 |
||
|
||
| ||
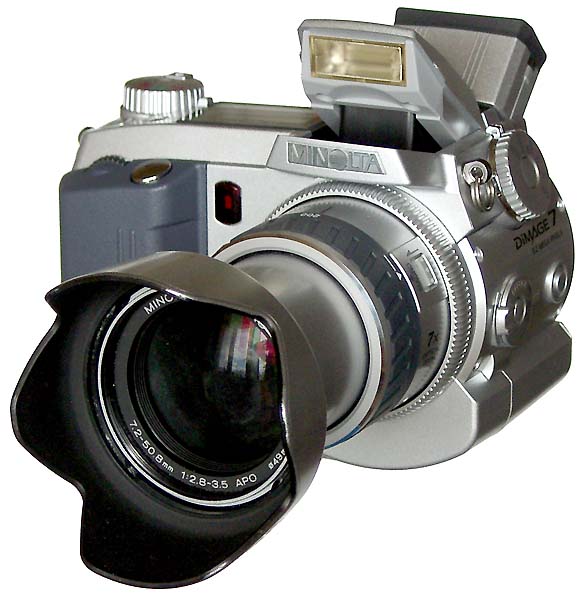 The Minolta DIMAGE 7 camera is, perhaps, an entirely finished conception of a digital camera. The experience will show whether this solution is viable. But I think that this camera starts the epoch of maturity of digital photo cameras. The matrix quality is rather high, and now one will hardly notice that the image quality is mainly determined by the lens whose resolution is higher in the center than on edges. But the price for good lenses does not usually drop with time or drops insignificantly. Further development and reduction of prices in the sphere of electronics will hardly affect cameras of this class. I think that in the future belongs to the digital cameras with removable optical instruments like Leica when anyone will be able to equip his camera with a lens he likes. So, what about the today's hero?The matrix contains 5.24M pixels with 4.95M enabled; the photo, thus, is made up of 2560 X 1920 pixels. This camera provides only a 20% increase in linear dimensions over 3Mpixel cameras. But you must be aware that each extra per cent costs a fortune in such cameras. The lens contains 16 elements in 13 groups. Two lenses are made of glass with anomalous dispersion (the dispersion is extremely low, i.e. refractive exponents for a blue and a red region almost coincide), and other 2 lenses have an aspherical surface. The focal length of the lens can be changed from 7.2 to 50.8 mm which is equal to 28-200 mm for 35mm photography. The maximum aperture of the lens is 2.8 at the focal length of 7.2 mm and 3.5 at the focal length being 50.8 mm. The focal length can be changed by turning a rubbered ring. I think it is much more convenient than a motor drive since you can change it immediately and you can estimate the length not only by looking into the viewfinder but also with your finger-tips when turning the ring. The motor drive treats mechanical parts gently and it allows using less strong materials. When I was shooting with this camera I felt that the lens is very reliable, and no backlash could be noticeable. On the lens you can see a thread 49 mm in diameter for color filters. When you change a focal length the thread doesn't turn, that is why you can easily use even polarizing filters. The camera is equipped with a lens hood with bayonet mounting.  The lens allows focusing objects situated 50cm - infinity from the CCD of the matrix. The focusing can be implemented either in an auto mode or manually. For the manual focusing there are two viewfinders to help you. One is a standard 46mm LCD monitor located on the rear panel of the camera while the other is a small 4.8mm LCD equipped with an eyepiece. Both viewfinders display almost a complete frame, and here you can see exactly what image which be received with the camera. Pixels of the microdisplay are almost unnoticeable, and it will be very easy for you to manually focus your camera. The eyepiece with a microdisplay can rotate, that is why focusing can be implemented with a camera being placed almost at the earth level. Besides, you can get a sharp image with the help of a ruler. The display will show you the distance to the object. Having made a shot you can immediately get all possible information on it. Since LCD monitors consume usually a lot of power, the displays can automatically turn on/off. For example, when you are looking into the eyepiece the camera will switch off the display on the rear panel and switch on the screen in front of the eyepiece. The manual focusing is implemented by turning the ring on the lens. The ring doesn't move optical elements but it orders the motor to do it, that is why the ring can't tell you what the distance is set at the moment. The lens has a special mode for macro-shooting. The focal length in this mode can be changed from 25 to 60 cm. During the shooting there is no need to use the menu. Usually, you use it for making preliminary settings. 