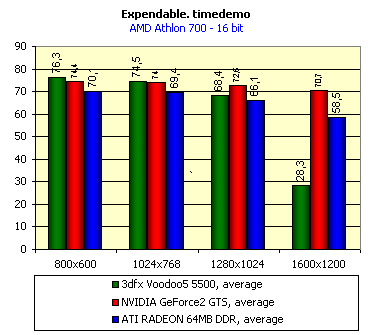 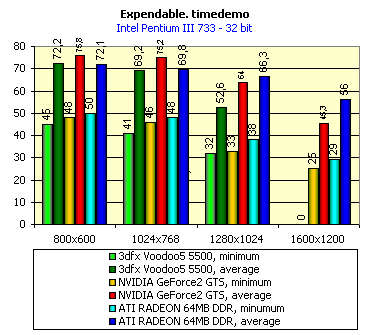 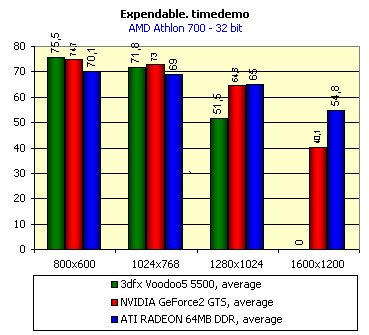 It is possible to see, that the situation shown above, repeats. Again backlog from GeForce2 GTS in 16-bit color and advancing in 32-bit takes place. Playability on minimum FPS is at a good level even in 1280õ1024õ32. MDK2This game through built in benchmark can show us not only productivity of a videocard in OpenGL, but also allows to compare speed of a card at usage Hardware T&L and without it. 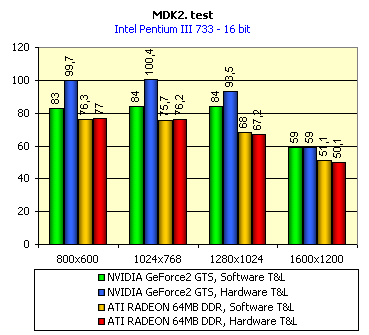 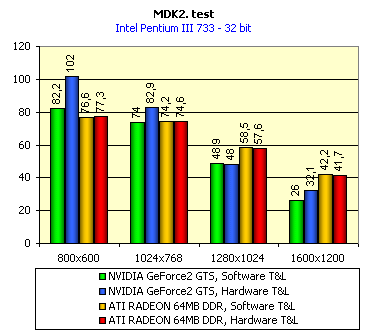 It is clearly that not only the situation with backlog in 16-bit and advancing in 32-bit colors is repeated but also that for RADEON Hardware T&L does not give any advantages and as a matter of fact it is weaker than for GeForce2 GTS. It does not answer promising from ATI. Therefore we shall look operation Hardware T&L On an example TreeMark (Grove). GroveThis benchmark allows to observe dependence the speed of a card operation at valuable usage Hardware T&L on complexity of the scene and quantity of light sources. 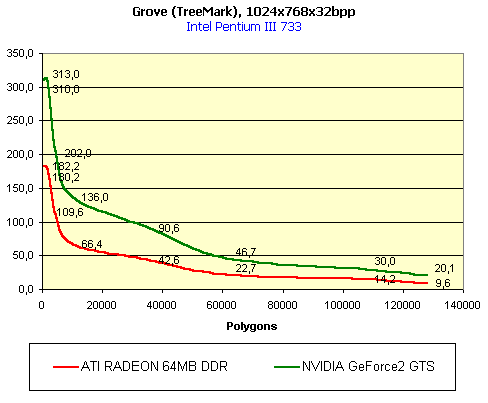 As we see something is wrong with T&L For RADEON. The geometrical coprocessor for RADEON yields on speed to the competitor. Dependence on quantity of light sources: 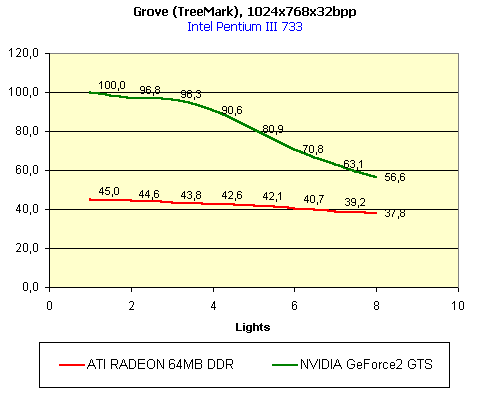 This schedule confirms the previous thesis about weakness Hardware T&L For RADEON however implementation promising of the corporation that for RADEON the geometrical coprocessor will depend to a lesser degree on number of light sources is clear. We see, that the falling on speed is minimum and approximately at a level 10 sources both graphics can be crossed, as GPU from NVIDIA does not cope any more with such load and the speed quickly falls. Thus the main conclusion of testing high-speed parameters of a videocard ATI RADEON is that it is nowadays the leader among game videocards in 32-bit color. The strong backlog in 16-bit color is not so critical and you soon will understand why. One more unexpected result is relative weakness of the geometrical coprocessor for RADEON though we were promised just opposite. It is difficult for me to say if it depends on the chip or on defect of drivers. Quality 3DFirst of all I want to analyze filterings. As is known at usage of the technology MIP-mapping that is at sharing of the scene on levels with different detailing the quality of filtering smoothing boundary between mip-levels becomes very important. Until recently everybody hoped on trilinear filtering and anisotropic filtering was considered to be unavailable because of both complexity of its algorithm and insistence to productivity which is reduced at usage of this sort of filtering. The epoch of cards on base NVIDIA GeForce2 GTS has brought us the present valuable anisotropic filtering: And what about RADEON? Among its features there is also support anisotropy. I have already mentioned it examining productivity. However what can we see actually? Actually, without any questions, RADEON has superior image quality in anisotropic mode. Interesting, that coloring of mip levels looks strange, because of the nature of anisotropic filtering. Like we simply move mip levels backwards. The reason why I didn't want to pay attention to backlogs on speed RADEON in 16-bit color is the quality of implementation this mode:  Does anybody need such 16-bit color at poor desiring? Hardly. I think, that the future owners RADEON will play only in 32-bit color because a card by the possibilities allows it. I even can assume, that the authors of the chip purposely did not begin to improve 16-bit color to show it unnecessity at present and to accustom the users "to live" permanently in 32-bit color. However it is not the worst situation. Look what we have at inclusion of the anti-aliasing mode in 16-bit color (left part screenshot): It looks like if we transfer in 256-colour or even in 16-colour mode. The situation is different in 32-bit color at switched on anti-aliasing.   