Operating features
Peltier modules are very reliable; they haven't got any moving parts, unlike coolers constructed according to the traditional technology.
But despite all the mentioned advantages, Peltier modules have some specific features, which must be taken into account when using as a part of a cooling unit. The most important characteristics are:
- The modules, dissipating much heat, require the relative fans and heatsinks which would manage to carry off the heat effectively. We should notice, that the thermoelectric modules have a quite low performance factor and they are themselves a powerful source of heat. The usage of these modules might cause overheating of the other components inside the system block. That's why it's necessary to install additional cooling systems inside the block. Besides, the modules consume a lot of energy, and in this connection a power supply unit capacity shouldn't be less that 250 W. Though there are sometimes Peltier coolers with its own power supply unit.
- In case of the module's failure the cooler becomes isolated from the cooled element. It might lead to fast overheating of the latter.
- Low temperatures might cause moisture condensation. This might lead to short circuits between the elements. That's why you should use the modules of the optimal power. Moisture condensation depends on the temperature inside the system block, the temperature of the cooled device and air moisture. The warmer air is and the more moisture is, the condensation is more probable. The table below shows the dependence between a condensation temperature on a cooled element and a temperature and moisture of the surrounding air.
Moisture condensation temperature
| Moisture, % |
| Ambient temperature, °C |
30 |
35 |
40 |
45 |
50 |
55 |
60 |
65 |
70 |
| 30 |
11 |
13 |
15 |
17 |
18 |
20 |
21 |
23 |
24 |
| 29 |
10 |
12 |
14 |
16 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
22 |
23 |
| 28 |
9 |
11 |
13 |
15 |
17 |
18 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
| 27 |
8 |
10 |
12 |
14 |
16 |
17 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
| 26 |
7 |
9 |
11 |
13 |
15 |
16 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
| 25 |
6 |
9 |
11 |
12 |
14 |
15 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
| 24 |
5 |
8 |
10 |
11 |
13 |
14 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
| 23 |
5 |
7 |
9 |
10 |
12 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
| 22 |
4 |
6 |
8 |
10 |
11 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
| 21 |
3 |
5 |
7 |
9 |
10 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
| 20 |
2 |
4 |
6 |
8 |
9 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
Besides, you have to take into account some peculiar features when installing a cooler near a high efficient CPU of powerful computers.
The architecture of the modern processors and some system programs provide different power consumption modes depending on CPU load. Some people use "cooling" programs, i.e. CpuIdle, or Windows NT/2000 and Linux. In this case the usage of Peltier modules is undesirable, since it's assigned for continuous work. In case of low power supply of a processor, the crystal temperature falls much. This might lead to buzz. Remember, that theoretically Intel's Pentium II and Pentium III processors can't work at the temperature below +5°C (though in practice, they endure lower temperature).
Some more problems can occur in case your motherboard supports a function allowing to control the fan speed depending on the power consumption of the processor. In the regular conditions it improves the thermal mode of the processor. In case of Peltier module usage, you might face some problems. It takes place, since the module is a source of heat itself and thus, it requires the heat to be carried off.
Peltier modules can be used for cooling of videocard chips as well. The work of videochipsets causes huge amount of heat evolved, and it's at the same time quite stable.
It's quite rational to use intelligence systems to control not only fans but also thermoelectric modules. It will help to avoid both supercooling and moisture condensation.
Not so long ago the experiments on installation of the miniature modules in processors were carried out. It's considered to be a rather perspective way of processors' cooling.
Peltier cooler examples
Below you can see examples of thermoelectric coolers (TECs).
Active Peltier coolers from Computernerd
| Model name |
Manufacturer/ supplier |
Fan parameters |
Processor |
| PAX56B |
Computernerd |
ball-bearing |
Pentium/MMX up to 200 MHz, 25 W |
| PA6EXB |
Computernerd |
dual ball-bearing, tachometer |
Pentium MMX up to 40 W |
| DT-P54A |
DesTech Solutions |
dual ball bearing |
Pentium |
| AC-P2 |
AOC Cooler |
ball bearing |
Pentium II |
| PAP2X3B |
Computernerd |
3 ball bearing |
Pentium II |
| STEP-UP-53X2 |
Step Thermodynamics |
2 ball bearing |
Pentium II, Celeron |
PAP2CX3B-10
BCool PC-Peltier |
Computernerd |
3 ball-bearing, tachometer |
Pentium II, Celeron |
PAP2CX3B-25
BCool-ER PC-Peltier |
Computernerd |
3 ball-bearing, tachometer |
Pentium II, Celeron |
PAP2CX3B-10S
BCool-EST PC-Peltier |
Computernerd |
3 ball-bearing, tachometer |
Pentium II, Celeron |
The PAX56B cooler is developed for Pentium and Pentium-MMX processors from Intel, Cyrix and AMD, working at the frequency up to 200 MHz. The thermoelectric module (30x30 mm) allows the temperature below 63°C at 25 W of dissipated power and the outer temperature of 25°C. It provides the lowest temperature than alternative fans and heatsinks. For normal work of this cooler it's necessary to provide 5 V and 1,5 A (maximum). The fan for this cooler require 12 V and 0,1 A (maximum). The fan parameters: ball-bearing, 47,5 mm, 65000 hours, 26 decibel. The whole size of the cooler is 25x25x28,7 mm. The guiding price is $35.