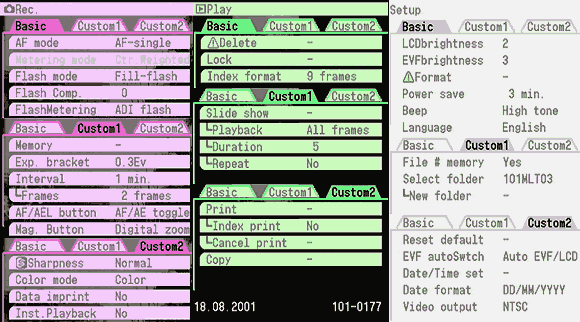 Although the camera is digital, there are a lot of switches on the case to control a shooting process.  Like other professional cameras, this one is also protected from unauthorized operations. So, any operation is implemented in 3 steps: first you choose the required mode by turning a ring, then you confirm your choice by pressing the button located in the center of the ring and then you set the required parameters with a ring near the release button.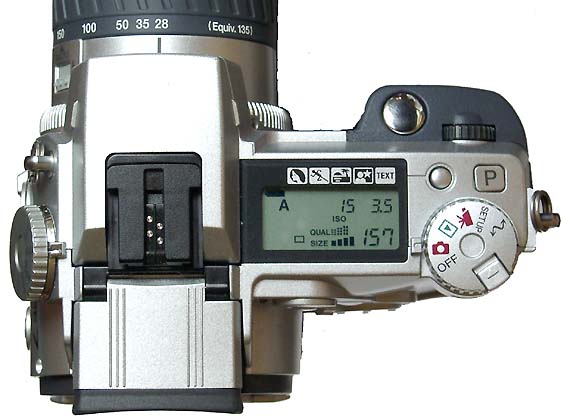  Shots are recorded onto memory cards CF Type 1 or Type 2 in TIFF, RAW (with MRW extension) or JPEG formats. Files recorded in the TIFF format are rather large: 14.444 MBytes, in the RAW - 9.715 MBytes. That is why the time of recording isn't very short. If you are going to record cards in this formats you must pay great attention to memory cards. For example, recording of one shot in TIFF onto CF cards with KTC FC controllers 120xN will take you 70 seconds. The IBM microdrive will help you save half time. Recording of the same file in the RAW format will take you 21 s. The CF cards coupled with Hitachi controllers provide the same speed as the IBM microdrive. In case of recording images in the JPEG format (e.g. 4.5 MBytes) the buffer of the memory cards is large enough to allow you to make the next shot in 1 second, though the LED is on about 10 sec. Of course the camera with viewfinders and IBM microdrive consumes too much power. That is why apart from 4 AA batteries you can take with you a power supply unit with 2 lithium batteries. To prevent damages you should use AC-1L or AC-2L network adapters.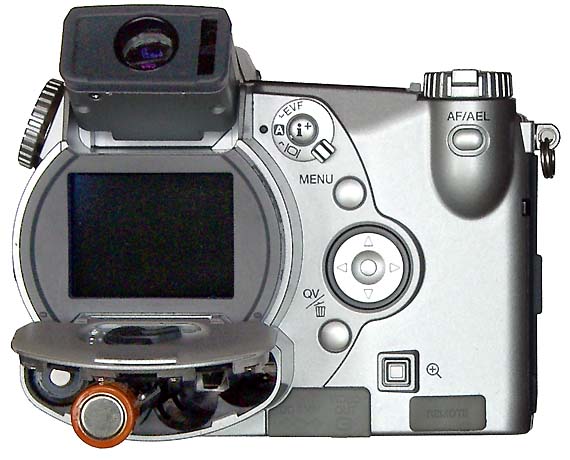   Energy from the batteries is not only for the camera but also for warming up hands of a photographer. This is very pleasant when you are working with the camera in winter. But in summer I wish the camera were covered with rubber pieces. The maximum focal length is considerable, the camera looks like a camera gun. The device is quite light, about 500 g without batteries and memory cards. That is why at the large exposure it is almost impossible to prevent shifting of the camera. Even 1/125 is not enough to avoid a blurry image. An exposure index can be 100, 200, 400 or 800 ISO. But if you want to make the best of the matrix and a 12-bit ACD you'd better shoot at the minimal sensitivity. Lack of light, in this case, can be compensated with flashes. The camera has a built-in pop-up flash can be attached with external compatible flashes from Minolta and other manufacturers, for instance, Sigma.  