 |
||
|
||
| ||
Technology
The Bluetooth technology was developed as a way of wireless connection for different devices. And it was mainly aimed at a small size of the equipment, low power consumption and a low price.
Today we will examine the following Bluetooth equipment:
And first of all, we will concern some general issues on the tests. The first one relates to protection of the Bluetooth connections. The standard provides for authentication and encryption, but there is no more detailed information to describe all possibilities. That is why all products were tested with the default settings and if it was possible to change something we will mark it. Besides, none of the devices provides with a possibility to check a level and quality of a signal which makes impossible to define borders of the coverage area accurately. The only possibility to check is to establish connection. The results are 6-9 m indoors and up to 12 m outdoors. Bluetake USB Dongle
 A set of the Bluetake USB Dongle consists of:
As you can see, the adapters are quite small and light. That is why stickers are enough to fix them. The adapter weighs less than its USB cable which is 59 cm long! One green LED indicates power supply. According to the manual I installed the software from the CD. It is called Widcomm Bluetooth Software 1.1.27 and meant for Windows 98SE/ME/2000. The tested computer had the Windows 2000. The installation brought in three icons: "Bluetooth Neighborhood" on the desktop, "Widcomm Bluetooth Console" in the tray and "Bluetooth Configuration" in the control panel. Two latter programs in fact open the same dialog window of software settings:
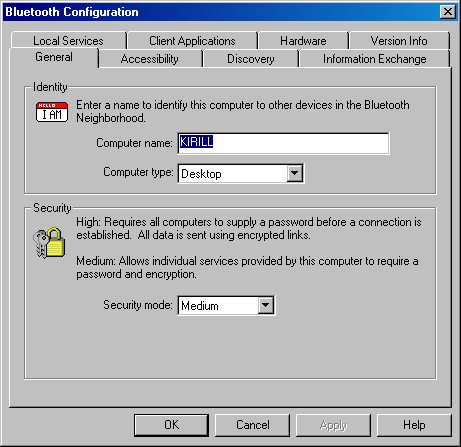 During the installation you can set a name of the device for the Bluetooth connection and its type - a desktop PC or a portable one. The software has a detailed help file. The installation procedure is not perfect yet. On the one hand, the installation is implemented by the Microsoft Installer, but the installer (which starts from a CD from a BAT file without any permission of a user) tries to copy a non-existant file from a CD into the system directories on drive C. The support software is very important for Bluetooth devices, and the most of executable functions are implemented by this software. Because the technology bases the interaction on client-server relations each device has a certain set of services and clients. In case of the Bluetake USB Dongle we have:
Each of these services has both a client and server part in the BTW. Now it is time to connect the adapter. As the drivers had already been recorded during the installation, no problems occurred. The device manager got the following line:
Apart from this record we received several COM ports (for servers and clients) and a network adapter ("Bluetooth LAN Access Server Driver") for network access. The second PC was set up the same way. First of all, let's take a look at the settings of the BTW configuration in its control panel:
Well, the default settings were chosen for all devices. Let's open the Bluetooth Neighborhood:
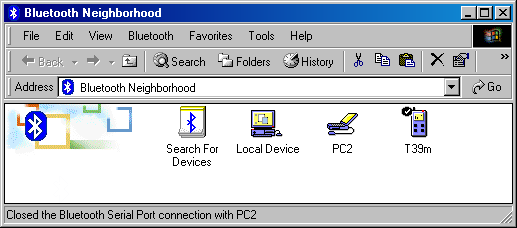 Local Device is our first PC, PC2 is our second PC with the Bluetake adapter and T39m is our cell phone. All icons are blue which means that the devices do not interract at the moment. Apart from these icons it is possible to display those of modems, printers, PDA, and access points. Let's see what we have on the PC2:
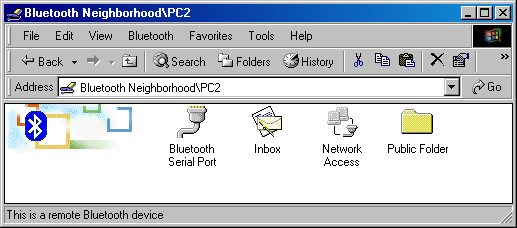 Each service has its own icon but they can be labeled differently. Besides, it is possible that we have two identical services (e.g., two faxes), and in this case figures are added to the name. The first item is a serial port. One double click... and now two (virtual) serial ports on two PCs are connected. By the way, numbers of the ports can be indicated in the BTW settings. Now let me estimate a data rate. I adjusted the HyperTerminal on both PCs and transferred a 7 MBytes file via the ZModem protocol. The ports were adjusted for 921600 bps, and the data rate for this file was 77529 cps. In our conditions it corresponds approximately to 75 KBps. Let's open the Inbox. Here we have only one icon - Business Card. If you activate this service on the PC2, opening of the icon will transfer data of this card in the vcf format to your PC. It seems to me that realization of all capabilities needs the PIM program (Personal Information Manager). At the moment the BTW supports only Microsoft Outlook. You can implement operations with remote services by double clicking (right button) on a service's icon. In case of the Inbox you can transfer a business