 |
||
|
||
| ||
Taiwan company EPoX is the youngest from all famous manufacturers of motherboards is well-known all over the world. The history of EPoX lasts only for 5 years from the foundation in February, 1995. The company has 250 workers and one factory with the square 30000 sq. ft which power is 300 thousand cards per month. It is interesting to find out why this company can compete with such companies as ASUS, Gigabyte, MSI which divided the motherboards market long ago.  EPoX has changed maximum possibilities and stability not saving on nothing and not overrating the production price. Overclockers of the whole world who use these motherboard to get higher productivity from Intel and AMD hardware products respect EPoX trade mark very much. The processors Intel are overclocked more than the products of the competitor, therefore incomparably more boards giving the extreme possibilities of the processors Intel rate increase are released. Intel 440BX chipset is still the basis for construction the majority of outstanding motherboards and it doesn't lose its relevance for more than two years since the moment of its appearance in May, 1998. Even the main competitor in the market of logic sets for motherboards construction - the company VIA supposes the chipset Intel 440BX to be a real masterpiece. However the possibilities of the legendary chip is limited by its age. Let's look once again at BX disadvantages to find out if it is possible to compensate them somehow.
So it is visible that none of the disadvantages effect the BX reputation. Though the last boards have got practically everything from this chipset and the excellent i815 is approaching, BX will be able to fight for its own hand for about half a year. And the motherboard EpoX EP-BX7+ which we have in our laboratory will help it. Specification
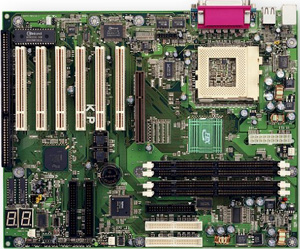 The delivery set contains a huge practically square box with the trade mark EPoX, the system board itself, FDD cable, 40-way and 80-way IDE, compact disk with drivers, monitoring means and utilities Norton Ghost and Norton AntiVirus, two diskettes with drivers for HighPoint controller and the user's guide in English. We shall examine board in detail. BoardLong ago when everybody only learnt to set-up computers, a lot of people thought that only the boards of the same colour gathered together can work well, i.e. if the motherboard is on the green board and the videocard - on the yellow one, then it is impossible for them to work together. The BX7+ is fulfilled on board of the noble green colour recalling the colour of the cards in our youth. The first thing you pay attention to at acquaintance with the card is its unusually large size. We already have got used that in fact the standard for system boards is 20,3x30,5 cm. Ours is wider on 4 centimetres, that allowed to arrange all the innovation components which the standard hardware products of the competitors don't have. No wonder that the box is so big. However don't be afraid that the card will not be located in your tank because the size 24,5x30,5 mm is the standard ATX which the tanks are designed for ( the majority of modern cards for Athlon/Duron have the same sizes). What is EpoX hardware product famous for? Firstly it is the external UltraDMA/66 RAID controller on the microcircuit HighPoint HPT368, secondly it is the additional power supply control block for the chipset, memory and AGP, and thirdly-two diagnostic seven-segment indicators for codes selfdiagnosis mapping at turning on (POST) and logic for handle them. BX7+ surprises with the quantity of capacitors and their capacity. There are 14 capacitors of capacity 2200mF on the board. Besides there are a lot of capacitors of smaller capacity placed near the slots DIMM, PCI and AGP. Stability or what capacitors are needed forCapacitors are included in the so-called pulse voltage converters - inverters. Such converters are needed to convert 5 V from the power supply unit into 1,65 V for processor core supply, 3,3 V for DIMM supply etc. The inverter consists of "energy-accumulator"- either the inductance coil or capacitor, transistor and capacitor - power supply filter. As a rule the inductance coil is placed at the input, it is possible to use the capacitor is possible, but the variant with inductance is more preferable because it allows to get smaller amplitude of