Toshiba Announces Highest Performance Physical Random-Number Generator Circuit
Toshiba Corporation today announced the development of a major advance in information security technology: A physical random-number generation circuit that achieves the world's highest output by area, and that generates random numbers at a data rate of 2.0 megabits a second. The newly developed random-number generator (RNG) has a circuit size of only 1,200 square micrometers but achieves the level of performance and reliability essential for integration into IC cards and mobile equipment.
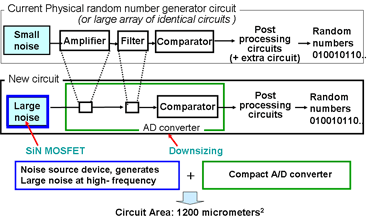
The new RNG technology adopts a compact analogue/digital (A/D) converter which effectively amplifies analog noise signals and converts them to digital random numbers. The technology also integrates a Toshiba-developed compact noise source device. This generates the noise signal by using stochastic physical phenomenon of electrons trapped in the silicon nitride (SiN) layer of a transistor; the layer traps and releases high density electrons at a high generation rate.
Toshiba also confirmed that the new RNG circuit is not subject to temperature dependence, a long-standing reliability issue for physical RNG.
Toshiba's new physical RNG circuit relies on a nanometer-scale noise source device that is not affected by temperature. This device generates large noise signals at high frequency. The newly developed circuit effectively digitizes these large, high frequency signals.
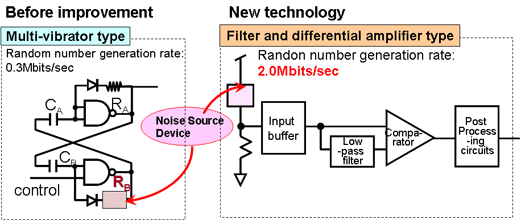
1. Filter and differential amplifier type A/D converter: In its previous work on development of a compact RNG circuit, Toshiba employed a multi-vibrator circuit, where the noise source device was connected to the digitizer circuit in series. As a result, there was a trade-off between the magnitude of the noise and the generation rate; in order to increase the magnitude of the noise, resistance of the noise source device needs to be high, but this leads to a reduction in the circuit's generation rate.
The new technology employs a filter and differential amplifier with a comparator, which is separated from the noise source device. It can selectively extract the high frequency noise signals generated by the new device and achieve a random number generation rate approximately seven times higher than the multi-vibrator circuit: the increases performance to a practical level of 2.0Mb/s, against 0.3Mb/s with the earlier technology.
2. Downsized A/D converter: The improved circuit downsizes the A/D converter. In general, there is a trade-off in RNG: the smaller the noise source device, the larger the circuit area. The high frequency noise signals generated by the noise source device allow Toshiba to reduce the size of the A/D converter, and to reduce entire RNG circuit area to 1,200 square micrometers, including the noise source device. This is 86.6% smaller than the next smallest physical RNG circuit yet announced, a breakthrough that realizes the world's highest performance in random number generation rate per area.
3. No temperature dependence: Experimental tests in a range from -50 to 100° centigrade have confirmed the high-quality randomness of the numbers generated. Results show that the generated numbers are not affected by temperature, verifying the possibility of stable generation of random numbers under the temperature conditions in which IC cards and mobile equipment are used.
Source: Toshiba Corporation
Write a comment below. No registration needed!