card, exchange business cards, transfer a contact, transfer a record in the calendar, tasks, messages etc. The next icon is Network Access. When we double clicked on the icon we got a remote access window with request for a name and a password... If there is some adapter on a USB bus then why it wouldn't work as a network controller? We tried to enter a name and a password of the remote PC but it didn't help. However, as you remember, the network folder got a network controller and BluetoothNullConnection; it means that Network Access is realized via a standard remote access! And a PC-server is not a bridge but a router regarding the wired connection; that is why it is necessary to establish Internet Connection Sharing to access a wired network from a remote Bluetooth device or install software like WinRoute. I didn't do that. But to check connection between the PCs I just adjusted IP addresses for the Bluetooth LAN Access Server Driver on the server's side and for the BluetoothNullConnection on the client's side. The measurements of the file transmission speed via the Bluetooth connection showed that it was 65KBps, although the system said that a connection speed was only 115Kbit. It should be noted also that I couldn't connect two PCs with the Xircom cards used simultaneously although officially more than one client can be supported. Well, one can actually use the Bluetooth for creation of a network, but it isn't very convenient. The last service available on the PV2 is Public Folder. A speed of file transmission into this folder is around 57 KBps, which coincides with the previous measurements. It looks like the PC2 doesn't possess wide capabilities, and not all BTW's functions can be realized here. Now we can try to exchange functions between the PCs. Or just look into the Local Device on the first PC:
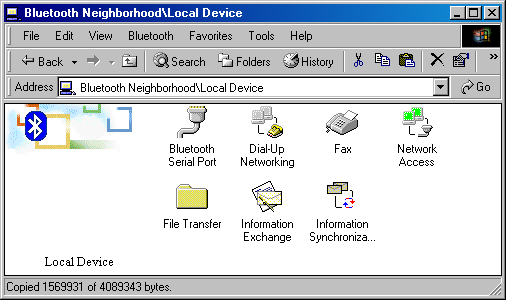 All services are available! There is a fax-modem, Microsoft Outlook etc. Here you can also suspend operation of any services on the Local PC or look into the dialog window to adjust their parameters. The "Network Access" icon is green which means that this service is enabled now. Dial-Up Networking. This function makes possible to use a modem on the server for remote access from a client. By the way, you can't use the Bluetooth Serial Port service mentioned earlier as it provides only virtual ports for the shared access. Wrong measurement of a connection speed of the modems on the client's side is not a merit - the speed was always 115Kbit. The second drawback is lack of all necessary Dial-Up settings (server, IP addresses etc.) in the Bluetooth Neighborhood window. That is why we had to open a usual window of network settings to adjust them. The Fax service allows a remote client to transfer a fax through the fax-modem installed on the server. This server, like the Dial-Up Networking, is given via a virtual modem and a fax-modem:
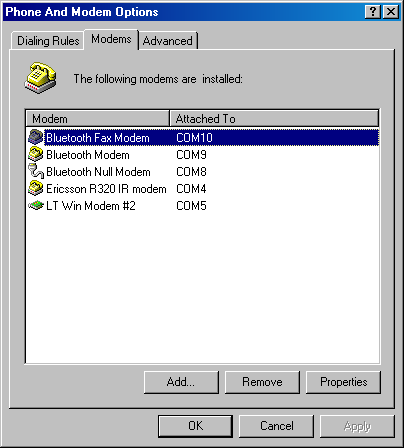 I'm not going to check all programs for operation with this service and I will dwell only on the one included into the Windows 2000. No problems with the fax were noticed. The BTW makes possible to add some more serial ports both for server and client parts. But as there is no possibility to choose a client port when connecting a remote port, these possibilities are not widely used. The Inbox functions have the following functions. The server can receive files of the following formats:
and either record them into a particular directory or transfer into the PIM installed in the PC. The Microsoft Outlook can use files of the Business Card and Calendar. For example, when you transfer a calendar even from a remote PC (or other device) it will get into the Outlook calendar. The client can transfer into the remote Inbox either its own Business Card or any file of vsc/vnt/vmg formats. Unfortunately, one can't transfer a vcf file such a way. The last interesting item is Information Synchronization. You can synchronize PIM on two different devices. For this purpose I installed Microsoft Outlook on both PCs. It should be noted that other platforms with their PIMs compatible with IrMC v1.1 and vCard v2.1 standards are also supported. Unfortunately, the current version supports only synchronization of the main folder of contacts of the Outlook. The synchronization of 107 contacts took only several minutes in our tests. Quite often the "Bluetooth Neighborhood" folder doesn't provide the latest information on remote device. In particular, sometimes I have to search for new services and update the "Public Folders" myself. On the whole, the devices made a positive impression on