the stabilised voltage ripples at the same capacities of power supply filters capacitors. The pulsating voltage with the defined pulsation is given on the transistor, and the transistor gives the voltage on the capacitor - power supply filter. Between this output capacitor and the transistor there is feedback - as soon as it is charged up to the necessary voltage, the transistor is closed and the capacitor starts to be discharged. It is necessary to convert pulsing voltage again into constant voltage. The capacity of this capacitor plays its role just here. The more it is, the more high-power converter is and the less the amplitude of output voltage pulsation is. Then it is necessary to mark how the developers solve the problem of choice transistors for usage them as the key elements of inverters and of their operation mode. The application of low-power key transistors makes the production cheaper, but it leads to the operation instability, overheat, and sometimes even to their failure. The normal transistors-invertors operation is characterised first of all by their thermal mode ~35-45°C. By the way at the transistors temperature measurement the professional voltmeter thermocouple marked the temperature 42°C. It confirms once again how serious the engineers of the corporation EPoX treated the calculation of the voltage supply stabilisers CPU and other motherboard components. It is necessary to mark that directed by the specification 3,3 V are not the voltage for chipset and the given board memory. Their voltage is 3,4 V that effects the operation stability. So the green heat sink of the same colour with the board with the "EpoX" trade mark installed on the chipset looks pleasant and diligently fulfils its direct duties. The slots DIMM are posed maximum close to the chipset that also prevent from failures. The card completely has equalled hopes, having demonstrated the remarkable stability even in matching with the competitor from ASUS - the card CUBX. The percent of BX7+ failures got as the result of 48 hours testings is only 33% from ASUS CUBX failures quantity. Something else about the boardThe transfer on Socket-370 has happened. BX7+ supporting all the released PPGA and FCPGA processors from Intel, and also legendary Cyrix III amused everybody by its productivity is not the exception. And the capacitors around Socket-370 are posed in such a way that famous cooler Golden Orb feels fine. The board BX7+ has one slot AGP, six slots PCI supporting Bus Mastering and also one slot ISA being divided with the last PCI. The happy owners of computer antiques can't give up ISA slots. It is good that they give up SIMM. The common design of the card is balanced up to trivialities, and this is not strange. For more than two year of the chipset BX existence only lazy-bones didn't take of all the users wishes on the hardware products modification. The only noted defect is the impossibility of the modules DIMM replacement at the installed AGP videocard. Four slots DIMM are installed on the board and it will allow the owners of hard purses to please themselves by a gigabyte of memory. Though the availability of four slots on this card does not look such ephemeral. You see at its stability and with RAID controller BX7+ can easily represent itself as the platform for the videowiring station. Why videowiring instead of for example server? The answer is simple. The main disadvantage of IDE controllers relative to SCSI is the strong central processor load at disk operations. However besides the tested UltraDMA66/RAID controller on the microcircuit HighPoint HPT368 skilfully loads the processor:) it also fulfils its duties rather well. The controller has its own BIOS and allows at the hardware level to actualise the RAID-arrays of levels 0, 1, 0+1. Though the possibilities for configuration are insignificant (for example as against FastTrak it is impossible to set the size of blocks), in whole HPT368 has shown itself rather good. The out-of-date driver from HighPoint delivered with the card force to spend some time for searches freshen versions. To search something new it is better at once on the site Iwill which for already half a year releases separate RAID on HPT368. With new drivers the controller even could work in RAID mode with new hard disks from IBM DTLA. It is possible to acquaint with the shown results in the section "Productivity". 