A tripod and a remote control will help you prevent shifting and shaking of the camera. The remote control ships separately. So you can buy it or make it at home since it is very simple: it consists of only two switches. Connect legs 1 and 2 and the camera will implement metering. Lock then all 3 legs and the camera will start shooting. Test resultsHere we will compare resolution in the center and on the edges. The analyses of circular and radial resolution charts was carried out with the program Levels by Dmitry Kuznetsov. First of all, let's give a mark to the lens at the focal length of 49 mm. The photos of the charts was taken in daylight; aperture - F:3.4, exposure - 1/32 s. 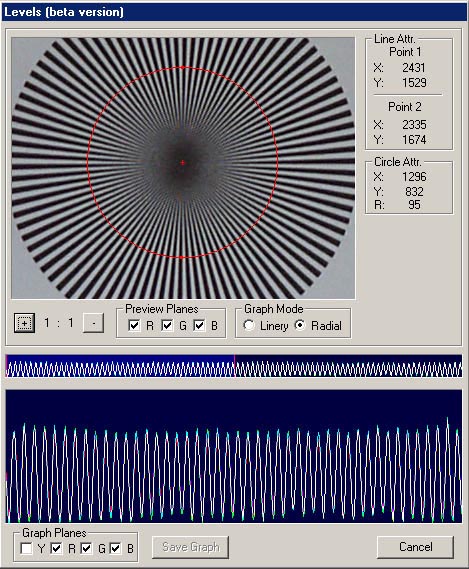 The graph demonstrates the dependence of the amplitude of brightness along the arc of circle which crosses a radial chart. The chart is located almost in the center of the frame. The distance from the center of the shot to the center of the chart is 130 pixels. The radius of the arc corresponds to the resolution of 0.3 stroke/pixel where black and white strokes are considered as two strokes. The length of the arc is 180 degrees. The reference point lies in the upper point of the circle. Now let's choose a resolution chart which lies 1,180 pixels from the center of the frame. 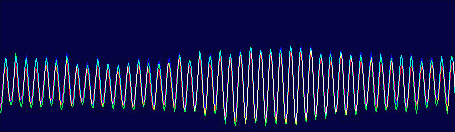 Here, both astigmatism and chromatic aberrations are well noticeable. To analyze it let's draw brightness graphs along the straight lines that cross a circular chart (the radius of each following ring is 0.9 of the previous ring's one) and lie in the sagittal and meridional planes. 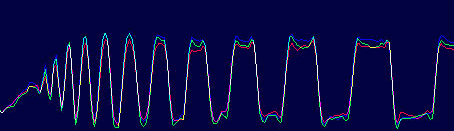 This is a contrast transfer function for the circular chart located near the frame center. The differences between graphs drawn for points lying in the sagittal and meridional planes are unnoticeable. So are the chromatic aberrations. The amplitude in the red and blue regions is a bit different but it means only an offset in the white balance. Now let's draw the contrast transfer function for the resolution chart whose center is located 1,280 pixels from the frame center towards the right lower corner. 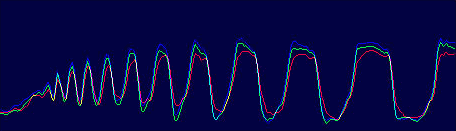 The dependence of brightness of pixels on the frequency of strikes was measured along the line which lies in the meridional plane. 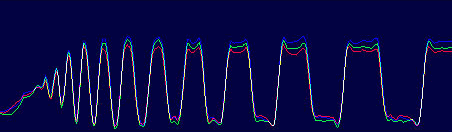 The dependence of brightness of pixels on the frequency of strokes was measured along the line which lies in the sagittal plane. Astigmatism and chromatic aberrations are quite clear on these graphs. Now let's change the parameters and draw these graphs again. Lens focal length: 7.5 mm, aperture - f:3.4, exposure - 1/32 s. 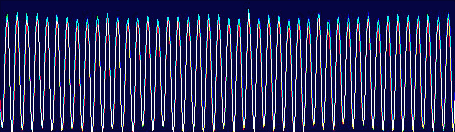 The distance from the frame center is 240 pixels. 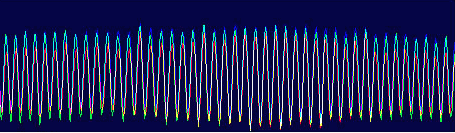 The distance from the frame center is 1,220 pixels. Now the astigmatism is much less. Let me compare the chromatic aberrations for a telelens and a wide-angle one: 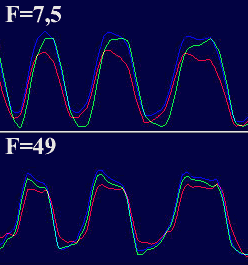 Here the wide-angle lens performs worse. But the contrast transfer function depends not only on a lens, but also on a matrix. Try to change a bit the angle the line is drawn at and the situation will be completely different. This effect will be much stronger if a line almost coincides with the direction of rows or columns of color filters in front of the matrix. 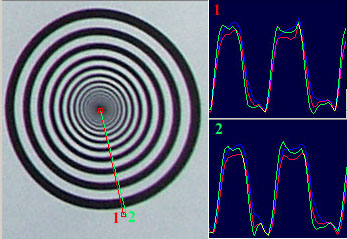 Photo Miniature. F= 7.5 mm  Miniature. F= 49 mm  Fragment. F=10 mm.  Fragment. F=49 mm. Write a comment below. No registration needed!
|
Platform · Video · Multimedia · Mobile · Other || About us & Privacy policy · Twitter · Facebook Copyright © Byrds Research & Publishing, Ltd., 1997–2011. All rights reserved. |