me. But after I turned off the adapter several times, rebooted the PC and other things of this kind, something failed in the software settings, none of repeat installations helped to enable the controller again, to search for devices and a general instability of operation. There are a lot of settings to protect Bluetooth connections. First of all, one can create a list of devices which can be used by services. Secondly, each service can be set to require authorization. A local PC will then get a window with a permission for such connection. The latest variant is creation of a list of paired devices. You have to enter the same passwords on both sides, and after that exchange within this pair won't require authentication anymore. The recommended retail price of the Bluetake is $220-$230 which is quite expensive for such a little product. Ericsson T39m
 Now let's see what the Bluetake can offer to an owner of a cell phone with the Bluetooth support. The market of such devices is not developed very much. The Ericsson T39m is one of the richest in communication capabilities - IrDA, GPRS, Bluetooth, internal modem etc. First of all, let's compare different possibilities of phone connection - cable, IR port and Bluetooth. Cable connection to the serial port is still the most reliable - you know exactly how all that is connected, how it must work and how to check operability. However, every phone needs its own cable. Besides, a mobile device is to be connected with a cable, and COM ports on PCs and PDAs are passing away. The second variant implies utilization of an IR port. It is not difficult to check everything as well, but it is required that all devices are positioned a definite way relative each other. If you have an IR port on a cable it makes no problems, but if it is located on a case at the height of 15 cm, it's quite a problem to place a phone nearby. The most convenient IrDA version in notebooks is an integrated device working at 1 or 4 Mbps and having a conveniently positioned window. The most of ports on desktop PCs have the maximum transfer rate of 115.2 Kbps. In such conditions utilization of the Bluetooth technology has a real advantage - any positions of devices, a great distance range - up to 10m, and a high transfer rate. But the software really matters a lot - if you have to meddle for a long time with software to establish connection, you will hardly like such a solution. During the operation the Bluetooth mode is displayed on the phone - activity, availability for search and data transfer. But this icon covers activity indicator of the IrDA connection. First of all, let's try to use the software only from Bluetake. So, the phone provides the following services:
 In the first case we just use an internal modem to connect the Internet or any other modem. This icon provides only basic options to adjust connection - phone number, name, and password. All other things are to be done in the control panel for network connections. Though it is not required if the Dial-Up server is realized correctly. I tried to connect a usual provider, to access the Internet via cellular connection (at 9600 bps) and to use the GPRS technology (with the data rate reaching 32 KBps). The Fax works similar; you just have to set the Fax Modem as a Bluetooth device, though you can also install a modem on the wireless serial port. No problems were found. The Inbox service provides functions for transmission of contacts and calendar records, messages and notes to the remote device. Besides, you can use it to exchange business cards. In case of the T39m, you have first to save calendar events in the vCalendar format. The two serial ports are identical in functions. As the phone has Dial-up Networking and Fax functions the direct connection to the port is mainly used for operation with special software of the phone; although it is also possible to install the Ericsson T39 Bluetooth modem on the PC via the series connection. The last item is IrMC Synchronization. However it is not of great interest as the BTW software supports only synchronization of the Outlook address book. This synchronization took 2:05 min, and we transferred only contacts from the phone to the PC (they were 107 totally). The Bluetooth technology provides the following things for the phone's software:
Each of this programs can work via cable, IR connection and the Bluetooth. For the Bluetooth one should connect the serial port of the phone from the BTW and make settings for the software to support this COM port. Its number can be found in the BTW control panel, Client Applications. When we connected the phone's port the software worked as if it were cable or IR connection. The synchronization time with Outlook (with the XTNDConnect software) reduced from 50 sec (115.2 Kbps IrDA) to 20 sec. The data volume was 107 contacts and 4 calendar events. As compared with the IrDA here you have to do some more things (connect the port) to start synchronization. One of the advantages of the Bluetooth is a high data rate. Of course, the IrDA supports 1 Mbps in the phone, and the most of IR ports on desktop PCs support a maximum of 115.2Kbps. It is not very important for synchronization of a phone book. But if a phone has a large memory (e.g. Siemens SL45 - up to 128 MBytes), it might be very handy. Just look: transmission of 64 MBytes via a serial port will take more than an hour, and at 1 Mbps it will be around 8 min. There are two variants to restrict a phone access via the Bluetooth. The first is to turn off the Bluetooth or put it in an auto mode when it becomes enabled only if necessary. The second is access restriction in devices which can use services of a mobile phone; it can be done in the list called "Paired Devices". To register a pair you have to initiate a process from one of the devices and enter the same password on both devices during this process. After that the client can use phone's services. The phone is currently available at about $300. Hewlett-Packard DeskJet 995C
 This is one more peripheral device with the Bluetooth support. I won't concern its quality of printing (though it is quite high), just communicational capabilities. The printer has USB, IrDA and Bluetooth interfaces. The first is rather popular now, and it makes no problems. As for the IrDA, an ordinary text transferred from the PC via an IR port can be printed out without problems. Besides, if you install the printer's driver and indicate that the DJ 995C is connected to the local IR port documents (even graphics) can be printed in color. But as the IR port is located too low on the printer one can use, in fact, only a notebook/PDA or an external IR port. Another downside is a low transfer rate for 115.2 Kbps IR ports of desktop PCs as a size of one transferred graphic page is quite large. Now let's look at the Bluetooth. There is one blue indicator at upper left. Well, it took me just several seconds to print out a contact from the phone book of the Ericsson T39m (Phone book - Business cards - Send contact - Via Bluetooth). The phone looked for a Bluetooth device for about 5 seconds and when the DeskJet 995c was found the printing started. The business card was color and looked excellently. The phone remembers a printer's address at the first time and next time it doesn't need to search it. The phone, above all, has "Send via IR" item which also works excellently with the DJ 995C. To print documents from a desktop PC via the Bluetooth adapter it is necessary to connect a serial port of the printer:
 The Inbox object allows printing out its business card without even installing the printer on the PC. However, I failed to print out Task from the PC, though it was done successfully from the cellular phone. Printing out via IR port and Bluetooth is supported for PDA devices (in particular, for the Palm families with Windows CE). The IrDA port also works with the HP Photosmart Digital Camera. It should be noted that the printer can use only one wireless device simultaneously that is why the Bluetooth technology can't completely replace a network card. The printer's settings support some protection technologies - "hp deskjet series 995c toolbox":
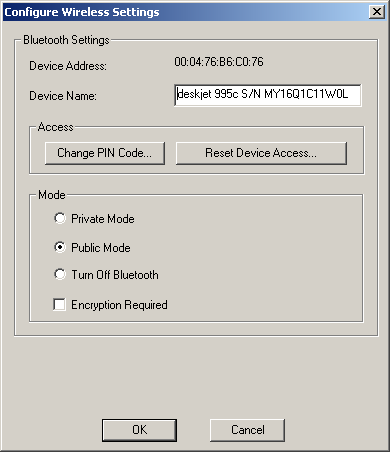 You can change settings of the printer only if it is connected via a USB port. The Private Mode allows the printer to work only with those devices which already know its name. A PIN code is required only if it is necessary to pair devices. Sometimes this code is used to establish connection. The printer is available at http://www.shopping.hp.com at $399.99 Xircom CreditCard Bluetooth Adapter
 This is the last participant of the today's review. As this adapter is designed for a PCMCIA bus it will be primarily used in notebooks because most of them have such slot. However, we will use it on a desktop PC connecting it via a PCMCIA PCI adapter. It should be noted that the manufacturer is Xircom, an Intel company. That is why look for support at the Intel's site. Well, the adapters are PCMCIA cards of a standard size. They also have an internal antenna and a power/activity LED. Below you can see information on the device in the device manager:
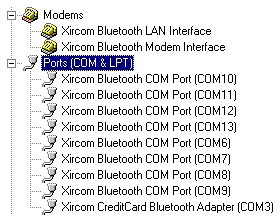 There are a lot of virtual serial ports and network's and modem's interfaces. The basic software for the Xircom CreditCard Bluetooth Adapter is called Xircom BlueView. When it works its icon in the tray makes possible to enable/disable the adapter and AutoConnect mode, and open a main window of the program:
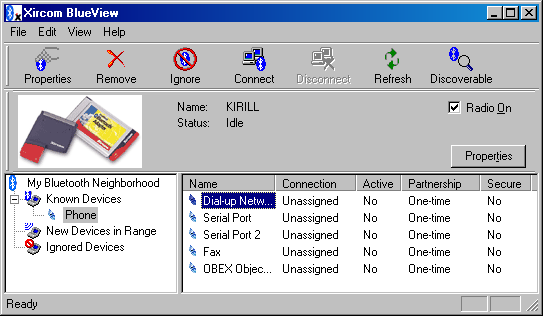 This software uses a form of representation of the Bluetooth devices and services different from BTW. First of all, you are to search for devices within the network area. Then you can set them as Known or Ignored. So that another device can connect the PC it is necessary to set the adapter into the Discoverable mode (usually it can be activated for 2-3 min). To connect remote services you should choose a certain service by clicking the right button. There will be two connection modes - Permanent and One-time. The first one is still enabled even if the port is not used anymore. The AutoConnect mode (for all connections at once) can also be enabled: it reestablishes connection with the device which went out of the network area and then became accessible again. When the port was disabled I had to reload the BlueView. The Dial-Up client connects the remote modem to the Xircom Bluetooth Modem used in the system. After that you can create as many dial-up connections as you want in the network control panel. Contrary to the BTW, a fax can be connected via a COM port that is why you should install the driver of the device (in our case, of the cell phone). I think the Dial-Up connection can also be used for the fax, however, I wasn't able to make it work as the modem hung up before a page was transferred. But there were no problems when the serial port was connected a standard way. The following client applications are supported:
The LAN Access is realized via the Dial-Up Networking technology with simulation of PC direct connection. That is why it is necessary either to have a DHCP server in the network or set IP addresses manually. I tried to use this profile to connect the PC with the Bluetake; it worked but the speed of reading files from the remote disc was only 23 KBps. I also measured a file transfer rate through the Hyperterminal with the serial ports connected. For different pairs (Xircom/Bluetake) and different directions the speed varied from 24 to 46 KBps. The basic service used in the adapters' software is connection of serial ports. The rest of functions (fax, data exchange) are realized via this connection. The program used here is Intellisync for Notebooks 2.15.00 from Pumatech. For the mobile phone we can use the above mentioned Ericsson Phone Settings, Ericsson Phone Book & Text Message Manager and XTNDConnect PC for Ericsson. The Intellisync for Notebooks makes possible to use a series connection to synchronize data on two PCs (or different PIMs on one PC). This version allows us to synchronize data of the Outlook and Lotus Organizer 5.0/97, as well as of any directories. Unfortunately, the program refused to work with the synchronization service on the mobile phone. It is also possible to use compatible profiles for exchanging of data and files and synchronization using the Intellisync software. However, I wasn't able to start them - the Bluetake showed us only three services of the serial ports:
 On the whole, the software has excellently realized functions (though they are quite few). For protection it is possible to make it visible for some time in the Bluetooth network and require authorization of each connection using the Passkey (which should be entered in both parts of the connection). The Xircom CreditCard Bluetooth Adapter card costs today $138.99 (www.shop-intel.com). ConclusionThe experiments show that the Bluetooth technology works. There were no any compatibility problems on the hardware level. The Bluetooth is better realized in separate products (phone and printer). Such finished products do need software support, and for them the Bluetooth is one more step in development. Besides, a suite of executable functions is predetermined and stable. The software for PC is developed by spoilt programmers who used to test their products on end-users. The dominant factor which doesn't allow the Bluetooth
to become popular today is a high price of the adapters. Moreover,
it is necessary to use complicated software so that all functions
could work. This technology is probably the only which has a good
chance to become widely available among PDAs and mobile devices.
Write a comment below. No registration needed!
|
Platform · Video · Multimedia · Mobile · Other || About us & Privacy policy · Twitter · Facebook Copyright © Byrds Research & Publishing, Ltd., 1997–2011. All rights reserved. |