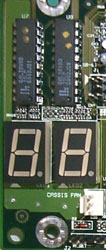 The large interest is caused by two seven-segment indicators of deep red colour. At turning on the computer the codes POST are sequentially mapped on them depending on what component of the system equipment is being checked. At failure or the lack of some component (for example the memory) the error code ñaused the selfdiagnosis operation stop remains on the indicators (the complete list of them is given in the user's guide). The given board function is not something outstanding, however it is rather useful especially at often change of components or at line computer assembly. The practical realisation of the given function is worse praising-the indicators are posed cose, much more demonstrably than the diodes D-LED from MSI and are just beautiful. BIOS EpoX EP-BX7+ is fulfilled on the basis of old checked out Award 4.51PG, and by quantity of configurations is just as good as the competitors. Especially it would be desirable to mark so necessary functions as the forced allocation IRQ on slots PCI and as much as possible detailed configuration of memory timings. The possibility of turning on the computer from the keyboard both after pushing one key and after the keyword enter is foreseen. And at last it is possible to ïðîøèòü the new version BIOS without the operating system load-the program for wearing is built in directly in BIOS. The hardware monitoring is carried out by the microcircuit Winbond W83782D representing the standard possibilities. The only circumstance worth paying attention to is that the temperature of the processor is taken out from the built in thermosensor that provides the large accuracy of the indications in matching with external variant. And at last the important information on light emitting diodes. And here EpoX walks away from everybody-there is a light emitting diode signalling about feed of the voltage on the slots DIMM - it is red and its "green friend" responsible for the voltage on slots PCI. It is really impossible to name something this board has the lack of and besides no saving on minutiae. OverclockingIt is obvious that the problem of stability at overclocking is very current - the small pulsation amplitude of the processor core voltage is especially important. Our theoretical researches from the units "Stability" allow to suppose that the board BX7+ will perfectly show itself at the processor overclocking on the nominal voltage. But do overclockers want this? No, they want their purchase with the sign "Intel" to show as many MHz as is in the RoadMap of the company for 2003. For this purpose the board should allow to change the bus rate smoothly, to increase the voltage on the processor ñore with the minimum step and to increase the voltage in the input-output circuits. All this is possessed by EpoX EP-BX7+, all the regulations are carried out through BIOS and are placed on the same page with the information on temperatures, voltages, revolutions etc. The bus rate is regulated in limits from 66 up to 200 MHz with the step 1 MHz. On the board one of most progressive for today of rate generators - the programmed microcircuit Realtek RTM520-39D is applied. The given microcircuit has two one-byte registers M and N, the frequent factors are set by their help. The resulting microcircuit output rate is calculated with the formula: Fout = Fin * (m+1) / (n+1) The input rate is determined by quartz which rate as a rule is 14,318 MHz. On page BIOS " Sensor and CPU Speed Setting " we introduce the coefficient çàøèòûé in our processor, and we start to switch the bus rate. Here the resulting processor rate, the multiplication factor for PCI, the resulting rate on PCI, the multiplication rate for AGP and the resulting rate on AGP are mapped. Also the multiplication rate for AGP and PCI can be installed manually. Let's admit that Celeron 600 refuses to work on the bus 100 MHz. Then 95 MHz can be installed in it, and the resulting rate will be 855 MHz. But how to be with PCI and AGP? Very simply - we install the divider 3/1 for PCI and 3/2 for AGP by force. In result we get normal 31,7 MHz on PCI instead of unreal 47,5 MHz and 63,3 MHz on AGP instead of 95 MHz. It is necessary to mark that as against many competitors it is possible to use the hand-held installation of dividers AGP and PCI already from 83 MHz (instead of 90-92). These are the