The PA6EXB cooler is developed for more powerful Pentium-MMX processors, dissipating heat up to 40 W. This cooler suits all processors from Intel, Cyrix and AMD intended for Socket 5 or Socket 7. The thermoelectric module (40x40 mm) consumes maximum 8 A (usually 3 A) and 5 V; the cooler uses a power supply unit of the computer. The whole size is 60x60x52,5 mm. For better performance it's necessary to provide at least 10 mm above and 2,5 mm on each side when installing the cooler. The cooler ensures the temperature of 62,7°C with 40 W of dissipated heat and the outer temperature of 45°C. To avoid moisture condensation and short circuits you should not use programs, which set a processor into a standby mode for a long time. The guiding price is $65.
The DT-P54A cooler (is known also as PA5B from Computernerd) is developed for Pentium processors. However, some companies recommend it also for Cyrix/IBM 6x86 and AMD K6. The heatsink is quite small (29x29 mm). The cooler has a thermode to prevent overheating. It controls a Peltier element as well. The complete set includes an external control device (it controls voltage, a Peltier element, a fan and temperature). The device gives an alarm signal in case of failure of a Peltier element or a fan, the fan rotates at the speed less than 70% of the standard value (4500 RPM) or processor's temperature goes up more than 145°F (63°C). The Peltier element switches on at the temperature of the processor more than 100°F (38°C). Since the element is firmly connected with the heatsink, you won't be able to install it on other one. The fan is quite reliable: 12 V, 4500 RPM, 6.0 CFM air supply speed, 1 W power input, 30 decibel. The price is $39 to $49.
The AC-P2 cooler is developed for Pentium II processors. The complete set includes 60 mm cooler, a heatsink and 40 mm Peltier element. The cooler doesn't suit Pentium II of 400 MHz and higher, since SRAM chips practically don't get cold. The guiding price is $59.
The PAP2X3B cooler (fig. 8) is similar to AOC AC-P2. It has 2 more fans (60 mm). The same problems with SRAM cooling. You shouldn't better use it together with "cooling" programs, such as CpuIdle, and under Windows NT and Linux, since moisture condensation may occur. The guiding price is $79.
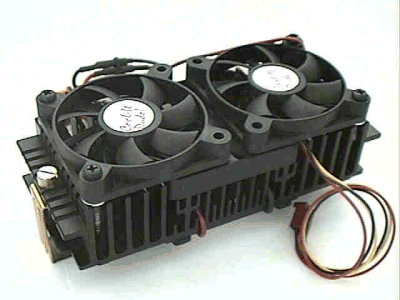
Fig.8. The PAP2X3B cooler
The STEP-UP-53X2 cooler is provided with 2 fans, which pump much air through the heatsink. The guiding price is $79 (Pentium II), $69 (Celeron).
The coolers of Bcool series from Computernerd (PAP2CX3B-10 BCool PC-Peltier, PAP2CX3B-25 BCool-ER PC-Peltier, PAP2CX3B-10S, BCool-EST PC-Peltier) are developed for Pentium II and Celeron processors and have similar characteristics (see the table below).
Bcool series coolers
| Model name |
PAP2CX3B-10
BCool PC-Peltier |
PAP2CX3B-25
BCool-ER PC-Peltier |
PAP2CX3B-10S
BCool-EST PC-Peltier |
| Advisable processors |
Pentium II and Celeron |
| The number of fans |
3 |
| Central fan type |
Ball-Bearing, tachometer (12 V, 120 mA) |
| Size of a central fan |
60x60x10 mm |
| Type of an external fan |
Ball-Bearing |
Ball-Bearing, tachometer |
Ball-Bearing, thermistor |
| Size of an external fan |
60x60x10 mm |
60x60x25 mm |
| Voltage, Current strength |
12 V, 90 mA |
12 V, 130 mA |
12 V, 80-225 mA |
| Area occupied by the cooler |
84.9 sm2 |
| Total current for fans (power) |
300 mA
(3.6 W) |
380 mA
(4.56 W) |
280-570 mA
(3.36-6.84 W) |
| Heatsink fins (center) |
63 long and 72 short |
| Heatsink fins (on each side) |
45 long and 18 short |
| Total heatsink fins |
153 long and 108 short |
| Heatsink size (center) |
57x59x27 mm (including the thermoelectric module) |
| Heatsink size (each side) |
41x59x32 mm |
| Total heatsink size |
145x59x38 mm (including the thermoelectric module) |
| Cooler size |
145x60x50 mm |
145x60x65 mm |
| Cooler weight |
357 g |
416 g |
422 g |
| Guarantee |
5 years |
| Guiding price (2000) |
$74.95 |
$79.95 |
$84.95 |
We should mention that the BCool group includes devices with similar features, but they lack for Peltier elements. These coolers are undoubtedly cheaper and not so effective.
"PC Overclocking, Optimization, & Tuning" book by E. Rudometov, V. Rudometov (ISBN 1-58450-079-4, bhv PUBLISHING HOUSE) used as major source for this article.
Write a comment below. No registration needed!