Here the quality is already more - less acceptable. And at last it would be desirable to mark, that those faults that were available for ATI RAGE FURY PRO in implementation of some functions leading to artifacts in RADEON completely have disappeared. I personally in general do not have any complaints to quality 3D for RADEON in 32-bit color: Certainly it is necessary to mean, that the implementation S3TC should be corrected in drivers (I have already mentioned about artifacts at operation with S3TC-levels in Quake3). I hope, that ATI rather fast will cope 5t with this task. Additional functionsAs I already have marked in the beginning of the article multimedia processor RAGE THEATER provides both reception (Video In) and output on TV (Video Out) analog signal. I shall not analyze these features in detail because you can learn about them from different ATI RAGE FURY PRO VIVO reviews. All customizations and possibilities of these functions have not undergone any changes from that time. As to operation with DVD-Video there is some complexity. Certainly, the admirers of production from ATI know, what exactly the cards of this corporation for a long time in the best way realize support DVD. The structure ATI Multimedia Center contains a DVD-player, however I could not force it to include the hardware support of a videocard, probably defect of the software included in the set has an effect. The utility DVD-Genie with which help it is possible to control many program players DVD could not help by anything. I could watch only perfect quality of a picture at rather high percent of loading the processor - 75-78 %. OutputsIn 2.5 months after issue of videocards on base NVIDIA GeForce2 GTS, the corporation ATI has put answer impact. Its new product th with the strange name RADEON inconsiderately has broken monopoly of products from NVIDIA and GeForce2 GTS has lost its leadership in 3D-graphics at 32-bit color. Yes, it already can be stated. Certainly, it is necessary to confirm the victory of production ATI by correct price policy and fast appearance of videocards on counters of shops (while the cards on sale are not present) or the victory remains illusive and the people will buy more habitual cards on chips from NVIDIA. By the way under the informal information we have got the real retail prices for cards on base RADEON will be much lower than for declared ATI in press release from July 17. Let's look. We can name RADEON the leader but with stipulations:
At execution of all these conditions we can tell that the competition will be! And NVIDIA won't be the leader in the market of videocards any longer. It will have a serious and even stronger contender. Unfortunately 3dfx has failed with the "stupid" policy and it can't be named a serious contender. Positive sides:
Negative sides:
Write a comment below. No registration needed!
|
Platform · Video · Multimedia · Mobile · Other || About us & Privacy policy · Twitter · Facebook Copyright © Byrds Research & Publishing, Ltd., 1997–2011. All rights reserved. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||