remarkable possibilities at the rate installation especially for Celeron having the bus 66 MHz! Now it is possible to add the voltage on the processor ñore - certainly it will get warmer but would be possible to win 50 MHz. The voltage is regulated from BIOS by adding 0,05 V to the nominal voltage on the core. The separate line maps how the nominal voltage is exceeded - the maximum exceeding is 0,3 V. It quite enough... It will be good to add some voltage to the chipset and memory - it is regulated in the range from 3,4 V with the step 0,05 V up to 3,75 V. The forced installation of the rate divider AGP in 1/1 has allowed to ñarry out a very interesting experiment on persistence for videocards on the basis GeForce2 GTS - to install the extreme rate level AGP, where the videosystem starts to fail. ASUS V7700 approach 111 MHz, and Leadtek GeForce2 GTS - 2 megahertz more. Thus the modern videocards allow to install on BX boards the bus rate up to 165 MHz. It is necessary only to choose the appropriate memory and to make sure that all PCI devices work normally. Don't think that we shall try ten processors the sake of prestige and very easily pass the barrier 1 GHz. We shall take the most usual accidentally selected processor Pentium III CuMine 700 MHz and the usual memory PC133. The results obtained at usage the standard cooler from Intel are given in the table:
For matching: the same processor on the board ASUS CUBX has lost stability on the rate 933 MHz. So we have got the most accurate instrument for processors overclocking. And taking into account that we used the most usual processor, memory and videocard some of you can boast that their processor has passed the barrier 1 GHz. ProductivityAt the productivity evaluation the following equipment was used:
And software:
At the motherboard productivity evaluation when motherboards are designed on the one chipset, the wide spread in values of productivity is not expected. Therefore the mutual productivity of different motherboards models on the chipset BX won't be analysed now, for now we shall examine how good the external UltraDMA/66 RAID controller from HighPoint is. The controller gives the possibility to use RAID of levels 0, 1, 0+1. The most interesting will be to determine the rate increase at usage the striping mode - reading and record of data sectors alternate on different disks for the regular load dispersion between hard disks and the increase of productivity. For the item we shall take the disks productivity in the mode UltraDMA/66 and for matching we shall examine the indexes of the controller UltraDMA/33 built in the chipset. 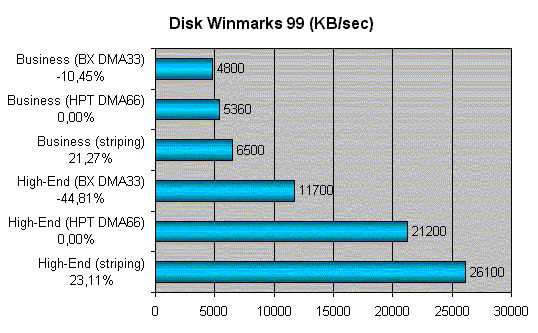 It is possible to add CD-ROM or ZIP to the "old bones" BX, but HighPoint has deserved its place under the sun both in the usual operation mode and in the mode RAID. As for the matching productivity of the motherboards on BX - it is necessary to be convinced that EpoX EP-BX7+ demonstrates the productivity at the analogs level and doesn't sacrify the productivity for stability or possibilities. And for this purpose the favourite Quake3 is quite enough: 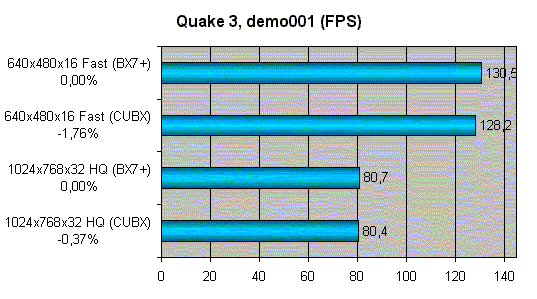 It is obviously that here EpoX EP-BX7+ is among the best. Thus, quite enough information is accumulated to make final summary. SummarySo the company EpoX has a real masterpiece. But why has it appeared in more than two years after the appearance of the legendary chipset and why don't the rest have it? Someone has the lack of possibilities, someone the lack of stability and many of the manufacturers do not tend to produce the products of such class. It is sad...Especially now when there are cards on Intel i815 and it is more and more difficult for BX to resist to the push of the young... And it is so pleasant that we have got the product that equal the hopes of 99 % the buyers. And if someone already has IDE or SCSI controller and does not want to have the external HighPoint, then it is necessary to examine carefully the card EpoX EP-BX7. Pluses:
Minuses:
P.S. The delivery of the refreshed motherboards BX7+ 100 with RAID controller HPT370 supporting UltraDMA/100 will start in a month. Write a comment below. No registration needed!
|
Platform · Video · Multimedia · Mobile · Other || About us & Privacy policy · Twitter · Facebook Copyright © Byrds Research & Publishing, Ltd., 1997–2011. All rights reserved. |